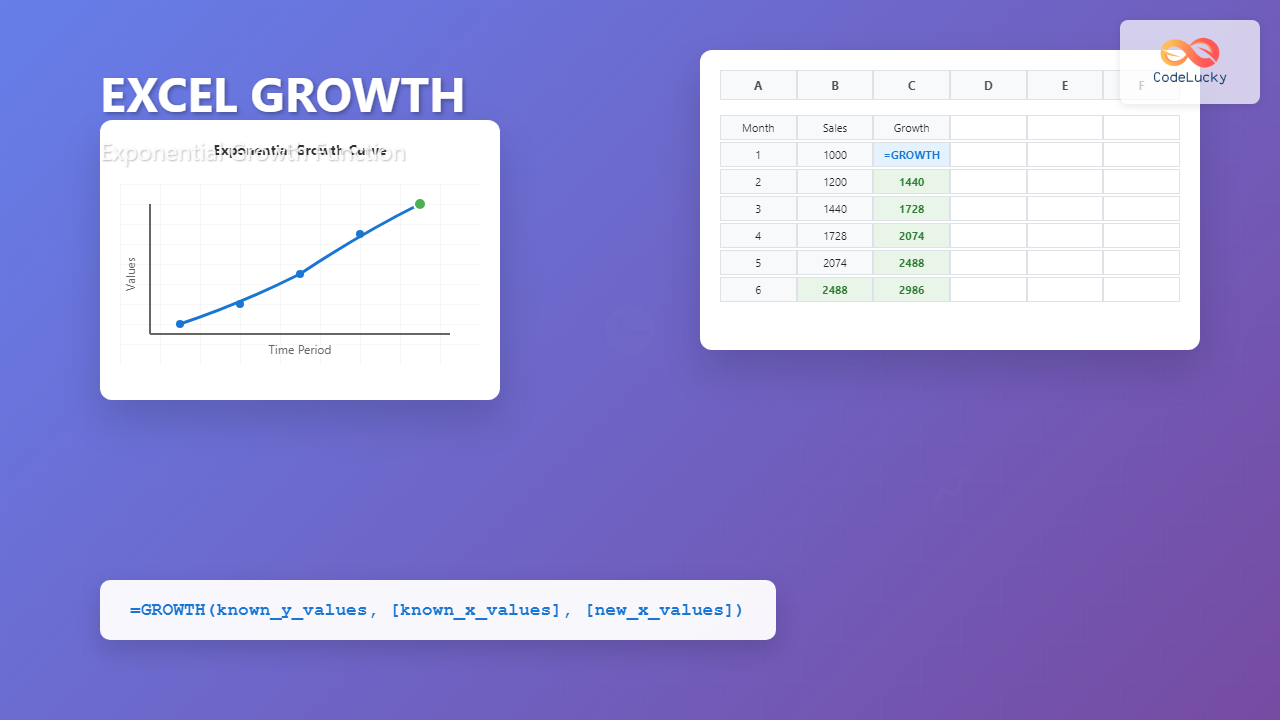
The Excel GROWTH function is a powerful statistical tool that calculates exponential growth by fitting data to an exponential curve. This function is essential for financial analysts, data scientists, and anyone working with growth projections or trend analysis in Excel.
What is the Excel GROWTH Function?
The GROWTH function returns the exponential growth trend for a given set of data points. It uses the exponential smoothing method to predict future values based on existing x-values and y-values, making it invaluable for forecasting scenarios where growth follows an exponential pattern.
Unlike linear growth functions, GROWTH assumes that data increases or decreases at an exponential rate, which is common in scenarios like population growth, compound interest calculations, and viral marketing metrics.
GROWTH Function Syntax
The syntax for the Excel GROWTH function is:
=GROWTH(known_y_values, [known_x_values], [new_x_values], [const])Parameters Explained
- known_y_values (Required): The set of y-values you already know in the relationship y = b*m^x
- known_x_values (Optional): An optional set of x-values that correspond to the known_y_values
- new_x_values (Optional): New x-values for which you want GROWTH to return corresponding y-values
- const (Optional): A logical value specifying whether to force the constant b to equal 1
How Excel GROWTH Function Works
The GROWTH function fits your data to the exponential equation y = b * m^x, where:
- y = the dependent variable (result)
- b = the y-intercept constant
- m = the base of the exponential function
- x = the independent variable
Excel calculates the values of b and m that best fit your existing data, then uses these values to predict future results based on the exponential growth pattern.
Basic GROWTH Function Examples
Example 1: Simple Exponential Growth
Let’s say you have sales data for the first 5 months and want to predict month 6:
| Month | Sales |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1000 |
| 2 | 1200 |
| 3 | 1440 |
| 4 | 1728 |
| 5 | 2074 |
Formula: =GROWTH(B2:B6, A2:A6, 6)
This formula will return the predicted sales value for month 6 based on the exponential growth pattern of the existing data.
Example 2: Multiple Future Predictions
To predict values for multiple future periods, you can specify a range for new_x_values:
Formula: =GROWTH(B2:B6, A2:A6, A7:A10)
This will return an array of predicted values for months 6 through 9.
