Managing CSS files in large projects can quickly become overwhelming without proper organization. Professional developers rely on structured approaches to maintain clean, scalable, and maintainable stylesheets. This comprehensive guide explores proven folder structures and import strategies that will transform your CSS workflow.
Why CSS File Organization Matters
Poor CSS organization leads to several critical issues that plague development teams:
- Code Duplication: Repeated styles scattered across multiple files
- Maintenance Nightmares: Difficulty locating and updating specific styles
- Performance Issues: Inefficient loading and bloated stylesheets
- Team Collaboration Problems: Conflicts and inconsistencies in multi-developer projects
- Scalability Limitations: Architecture that breaks down as projects grow
A well-organized CSS architecture solves these problems by creating predictable patterns, improving maintainability, and enabling efficient collaboration.
Popular CSS Organization Methodologies
ITCSS (Inverted Triangle CSS)
ITCSS organizes CSS in layers from generic to specific, creating a natural cascade that minimizes specificity conflicts:
/scss /01-settings # Variables, config /02-tools # Mixins, functions /03-generic # Normalize, reset /04-elements # Base HTML elements /05-objects # Layout patterns /06-components # UI components /07-utilities # Helper classes
7-1 Pattern (Sass Architecture)
The 7-1 pattern divides CSS into seven folders and one main file for imports:
/scss /abstracts # Variables, mixins, functions /base # Reset, typography, base styles /components # Buttons, cards, forms /layout # Header, footer, grid /pages # Page-specific styles /themes # Theme variations /vendors # Third-party CSS main.scss # Main import file
Atomic Design CSS
Based on Brad Frost’s Atomic Design, this approach organizes CSS by component complexity:
/scss /atoms # Basic elements (buttons, inputs) /molecules # Simple components (search form) /organisms # Complex components (header, sidebar) /templates # Page layouts /pages # Specific page styles
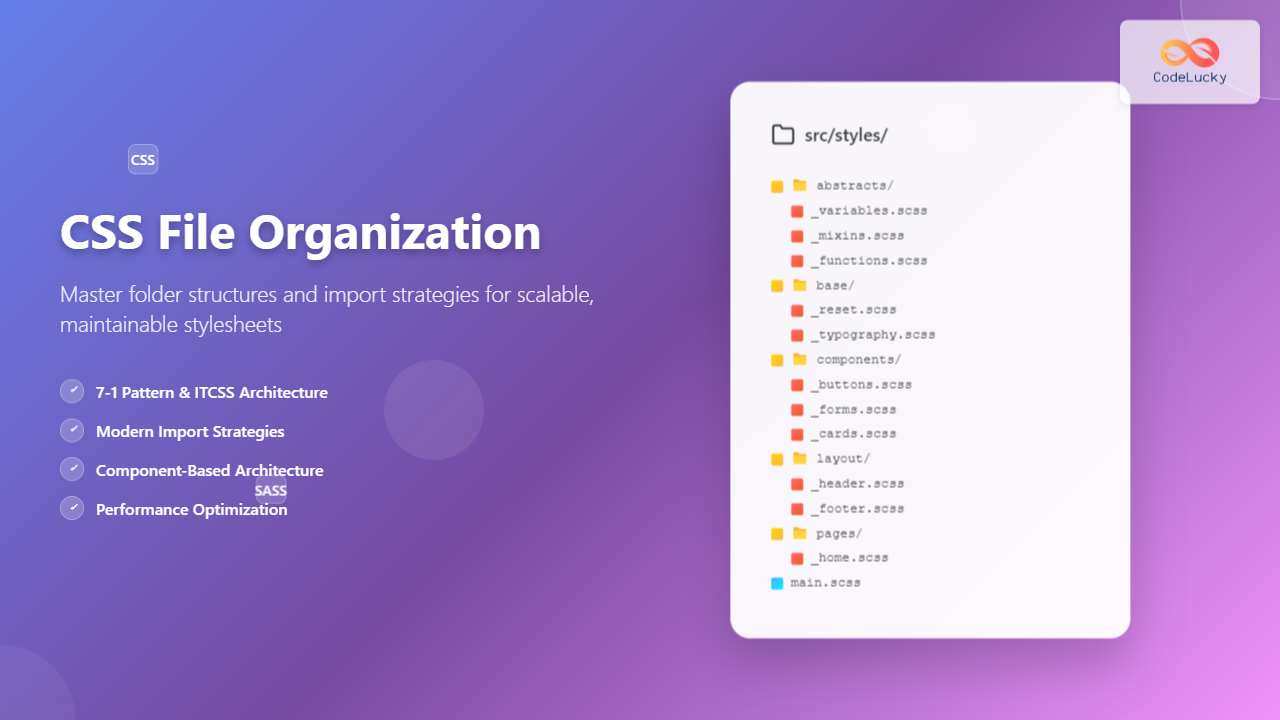
Recommended Folder Structure for Modern Projects
Here’s a comprehensive folder structure that combines the best practices from multiple methodologies:
project-root/ ├── src/ │ └── styles/ │ ├── abstracts/ │ │ ├── _variables.scss │ │ ├── _mixins.scss │ │ ├── _functions.scss │ │ └── _index.scss │ ├── base/ │ │ ├── _reset.scss │ │ ├── _typography.scss │ │ ├── _base.scss │ │ └── _index.scss │ ├── components/ │ │ ├── _buttons.scss │ │ ├── _forms.scss │ │ ├── _cards.scss │ │ ├── _modals.scss │ │ └── _index.scss │ ├── layout/ │ │ ├── _header.scss │ │ ├── _footer.scss │ │ ├── _sidebar.scss │ │ ├── _grid.scss │ │ └── _index.scss │ ├── pages/ │ │ ├── _home.scss │ │ ├── _about.scss │ │ ├── _contact.scss │ │ └── _index.scss │ ├── themes/ │ │ ├── _light.scss │ │ ├── _dark.scss │ │ └── _index.scss │ ├── utilities/ │ │ ├── _helpers.scss │ │ ├── _utilities.scss │ │ └── _index.scss │ ├── vendors/ │ │ ├── _normalize.scss │ │ ├── _bootstrap.scss │ │ └── _index.scss │ └── main.scss └── dist/ └── styles.css
File Naming Conventions
Consistent naming conventions are crucial for maintainable CSS architecture:
Sass Partials
Use underscores for partial files that shouldn’t compile independently:
✅ Good: _variables.scss, _buttons.scss, _header.scss ❌ Bad: variables.scss, buttons.scss, header.scss
Component-Based Naming
Name files based on their purpose and component responsibility:
