PostCSS has revolutionized how developers write and process CSS by providing a powerful, plugin-based ecosystem that transforms your stylesheets with JavaScript. Unlike traditional CSS preprocessors like Sass or Less, PostCSS operates as a postprocessor, allowing you to use future CSS syntax today while maintaining backward compatibility.
What is PostCSS?
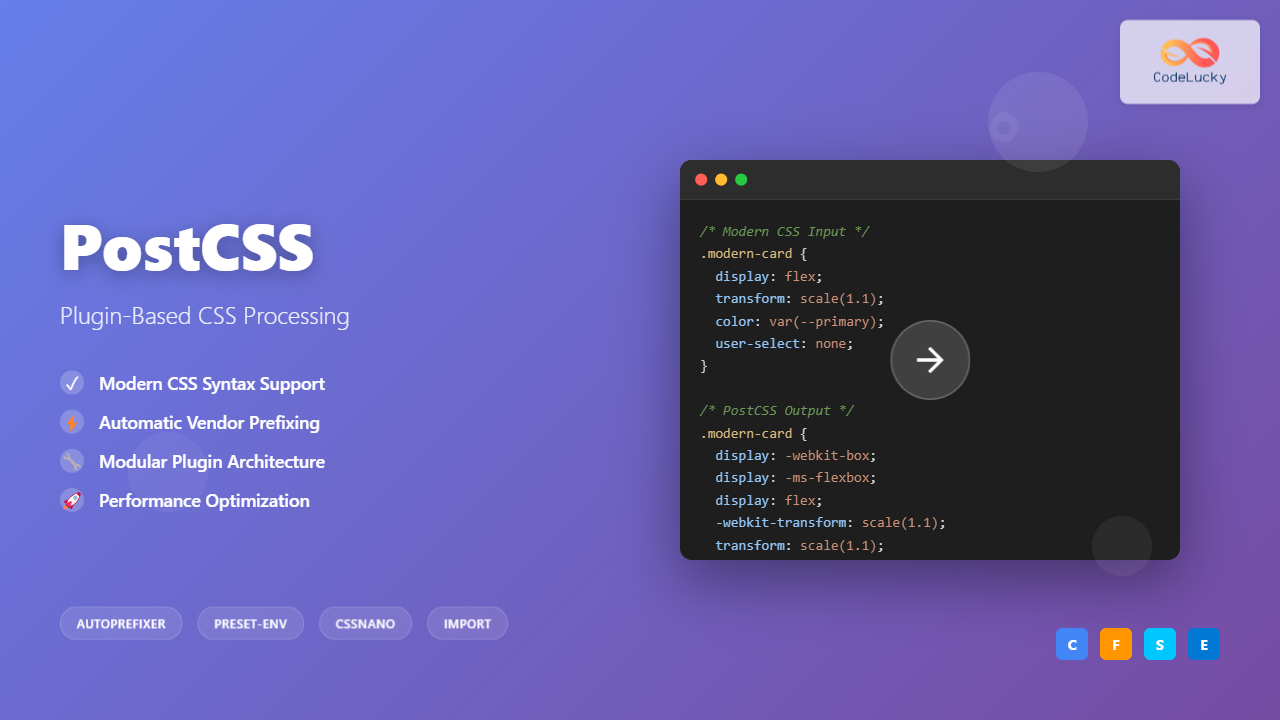
PostCSS is a tool for transforming CSS using JavaScript plugins. It parses CSS into an Abstract Syntax Tree (AST), applies transformations through plugins, and outputs the modified CSS. This approach makes it incredibly flexible and performant compared to traditional preprocessors.
- Modular architecture – use only what you need
- Future CSS syntax support
- Automatic vendor prefixing
- Custom property fallbacks
- Performance optimization
Setting Up PostCSS
PostCSS can be integrated into your build process through various methods. Here’s how to set it up with different tools:
Installation via npm
# Install PostCSS CLI and core package
npm install --save-dev postcss postcss-cli
# Install essential plugins
npm install --save-dev autoprefixer postcss-preset-env cssnanoConfiguration File
Create a postcss.config.js file in your project root:
module.exports = {
plugins: [
require('postcss-preset-env')({
stage: 1,
features: {
'custom-properties': false
}
}),
require('autoprefixer'),
require('cssnano')({
preset: 'default'
})
]
}Essential PostCSS Plugins
1. Autoprefixer
Automatically adds vendor prefixes to CSS rules based on browser support data from Can I Use.
Input CSS:
.box {
display: flex;
transform: scale(1.2);
user-select: none;
}Output CSS:
.box {
display: -webkit-box;
display: -ms-flexbox;
display: flex;
-webkit-transform: scale(1.2);
transform: scale(1.2);
-webkit-user-select: none;
-moz-user-select: none;
-ms-user-select: none;
user-select: none;
}2. PostCSS Preset Env
Enables modern CSS features by converting them into browser-compatible CSS. It includes autoprefixer and supports stage-based feature adoption.
Modern CSS Input:
:root {
--main-color: #3498db;
--spacing: 1rem;
}
.card {
color: var(--main-color);
margin: var(--spacing);
/* Modern nesting */
& .title {
font-size: 1.5rem;
}
/* Custom media queries */
@media (--viewport-medium) {
padding: 2rem;
}
}Compatible Output:
:root {
--main-color: #3498db;
--spacing: 1rem;
}
.card {
color: #3498db;
color: var(--main-color);
margin: 1rem;
margin: var(--spacing);
}
.card .title {
font-size: 1.5rem;
}
@media (min-width: 768px) {
.card {
padding: 2rem;
}
}3. CSSnano
Optimizes and minifies CSS for production, reducing file size significantly.
