The Excel INTERCEPT function is a powerful statistical tool that calculates the y-intercept of a linear regression line through a set of data points. This function is essential for predictive modeling, trend analysis, and understanding the relationship between variables in your datasets.
What is the INTERCEPT Function in Excel?
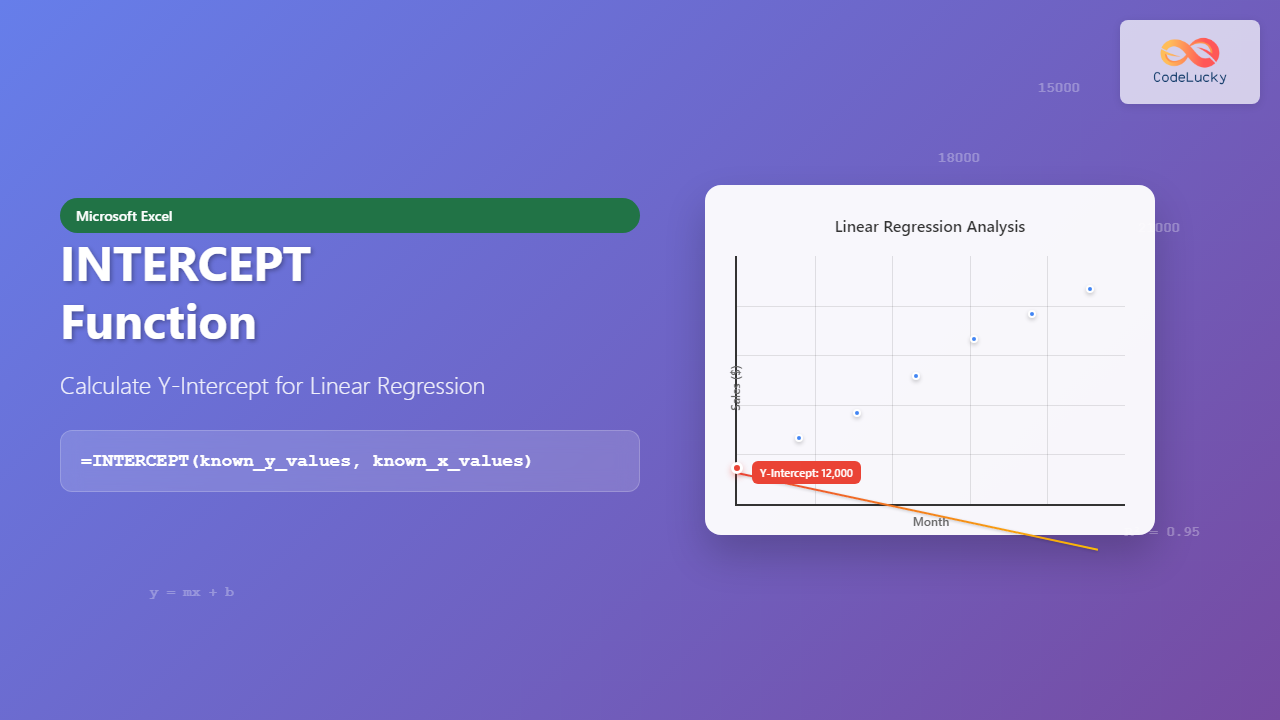
The INTERCEPT function calculates the point where a linear regression line crosses the y-axis (when x equals zero). This statistical function uses the least squares method to determine the best-fit line through your data points and returns the y-intercept value of that line.
Understanding the y-intercept is crucial for:
- Predicting future values based on historical data
- Analyzing business trends and patterns
- Creating forecasting models
- Understanding baseline values in your data
INTERCEPT Function Syntax
The syntax for the INTERCEPT function is straightforward:
=INTERCEPT(known_y_values, known_x_values)Parameters Explained:
known_y_values (required): An array or range of dependent data points (y-values). These represent the outcomes or results you’re trying to predict or analyze.
known_x_values (required): An array or range of independent data points (x-values). These represent the input variables or factors that influence the y-values.
How INTERCEPT Function Works
The INTERCEPT function uses linear regression analysis to find the best-fit line through your data points. The mathematical formula behind this calculation is:
y = mx + b
Where:
- y = dependent variable
- m = slope of the line
- x = independent variable
- b = y-intercept (what INTERCEPT function calculates)
The function calculates the intercept using the least squares method, which minimizes the sum of squared differences between actual and predicted values.
Basic INTERCEPT Function Examples
Example 1: Simple Sales Data Analysis
Let’s analyze monthly sales data to find the baseline sales intercept:
| Month | Sales ($) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 15000 |
| 2 | 18000 |
| 3 | 21000 |
| 4 | 24000 |
| 5 | 27000 |
Formula: =INTERCEPT(B2:B6, A2:A6)
Result: 12000
This means that at month 0 (the starting point), the projected sales would be $12,000, representing the baseline sales figure.
Example 2: Temperature and Energy Consumption
Analyzing the relationship between temperature and energy consumption:
| Temperature (°F) | Energy Usage (kWh) |
|---|---|
| 32 | 850 |
| 45 | 720 |
| 60 | 580 |
| 75 | 450 |
| 90 | 620 |
Formula: =INTERCEPT(B2:B6, A2:A6)
Result: 1031.43
This indicates that at 0°F, the theoretical energy usage would be approximately 1,031 kWh.
