The xrdp command is a powerful Linux utility that implements Microsoft’s Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) server functionality on Unix-like systems. This open-source solution enables seamless remote desktop access to Linux machines from Windows, macOS, or other Linux systems using standard RDP clients.
What is xrdp?
xrdp (X Remote Desktop Protocol) is a free and open-source implementation of Microsoft RDP server that allows users to access Linux desktops remotely. Unlike traditional VNC solutions, xrdp provides better performance, security features, and native integration with Windows Remote Desktop clients.
Key Features of xrdp
- Protocol Compatibility: Full RDP protocol support
- Multi-session Support: Multiple simultaneous user sessions
- Security: SSL/TLS encryption and authentication
- Performance: Optimized for low-bandwidth connections
- Cross-platform: Works with various RDP clients
Installing xrdp on Different Linux Distributions
Ubuntu/Debian Installation
# Update package repositories
sudo apt update
# Install xrdp
sudo apt install xrdp
# Install additional desktop environment (if needed)
sudo apt install ubuntu-desktop-minimal
CentOS/RHEL/Fedora Installation
# Enable EPEL repository (CentOS/RHEL)
sudo yum install epel-release
# Install xrdp
sudo yum install xrdp
# For Fedora
sudo dnf install xrdp
Arch Linux Installation
# Install from AUR
yay -S xrdp
# Or using pacman (if available in repos)
sudo pacman -S xrdp
Basic xrdp Commands and Usage
Service Management Commands
# Start xrdp service
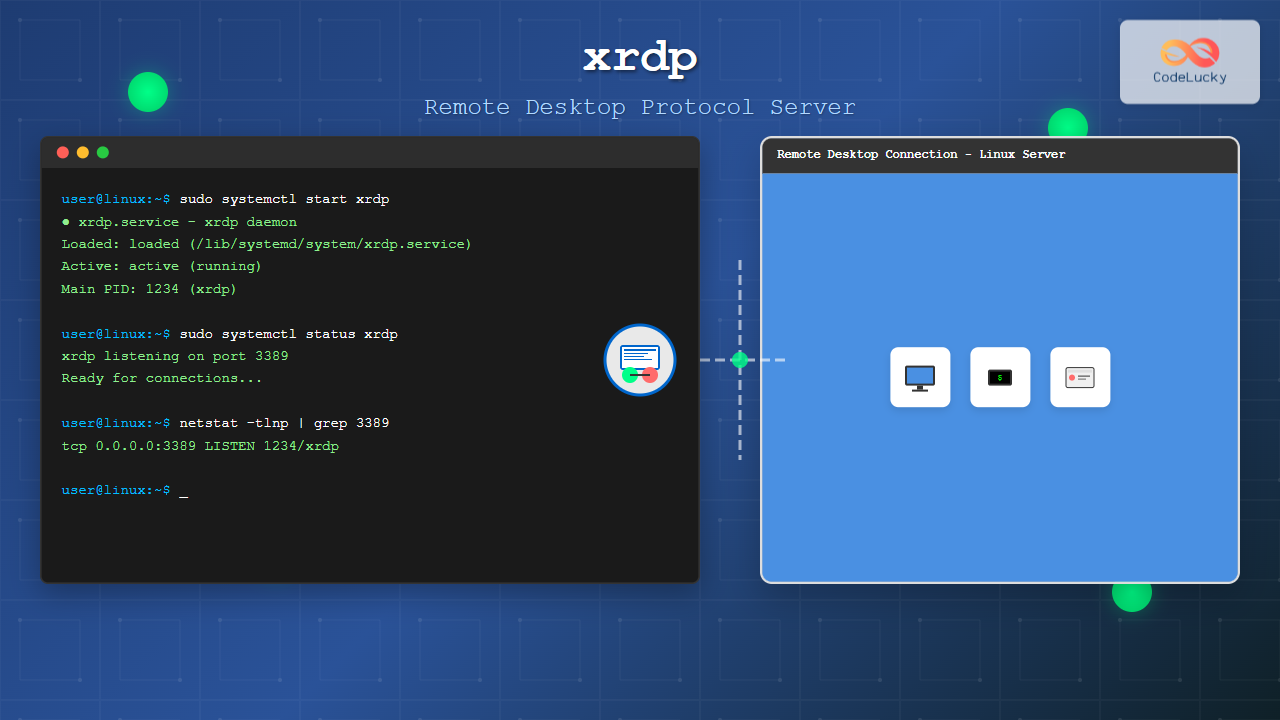
sudo systemctl start xrdp
# Enable xrdp to start at boot
sudo systemctl enable xrdp
# Check xrdp service status
sudo systemctl status xrdp
# Stop xrdp service
sudo systemctl stop xrdp
# Restart xrdp service
sudo systemctl restart xrdp
Expected output for status check:
● xrdp.service - xrdp daemon
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/xrdp.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2025-08-26 04:30:15 IST; 2min 14s ago
Docs: man:xrdp(8)
man:xrdp.ini(5)
Main PID: 12345 (xrdp)
CGroup: /system.slice/xrdp.service
└─12345 /usr/sbin/xrdp --nodaemon
Configuration Commands
# View current xrdp configuration
sudo cat /etc/xrdp/xrdp.ini
# Edit xrdp configuration
sudo nano /etc/xrdp/xrdp.ini
# Check xrdp configuration syntax
sudo xrdp --help
# View xrdp version
xrdp --version
xrdp Configuration Files
Main Configuration File: /etc/xrdp/xrdp.ini
[globals]
; xrdp.ini file version number
ini_version=1
; fork a new process for each incoming connection
fork=true
; ports to listen on, number alone means listen on all interfaces
; 0.0.0.0 or :: if ipv6 is configured
; space between multiple occurrences
port=3389
; regulate if the listening socket use socket option tcp_nodelay
; no buffering will be performed in the TCP stack
tcp_nodelay=true
; regulate if the listening socket use socket option keepalive
