Product-market fit represents the holy grail of product development – that magical moment when your product perfectly satisfies a strong market demand. It’s the foundation upon which sustainable businesses are built, determining whether your venture will thrive or struggle to gain traction.
In today’s competitive landscape, achieving product-market fit isn’t just about building a great product; it’s about creating something that customers genuinely need, want, and are willing to pay for repeatedly. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about product-market fit and how to achieve lasting customer satisfaction.
Understanding Product-Market Fit
Product-market fit occurs when you’ve built a product that satisfies a strong market demand. Marc Andreessen, who coined the term, describes it as “being in a good market with a product that can satisfy that market.” It’s the sweet spot where your product’s value proposition aligns perfectly with customer needs and market dynamics.
The concept goes beyond simple customer satisfaction. It represents a state where customers are not just happy with your product – they’re actively recommending it, returning for repeat purchases, and demonstrating clear signs of engagement and retention.
Key Characteristics of Product-Market Fit
Strong product-market fit exhibits several unmistakable signs. Customers begin using your product organically, often discovering it through word-of-mouth recommendations rather than expensive marketing campaigns. Usage grows consistently without requiring significant promotional pushes, and customer retention rates remain high over extended periods.
Additionally, customers express genuine disappointment when they can’t access your product, and they struggle to find adequate alternatives. Revenue growth becomes more predictable, and the unit economics of your business model start making sense without relying on unsustainable acquisition costs.
The Journey to Product-Market Fit
Achieving product-market fit is rarely a linear process. Most successful companies iterate through multiple versions of their product, constantly refining their understanding of customer needs and market dynamics. The journey typically involves three distinct phases: pre-product-market fit, the search for fit, and post-product-market fit optimization.
Pre-Product-Market Fit Phase
During this initial phase, teams focus on understanding the problem space and identifying potential customer segments. This involves extensive market research, customer interviews, and competitive analysis. The goal isn’t to build the perfect product immediately but to develop a deep understanding of the problems worth solving.
Many teams make the mistake of rushing through this phase, eager to start building. However, time invested in truly understanding your target market pays dividends throughout the development process. Document your assumptions about customer needs, market size, and competitive landscape to create a foundation for future validation efforts.
The Search Phase
This phase involves building and testing minimum viable products (MVPs) to validate your hypotheses about customer needs. The focus shifts from research to experimentation, using real customer feedback to guide product decisions. Teams typically cycle through multiple iterations, each designed to test specific assumptions about product-market fit.
During this phase, it’s crucial to maintain a hypothesis-driven approach. Each feature, design decision, and go-to-market strategy should be treated as an experiment with measurable outcomes. This scientific approach helps teams avoid the common trap of building features based on opinions rather than evidence.
Measuring Product-Market Fit
Measuring product-market fit requires a combination of quantitative metrics and qualitative indicators. While no single metric perfectly captures the concept, several key indicators can help you assess your progress toward achieving strong market alignment.
Quantitative Metrics
Net Promoter Score (NPS) serves as one of the most reliable indicators of product-market fit. Customers who rate your product 9 or 10 on the likelihood-to-recommend scale demonstrate the kind of enthusiasm that drives organic growth. Aim for an NPS above 50, with the top performers often achieving scores above 70.
Retention rates provide another crucial indicator. Strong product-market fit typically correlates with high customer retention, particularly in the first 30, 60, and 90 days after initial use. Monthly and annual churn rates should steadily decrease as you approach stronger market alignment.
Usage intensity metrics reveal how deeply customers engage with your product. Track daily active users, session duration, and feature adoption rates to understand whether customers find genuine value in your offering. Products with strong market fit often see increasing usage over time as customers discover additional value.
Qualitative Indicators
Customer feedback quality changes dramatically as you approach product-market fit. Early feedback often focuses on missing features or usability issues. As fit improves, customers begin discussing outcomes and results rather than features, indicating that your product is solving real problems effectively.
Sales cycle dynamics also shift with stronger product-market fit. Prospects become easier to convert, requiring less convincing about the value proposition. Customers begin reaching out proactively, often through referrals or word-of-mouth recommendations rather than responding to marketing campaigns.