_button-primary.scss # Specific button variant _form-contact.scss # Contact form styles _card-product.scss # Product card component _layout-dashboard.scss # Dashboard layout
Import Strategies and Best Practices
Master Import File (main.scss)
Create a single entry point that imports all other files in the correct order:
// main.scss // ============================================================================= // ABSTRACTS - Variables, mixins, functions // ============================================================================= @import 'abstracts/index'; // ============================================================================= // VENDORS - Third party CSS // ============================================================================= @import 'vendors/index'; // ============================================================================= // BASE - Reset, typography, base elements // ============================================================================= @import 'base/index'; // ============================================================================= // LAYOUT - Grid, header, footer, navigation // ============================================================================= @import 'layout/index'; // ============================================================================= // COMPONENTS - Buttons, forms, cards // ============================================================================= @import 'components/index'; // ============================================================================= // PAGES - Page-specific styles // ============================================================================= @import 'pages/index'; // ============================================================================= // THEMES - Theme variations // ============================================================================= @import 'themes/index'; // ============================================================================= // UTILITIES - Helper classes, overrides // ============================================================================= @import 'utilities/index';
Index Files for Each Folder
Use index files to manage imports within each folder. Example components/_index.scss:
// components/_index.scss @forward 'buttons'; @forward 'forms'; @forward 'cards'; @forward 'modals'; @forward 'navigation'; // Alternative using @import (Sass legacy) // @import 'buttons', 'forms', 'cards', 'modals', 'navigation';
Modern CSS Import Methods
Sass @use and @forward
Modern Sass projects should use @use and @forward instead of @import:
// Using @use for better namespace control @use 'abstracts/variables' as vars; @use 'abstracts/mixins' as mix; .button { background-color: vars.$primary-color; @include mix.border-radius(8px); } // Using @forward to re-export modules // In abstracts/_index.scss @forward 'variables'; @forward 'mixins'; @forward 'functions';
CSS @import for Production
While Sass handles compilation, understand CSS native imports for specific use cases:
/* CSS @import (use sparingly in production) */ @import url('https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Inter:wght@300;400;600&display=swap'); @import 'components/critical.css'; /* Better: Use link tags in HTML for external resources */
Component-Based CSS Architecture
Modern web development favors component-based architectures. Here’s how to structure CSS for component systems:
Single File Components (SFC)
/components
/Button
Button.jsx
Button.module.scss
Button.test.js
index.js
/Card
Card.jsx
Card.module.scss
Card.test.js
index.js
BEM Methodology Integration
Combine folder organization with BEM naming for maximum clarity:
