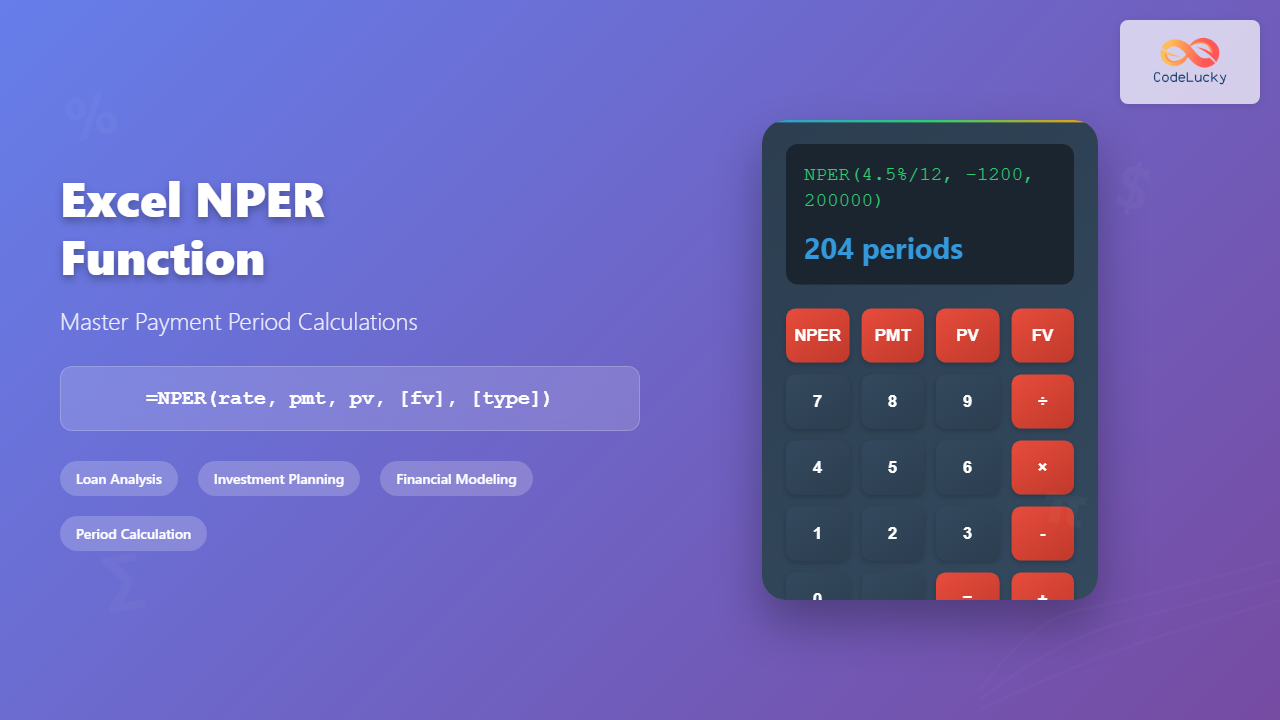
What is the Excel NPER Function?
The NPER function in Microsoft Excel is a powerful financial function that calculates the number of payment periods for an investment or loan based on constant payments and a constant interest rate. NPER stands for “Number of PERiods” and is essential for financial analysis, loan calculations, and investment planning.
Whether you’re determining how long it will take to pay off a mortgage, calculating the duration of an investment to reach a target value, or analyzing loan terms, the NPER function provides accurate period calculations that form the foundation of financial decision-making.
Excel NPER Function Syntax
The complete syntax for the NPER function is:
=NPER(rate, pmt, pv, [fv], [type])Required Parameters
- rate: The interest rate per period (must match the payment frequency)
- pmt: The payment amount made each period (constant value)
- pv: Present value or the initial amount of the loan/investment
Optional Parameters
- fv: Future value or desired balance after the last payment (defaults to 0)
- type: When payments are due (0 for end of period, 1 for beginning of period)
Understanding NPER Function Parameters
Rate Parameter Details
The rate parameter must correspond to your payment frequency. If you make monthly payments, use the monthly interest rate. If you make annual payments, use the annual rate. Common conversions include:
- Monthly rate = Annual rate ÷ 12
- Quarterly rate = Annual rate ÷ 4
- Semi-annual rate = Annual rate ÷ 2
Payment (PMT) Considerations
The payment amount should be entered as a negative value when representing outgoing payments (like loan payments) and positive for incoming payments (like investment returns). This follows Excel’s cash flow convention where outflows are negative and inflows are positive.