Strategies for Achieving Product-Market Fit
Successful product-market fit strategies combine deep customer understanding with systematic experimentation. The most effective approaches focus on identifying and serving specific customer segments exceptionally well rather than trying to appeal to everyone.
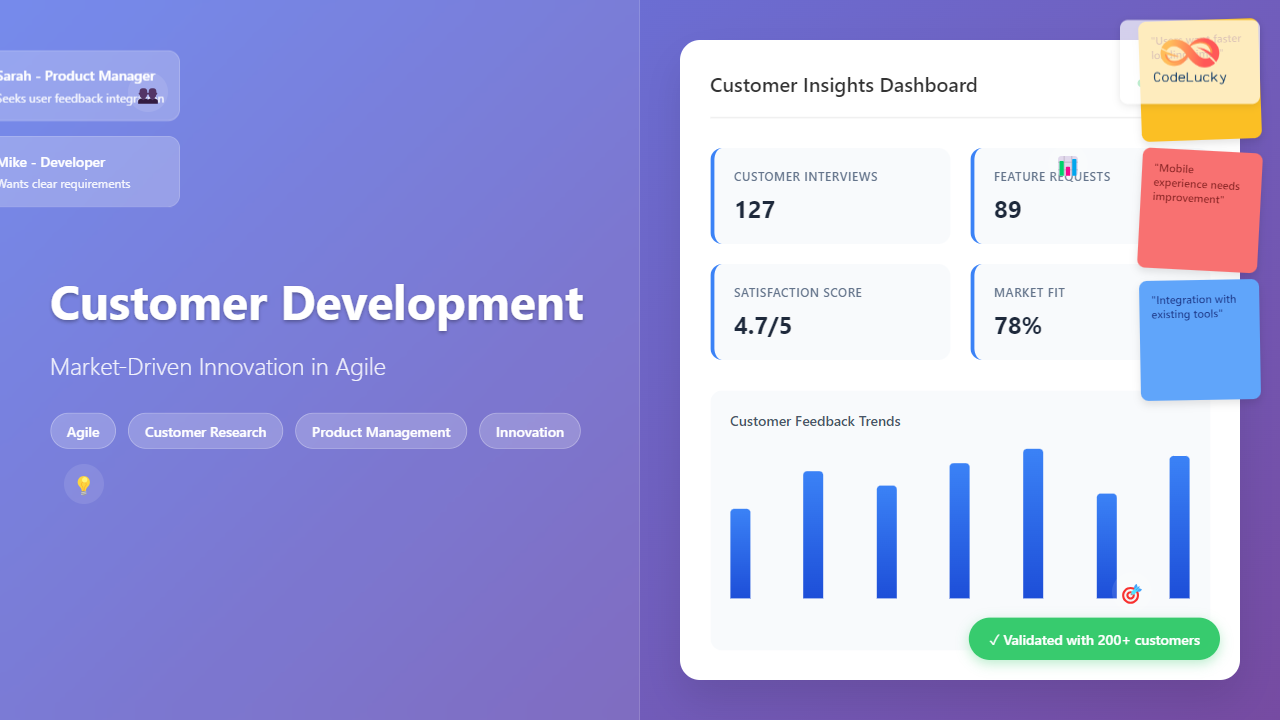
Customer Development Process
Implement a structured customer development process that emphasizes learning over building. Start by conducting extensive customer interviews to understand pain points, current solutions, and desired outcomes. Focus on understanding the customer’s entire workflow and how your product might fit into their existing processes.
Create detailed customer personas based on real data rather than assumptions. These personas should include demographic information, pain points, goals, current solutions, and decision-making processes. Use these personas to guide product decisions and prioritize features that address the most critical customer needs.
Iterative Product Development
Adopt an iterative approach to product development that emphasizes rapid learning cycles. Build small, testable versions of your product that allow you to gather customer feedback quickly and cost-effectively. Each iteration should test specific hypotheses about customer needs and product-market fit.
Prioritize features based on their potential impact on key product-market fit metrics rather than ease of implementation. This approach ensures that development efforts focus on the most critical aspects of customer satisfaction and market alignment.
Market Segmentation and Targeting
Identify specific market segments where your product provides exceptional value rather than trying to serve everyone adequately. Strong product-market fit often emerges from deep specialization in serving particular customer types exceptionally well.