# Before optimization (expanded)
.button {
background-color: #3498db;
border-radius: 4px;
padding: 12px 24px;
margin: 0px;
border: none;
}
# After CSSnano optimization
.button{background-color:#3498db;border-radius:4px;padding:12px 24px;margin:0;border:none}Advanced PostCSS Plugins
PostCSS Import
Enables CSS file imports with intelligent dependency resolution and inline processing.
/* main.css */
@import "normalize.css";
@import "components/buttons.css";
@import "utilities/spacing.css";PostCSS Mixins
Provides Sass-like mixins functionality for reusable CSS patterns.
/* Define mixin */
@define-mixin button-style $bg-color, $text-color {
background-color: $(bg-color);
color: $(text-color);
padding: 12px 24px;
border-radius: 4px;
border: none;
cursor: pointer;
&:hover {
opacity: 0.8;
}
}
/* Use mixin */
.primary-btn {
@mixin button-style #3498db, white;
}
.secondary-btn {
@mixin button-style #95a5a6, white;
}Interactive PostCSS Playground
Try PostCSS Transformations
Build Integration Examples
Webpack Integration
// webpack.config.js
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [
'style-loader',
'css-loader',
{
loader: 'postcss-loader',
options: {
postcssOptions: {
plugins: [
require('postcss-preset-env'),
require('autoprefixer'),
]
}
}
}
]
}
]
}
}Vite Integration
// vite.config.js
import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
export default defineConfig({
css: {
postcss: {
plugins: [
require('postcss-preset-env')({
stage: 1
}),
require('autoprefixer'),
require('cssnano')
]
}
}
})Performance Optimization with PostCSS
PostCSS can significantly optimize your CSS performance through various techniques:
Critical CSS Extraction
const criticalCSS = require('postcss-critical-css');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
criticalCSS({
preserve: false,
minify: true,
width: 1920,
height: 1080
})
]
}Unused CSS Removal
const purgecss = require('@fullhuman/postcss-purgecss');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
purgecss({
content: ['./src/**/*.html', './src/**/*.js'],
defaultExtractor: content => content.match(/[\w-/:]+(?Custom PostCSS Plugin Development
Creating custom plugins allows you to extend PostCSS functionality for specific needs:
// custom-plugin.js
const postcss = require('postcss');
module.exports = postcss.plugin('postcss-custom-rem', (opts = {}) => {
return (root, result) => {
const baseFontSize = opts.baseFontSize || 16;
root.walkDecls(decl => {
if (decl.value.includes('rem(')) {
decl.value = decl.value.replace(/rem\((\d+(?:\.\d+)?)\)/g, (match, value) => {
const remValue = parseFloat(value) / baseFontSize;
return `${remValue}rem`;
});
}
});
};
});Debugging and Development Tools
Source Maps
Enable source maps for easier debugging in development:
module.exports = {
plugins: [
require('postcss-preset-env'),
require('autoprefixer')
],
map: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development' ? { inline: false } : false
}PostCSS Reporter
const reporter = require('postcss-reporter');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
require('postcss-preset-env'),
reporter({
clearReportedMessages: true,
throwError: true
})
]
}Best Practices and Tips
⚡ Performance Tips
- Plugin Order Matters: Place optimization plugins (cssnano) last
- Use Stage-Based Features: Start with stage 2-3 for better stability
- Enable Caching: Configure build tools to cache PostCSS results
- Minimize Plugin Usage: Only include plugins you actually need
Common Configuration Patterns
// Production-optimized configuration
const isProduction = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production';
module.exports = {
plugins: [
require('postcss-import'),
require('postcss-mixins'),
require('postcss-preset-env')({
stage: 2,
autoprefixer: { grid: true }
}),
...(isProduction ? [
require('cssnano')({
preset: ['advanced', {
discardComments: { removeAll: true },
normalizeWhitespace: true
}]
})
] : [])
]
}Troubleshooting Common Issues
Plugin Conflicts
When plugins conflict, check the order and compatibility:
// Correct order: Import → Process → Optimize
module.exports = {
plugins: [
require('postcss-import'), // First: resolve imports
require('postcss-mixins'), // Second: expand mixins
require('postcss-preset-env'), // Third: transform syntax
require('autoprefixer'), // Fourth: add prefixes
require('cssnano') // Last: optimize output
]
}Browser Support Configuration
// .browserslistrc file
> 1%
last 2 versions
not dead
not ie 11Future of PostCSS
PostCSS continues evolving with new features and improvements. Recent developments include better CSS-in-JS support, enhanced TypeScript integration, and improved performance through parallel processing. The ecosystem grows constantly with new plugins addressing modern development needs.
🚀 Next Steps
Start with basic plugins like autoprefixer and postcss-preset-env, then gradually add specialized plugins as your project needs grow. PostCSS’s modular approach means you can adopt it incrementally without disrupting existing workflows.
PostCSS transforms how we approach CSS development by providing a flexible, plugin-based architecture that grows with your project needs. Whether you’re building a simple website or a complex application, PostCSS offers the tools to write modern, maintainable CSS while ensuring broad browser compatibility.