Advanced GROWTH Function Techniques
Using GROWTH with Array Formulas
When predicting multiple values, enter the GROWTH function as an array formula by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Enter after typing the formula. This ensures Excel processes all the predictions simultaneously.
Forcing the Constant Parameter
The const parameter allows you to control whether Excel calculates the y-intercept automatically or forces it to equal 1:
- TRUE or omitted: Excel calculates b normally
- FALSE: Forces b to equal 1, fitting the curve y = m^x
Example: =GROWTH(B2:B6, A2:A6, A7:A10, FALSE)
Common Use Cases for GROWTH Function
Financial Forecasting
The GROWTH function excels in financial scenarios where compound growth is expected:
- Revenue projections with consistent growth rates
- Investment value predictions
- Population growth modeling
- Market expansion forecasting
Business Analytics
In business analytics, GROWTH helps with:
- Customer acquisition rate predictions
- Website traffic growth analysis
- Product adoption curve modeling
- Viral coefficient calculations
GROWTH vs Other Excel Functions
GROWTH vs TREND
While both functions predict future values, they use different mathematical approaches:
- GROWTH: Uses exponential regression (y = b * m^x)
- TREND: Uses linear regression (y = mx + b)
Choose GROWTH when your data shows exponential patterns, and TREND for linear relationships.
GROWTH vs FORECAST
The FORECAST function (and its variants like FORECAST.LINEAR) provides linear predictions, while GROWTH specializes in exponential forecasting. GROWTH is more suitable for data that compounds over time.
Tips for Accurate GROWTH Predictions
Data Quality Considerations
- Ensure your known_y_values contain positive numbers only
- Check for outliers that might skew the exponential curve
- Use sufficient historical data points for reliable predictions
- Verify that your data actually follows an exponential pattern
Validation Techniques
To validate your GROWTH function results:
- Plot your historical data and predicted values on a chart
- Calculate the R-squared value to measure fit quality
- Compare predictions with actual results when available
- Test the function with known exponential datasets
Troubleshooting GROWTH Function Errors
Common Error Messages
#NUM! Error: Occurs when known_y_values contain zero or negative numbers, or when arrays are incompatible sizes.
#REF! Error: Happens when cell references are invalid or when ranges don’t match properly.
#VALUE! Error: Results from non-numeric data in the y-values or x-values ranges.
Error Solutions
- Verify all y-values are positive numbers
- Check that known_x_values and known_y_values have the same number of data points
- Ensure new_x_values are numeric
- Remove or replace any text values in your data ranges
Real-World GROWTH Function Application
E-commerce Growth Projection
Consider an e-commerce business tracking monthly revenue growth:
| Month | Revenue ($) | Predicted Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| Jan | 50,000 | – |
| Feb | 55,000 | – |
| Mar | 61,500 | – |
| Apr | 68,200 | – |
| May | 75,500 | =GROWTH($B$2:$B$6,$A$2:$A$6,A7) |
This application helps businesses plan inventory, staffing, and investment decisions based on exponential growth trends.
Best Practices for GROWTH Function
Data Preparation
- Clean your data by removing anomalies and ensuring consistency
- Use at least 4-5 historical data points for reliable predictions
- Consider seasonal adjustments if your data has cyclical patterns
- Document your assumptions and methodology for future reference
Implementation Guidelines
- Always visualize your results with charts to verify logical trends
- Use named ranges to make formulas more readable and maintainable
- Include confidence intervals or sensitivity analysis for critical forecasts
- Regularly update your models with new actual data
Advanced GROWTH Function Combinations
Combining with Statistical Functions
Enhance your GROWTH analysis by combining it with other Excel functions:
- RSQ function: Calculate R-squared values to measure fit quality
- STDEV function: Determine prediction confidence intervals
- CORREL function: Assess correlation strength between variables
Dynamic GROWTH Models
Create dynamic models using INDIRECT and OFFSET functions to automatically adjust data ranges as you add new information:
=GROWTH(INDIRECT("B2:B"&ROW()-1), INDIRECT("A2:A"&ROW()-1), ROW())
Limitations and Considerations
When Not to Use GROWTH
The GROWTH function may not be appropriate when:
- Your data shows linear rather than exponential patterns
- External factors significantly influence future growth
- Market saturation or resource constraints limit exponential growth
- Historical data is insufficient or unreliable
Alternative Approaches
Consider these alternatives when GROWTH isn’t suitable:
- TREND function for linear projections
- Moving averages for smoothed predictions
- Regression analysis add-ins for complex modeling
- External forecasting software for sophisticated scenarios
Conclusion
The Excel GROWTH function is an invaluable tool for anyone working with exponential growth scenarios. By understanding its syntax, applications, and limitations, you can leverage this function to create accurate forecasts and make data-driven decisions.
Remember to validate your results, consider the context of your data, and combine GROWTH with other analytical techniques for comprehensive insights. With practice and proper application, the GROWTH function becomes a cornerstone of effective Excel-based data analysis and forecasting.
Whether you’re projecting business revenue, analyzing population trends, or modeling compound growth scenarios, mastering the GROWTH function will significantly enhance your Excel analytical capabilities and improve the accuracy of your predictions.