Analyze your customer base to identify patterns among your most satisfied users. Look for common characteristics, use cases, or outcomes that distinguish highly engaged customers from those who churn quickly. Use these insights to refine your target market and improve your value proposition.
Common Challenges and Solutions
The path to product-market fit is fraught with challenges that can derail even well-intentioned teams. Understanding these common pitfalls and their solutions can help you navigate the journey more effectively.
Premature Scaling
Many teams make the mistake of scaling their operations before achieving strong product-market fit. This often leads to increased customer acquisition costs, higher churn rates, and operational complexity that makes it harder to iterate on the product effectively.
Resist the temptation to scale until you have clear evidence of product-market fit. Focus on perfecting your product and go-to-market strategy with a smaller customer base before expanding your reach. This approach allows for more agile iteration and reduces the risk of scaling ineffective processes.
Feature Bloat
Teams often respond to customer requests by adding features without considering their impact on overall product coherence and user experience. This approach can dilute your value proposition and make it harder for customers to understand and use your product effectively.
Implement a rigorous feature prioritization process that evaluates each potential addition based on its alignment with core customer needs and strategic objectives. Sometimes saying no to feature requests is more important than saying yes, particularly when those features might confuse your core value proposition.
Ignoring Market Dynamics
Product-market fit isn’t static – it can change as markets evolve, competitors emerge, or customer needs shift. Teams that achieve initial fit but fail to monitor market dynamics risk losing their competitive advantage over time.
Establish ongoing processes for monitoring market changes, competitive developments, and evolving customer needs. Regular customer feedback sessions, market research, and competitive analysis help ensure that your product continues to meet market demands as they evolve.
Case Studies in Product-Market Fit
Learning from successful examples can provide valuable insights into how different companies have achieved and maintained strong product-market fit across various industries and market conditions.
Slack: Transforming Team Communication
Slack achieved remarkable product-market fit by solving a universal problem that most teams didn’t realize they had. Rather than positioning itself as another messaging app, Slack focused on transforming how teams collaborate and share information.
The company’s success stemmed from understanding that team communication was fragmented across email, meetings, and various tools. By creating a centralized platform that integrated with existing workflows, Slack achieved strong adoption and retention rates that demonstrated clear product-market fit.
Airbnb: Redefining Travel Accommodation
Airbnb’s path to product-market fit involved multiple iterations and market repositioning. Initially focused on budget travelers, the company eventually discovered that many customers valued unique experiences and local connections as much as cost savings.
The company’s breakthrough came from understanding that they weren’t just competing with hotels but creating an entirely new category of travel experience. This insight helped them refine their product and marketing to emphasize community, authenticity, and unique accommodations.
Maintaining Product-Market Fit
Achieving product-market fit is just the beginning – maintaining it requires ongoing attention and adaptation. Markets evolve, customer needs change, and competitors emerge, all of which can impact your market position over time.
Continuous Customer Feedback
Establish systematic processes for gathering and analyzing customer feedback on an ongoing basis. This includes regular surveys, user interviews, support ticket analysis, and usage data review. The goal is to identify trends and changes in customer needs before they impact your market position.
Create feedback loops that connect customer insights directly to product development decisions. Ensure that customer feedback influences roadmap prioritization and strategic planning processes.
Innovation and Adaptation
Maintain a culture of innovation that balances core product stability with the need to evolve and improve. This involves continuously exploring adjacent markets, new customer segments, and emerging technologies that might impact your industry.
Allocate resources for experimental projects and new feature development while maintaining focus on your core value proposition. This balanced approach helps ensure long-term relevance without sacrificing current market position.
Conclusion
Product-market fit represents the foundation of sustainable business success, but achieving it requires patience, discipline, and a systematic approach to understanding and serving customer needs. The journey involves continuous learning, iteration, and adaptation based on real market feedback rather than assumptions.
Success comes to teams that maintain focus on customer value creation while remaining flexible enough to adapt their approach based on new insights and market changes. By implementing the strategies and frameworks outlined in this guide, you’ll be better equipped to achieve and maintain strong product-market fit that drives sustainable customer satisfaction and business growth.
Remember that product-market fit is not a destination but an ongoing process of alignment between your product and market needs. Stay curious, remain customer-focused, and be prepared to evolve your approach as you learn more about the markets you serve.