Present Value (PV) Guidelines
For loans, the present value is typically the loan amount entered as a positive value. For investments, it’s the initial investment amount, usually entered as a negative value since it’s an outflow.
Practical NPER Function Examples
Example 1: Mortgage Payment Periods
Calculate how many monthly payments are needed for a $200,000 mortgage at 4.5% annual interest with $1,200 monthly payments:
=NPER(4.5%/12, -1200, 200000)Result: Approximately 204 payments (17 years)
Example 2: Investment Growth Timeline
Determine how long it takes for monthly $500 investments to grow to $100,000 at 7% annual return:
=NPER(7%/12, -500, 0, 100000)Result: Approximately 156 payments (13 years)
Example 3: Loan Payoff with Balloon Payment
Calculate periods for a $50,000 loan at 6% annual interest with $400 monthly payments and a $10,000 balloon payment:
=NPER(6%/12, -400, 50000, -10000)Result: Approximately 156 payments before the balloon payment
Advanced NPER Function Applications
Comparing Payment Scenarios
Use NPER to compare different payment amounts and their impact on loan duration. Create a table with various payment amounts to visualize how increased payments reduce the total number of periods:
| Payment Amount | Number of Periods | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| $1,000 | =NPER(5%/12, -1000, 150000) | Approximately 200 months |
| $1,500 | =NPER(5%/12, -1500, 150000) | Approximately 118 months |
Break-Even Analysis
Combine NPER with other financial functions to determine break-even points for investments or business decisions. This helps in strategic planning and financial forecasting.
Common NPER Function Errors and Solutions
#NUM! Error
This error occurs when the payment amount is insufficient to cover the interest, making it impossible to pay off the loan. Solutions include:
- Increasing the payment amount
- Reducing the interest rate
- Decreasing the principal amount
#VALUE! Error
This error happens when non-numeric values are entered in numeric parameters. Ensure all rate, payment, and value fields contain valid numbers.
Negative Results
Negative NPER results indicate that your current parameters won’t achieve the desired outcome. Review your cash flow signs and parameter values.
NPER Function Best Practices
Consistency in Time Periods
Always ensure your interest rate and payment frequency match. Annual rates require annual payments, monthly rates require monthly payments, and so forth.
Cash Flow Convention
Follow Excel’s cash flow convention consistently: outgoing payments are negative, incoming payments are positive. This prevents calculation errors and ensures accurate results.
Documentation and Validation
Document your assumptions and validate results using alternative calculation methods or financial calculators to ensure accuracy.
Combining NPER with Other Excel Functions
NPER and PMT Integration
Use NPER with the PMT function to create comprehensive loan analysis tools:
=PMT(rate, NPER(rate, pmt_estimate, pv), pv)NPER and IF Statements
Create conditional calculations using IF statements with NPER:
=IF(NPER(rate, pmt, pv) > 360, "Loan term exceeds 30 years", "Acceptable term")Array Formulas with NPER
Use NPER in array formulas to calculate multiple scenarios simultaneously, enabling comprehensive financial modeling and scenario analysis.
Real-World NPER Applications
Personal Finance Planning
Individuals use NPER for retirement planning, mortgage analysis, and debt consolidation strategies. It helps determine realistic timelines for financial goals.
Business Financial Modeling
Businesses employ NPER for equipment financing, cash flow projections, and investment analysis. It’s crucial for capital budgeting decisions.
Investment Analysis
Investment professionals use NPER to evaluate investment durations, compare different investment vehicles, and optimize portfolio strategies.
Tips for Mastering the NPER Function
Practice with Real Scenarios
Apply NPER to actual financial situations you encounter. This reinforces learning and builds practical expertise.
Create Templates
Develop reusable templates with NPER functions for common calculations like loan analysis, investment planning, and savings goals.
Understand Related Functions
Learn PMT, PV, FV, and RATE functions alongside NPER to become proficient in Excel’s complete financial function suite.
Conclusion
The Excel NPER function is an indispensable tool for financial analysis and planning. By understanding its syntax, parameters, and applications, you can make informed financial decisions and create sophisticated financial models. Whether calculating loan terms, investment durations, or savings timelines, NPER provides the accuracy and flexibility needed for professional financial analysis.
Master the NPER function by practicing with various scenarios, understanding its relationship with other financial functions, and applying it to real-world situations. This knowledge will enhance your Excel skills and improve your financial decision-making capabilities.