// _card.scss .card { border-radius: 8px; box-shadow: 0 2px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1); // BEM modifier &--featured { border: 2px solid gold; } // BEM element &__header { padding: 1rem; border-bottom: 1px solid #eee; } &__content { padding: 1rem; } }
Performance Optimization Strategies
Critical CSS Separation
Separate critical above-the-fold styles for faster initial rendering:
/styles
/critical # Above-the-fold styles
_layout.scss
_typography.scss
_header.scss
/non-critical # Below-the-fold styles
_components.scss
_pages.scss
_utilities.scss
Lazy Loading Strategies
Organize CSS for conditional and lazy loading:
// Dynamic imports for page-specific styles const loadPageStyles = async (pageName) => { await import(`./pages/${pageName}.scss`); }; // Conditional component styles if (shouldLoadModal) { import('./components/modal.scss'); }
Build Tool Integration
Webpack Configuration
// webpack.config.js module.exports = { entry: './src/styles/main.scss', module: { rules: [ { test: /\.scss$/, use: [ 'style-loader', 'css-loader', { loader: 'sass-loader', options: { sassOptions: { includePaths: ['src/styles'] } } } ] } ] } };
Vite Configuration
// vite.config.js export default { css: { preprocessorOptions: { scss: { additionalData: `@import "src/styles/abstracts/index.scss";` } } } };
Documentation and Team Guidelines
CSS Style Guide Template
Create a comprehensive style guide for your team:
Team CSS Guidelines
- File Naming: Use lowercase with hyphens (_component-name.scss)
- Class Naming: Follow BEM methodology consistently
- Import Order: Follow the established layer hierarchy
- Comments: Use section headers and inline explanations
- Variables: Store all reusable values in abstracts/variables
- Mixins: Create reusable patterns in abstracts/mixins
- Specificity: Keep specificity low, avoid !important
- Media Queries: Use mobile-first approach
Interactive CSS Architecture Example
Live CSS Organization Demo
✅ Well-Organized
// _button.scss
.btn {
@include button-base;
&--primary {
background: $primary-color;
}
&--secondary {
background: $secondary-color;
}
}
❌ Poorly Organized
// styles.css (everything mixed)
.btn-primary { background: blue; }
.header { padding: 20px; }
.btn-secondary { background: gray; }
.footer { margin-top: 50px; }
Styles scattered throughout single file, hard to maintain and scale.
Key Difference: The organized approach groups related styles, uses variables for consistency, and follows a predictable pattern that scales with project growth.
Common Pitfalls and Solutions
Avoiding CSS Bloat
⚠️ Warning: CSS Bloat
Problem: Importing everything everywhere leads to massive CSS bundles.
Solution: Use tree-shaking, code splitting, and conditional imports.
// Instead of importing everything @import 'components/index'; // 50+ components // Import only what you need @import 'components/button'; @import 'components/form';
Specificity Conflicts
❌ Specificity Wars
Poor organization leads to increasingly specific selectors and !important abuse.
// Bad: Increasing specificity .page .section .card .button { /* specificity: 0,0,4,0 */ } .homepage .hero .card .button
- Why CSS File Organization Matters
- Popular CSS Organization Methodologies
- Recommended Folder Structure for Modern Projects
- File Naming Conventions
- Import Strategies and Best Practices
- Modern CSS Import Methods
- Component-Based CSS Architecture
- Performance Optimization Strategies
- Build Tool Integration
- Documentation and Team Guidelines
- Interactive CSS Architecture Example
- Common Pitfalls and Solutions