Advanced INTERCEPT Function Applications
Financial Forecasting
The INTERCEPT function is invaluable for financial analysis and forecasting. You can use it to:
- Revenue Projections: Calculate baseline revenue figures
- Cost Analysis: Determine fixed costs in variable cost structures
- Investment Analysis: Project initial investment values
- Budget Planning: Establish baseline budget requirements
Quality Control and Manufacturing
In manufacturing scenarios, INTERCEPT helps analyze:
- Production Efficiency: Baseline production rates
- Quality Metrics: Starting quality levels
- Resource Utilization: Minimum resource requirements
- Process Optimization: Initial process parameters
Combining INTERCEPT with Other Excel Functions
INTERCEPT and SLOPE Functions
Use INTERCEPT with SLOPE to create complete linear regression models:
=SLOPE(known_y_values, known_x_values) * x_value + INTERCEPT(known_y_values, known_x_values)This combination allows you to predict y-values for any given x-value.
INTERCEPT with FORECAST Function
Compare INTERCEPT results with Excel’s FORECAST function for validation:
=FORECAST(0, known_y_values, known_x_values)This should return the same result as the INTERCEPT function.
Common Errors and Troubleshooting
#N/A Error
The #N/A error typically occurs when:
- The known_x_values and known_y_values arrays have different sizes
- One of the arrays is empty
- All x-values are identical (no variation in data)
Solution: Ensure both arrays have the same number of elements and contain valid numerical data with variation.
#VALUE! Error
This error appears when:
- Non-numeric values are included in the data ranges
- Text values are mixed with numerical data
Solution: Clean your data to include only numerical values or use data validation techniques.
#DIV/0! Error
Occurs when there’s insufficient variation in the x-values to calculate a meaningful regression line.
Solution: Ensure your x-values have sufficient range and variation.
Best Practices for Using INTERCEPT Function
Data Quality Guidelines
To get accurate results from the INTERCEPT function:
- Use Clean Data: Remove outliers and ensure data accuracy
- Sufficient Sample Size: Use at least 10-15 data points for reliable results
- Check for Linearity: Ensure your data follows a linear relationship
- Validate Results: Cross-check with scatter plots and other statistical measures
Interpretation Tips
When interpreting INTERCEPT results:
- Context Matters: Consider whether a zero x-value makes practical sense
- Extrapolation Caution: Be careful when extrapolating beyond your data range
- Correlation Strength: Use CORREL function to check relationship strength
- R-squared Value: Calculate coefficient of determination for model accuracy
Practical Business Scenarios
Marketing Campaign Analysis
Analyze the relationship between advertising spend and revenue generation:
- X-values: Monthly advertising budget
- Y-values: Monthly revenue
- Intercept: Expected revenue with zero advertising (organic sales)
Employee Performance Metrics
Evaluate training effectiveness:
- X-values: Training hours completed
- Y-values: Performance scores
- Intercept: Baseline performance level without training
Inventory Management
Optimize stock levels:
- X-values: Time periods
- Y-values: Inventory turnover rates
- Intercept: Initial inventory efficiency
Alternative Functions and Methods
LINEST Function
For more comprehensive regression analysis, consider using LINEST:
=LINEST(known_y_values, known_x_values, TRUE, TRUE)This returns multiple statistics including the intercept, slope, and correlation measures.
Data Analysis ToolPak
Excel’s Data Analysis ToolPak provides regression analysis tools that include intercept calculations along with detailed statistical output.
Scatter Plot with Trendline
Create visual representations of your data with trendlines that display intercept values automatically.
Performance Optimization Tips
Large Dataset Handling
When working with large datasets:
- Use Named Ranges: Improve formula readability and maintenance
- Array Formulas: Consider array formulas for complex calculations
- Calculation Mode: Set Excel to manual calculation for better performance
- Data Sampling: Use representative samples for initial analysis
Memory Management
Optimize Excel performance when using INTERCEPT:
- Limit Range References: Use specific ranges rather than entire columns
- Avoid Volatile Functions: Minimize use of functions that recalculate frequently
- Data Types: Ensure consistent data types in your ranges
Real-World Case Study
E-commerce Sales Analysis
An online retailer wants to understand the relationship between website traffic and sales conversion:
Scenario: Monthly website visitors vs. monthly sales over 12 months
Data Analysis:
- X-values: Monthly unique visitors (thousands)
- Y-values: Monthly sales ($)
- INTERCEPT result: $45,000
Business Insight: The company has a baseline sales level of $45,000 per month even with minimal website traffic, indicating strong repeat customer loyalty and direct sales channels.
Action Items:
- Focus on maintaining the $45K baseline through customer retention
- Develop strategies to increase the slope (conversion rate improvement)
- Monitor monthly performance against the regression model
Conclusion
The Excel INTERCEPT function is an essential tool for statistical analysis and business forecasting. By understanding how to properly implement and interpret intercept calculations, you can gain valuable insights into your data relationships and make more informed business decisions.
Remember to always validate your results with visual representations, check for data quality issues, and consider the practical implications of your intercept values in real-world contexts. The combination of INTERCEPT with other Excel statistical functions provides a powerful toolkit for comprehensive data analysis.
Whether you’re analyzing sales trends, optimizing business processes, or conducting research, mastering the INTERCEPT function will enhance your analytical capabilities and improve the accuracy of your predictive models.