; if the network connection disappear without close messages the connection will be closed
tcp_keepalive=true
[Xorg]
name=Xorg
lib=libxup.so
username=ask
password=ask
ip=127.0.0.1
port=-1
code=20
Session Manager Configuration: /etc/xrdp/sesman.ini
[Globals]
ListenPort=3350
EnableUserWindowManager=true
UserWindowManager=startwm.sh
DefaultWindowManager=startwm.sh
ReconnectSH=reconnectwm.sh
[Security]
AllowRootLogin=false
MaxLoginRetry=4
TerminalServerUsers=tsusers
TerminalServerAdmins=tsadmins
[Sessions]
X11DisplayOffset=10
MaxSessions=50
KillDisconnected=false
IdleTimeLimit=0
DisconnectedTimeLimit=0
Advanced xrdp Configuration
Configuring SSL/TLS Security
# Generate SSL certificate
sudo openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout /etc/xrdp/key.pem -out /etc/xrdp/cert.pem -days 365
# Set proper permissions
sudo chmod 400 /etc/xrdp/key.pem
sudo chmod 444 /etc/xrdp/cert.pem
# Update xrdp.ini for SSL
sudo nano /etc/xrdp/xrdp.ini
Add the following SSL configuration:
[globals]
security_layer=tls
certificate=/etc/xrdp/cert.pem
key_file=/etc/xrdp/key.pem
ssl_protocols=TLSv1.2
Firewall Configuration
# UFW (Ubuntu/Debian)
sudo ufw allow 3389/tcp
# Firewalld (CentOS/RHEL/Fedora)
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3389/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
# iptables
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 3389 -j ACCEPT
User Management for xrdp
Adding Users to xrdp Group
# Add user to ssl-cert group (Ubuntu/Debian)
sudo usermod -a -G ssl-cert username
# Create xrdp user group
sudo groupadd xrdp-users
# Add user to xrdp-users group
sudo usermod -a -G xrdp-users username
# Verify user groups
groups username
Setting Up Desktop Environment
# Create .xsession file for user
echo "gnome-session" > ~/.xsession
# Or for XFCE
echo "startxfce4" > ~/.xsession
# Make it executable
chmod +x ~/.xsession
xrdp Performance Optimization
Bandwidth Optimization
# Edit xrdp.ini for performance
[globals]
; Set bitmap compression
bitmap_compression=true
; Optimize for WAN connections
tcp_send_buffer_bytes=32768
tcp_recv_buffer_bytes=32768
; Enable bitmap cache
bitmap_cache=true
Session Optimization
# Configure session limits in sesman.ini
[Sessions]
; Maximum concurrent sessions per user
MaxSessions=10
; Session timeout settings
IdleTimeLimit=3600
DisconnectedTimeLimit=600
; Kill disconnected sessions
KillDisconnected=true
Troubleshooting xrdp Issues
Common Diagnostic Commands
# Check if xrdp is listening on port 3389
sudo netstat -tlnp | grep 3389
# View xrdp logs
sudo tail -f /var/log/xrdp.log
# Check sesman logs
sudo tail -f /var/log/xrdp-sesman.log
# Test local RDP connection
telnet localhost 3389
Expected netstat output:
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3389 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 12345/xrdp
tcp6 0 0 :::3389 :::* LISTEN 12345/xrdp
Common Issues and Solutions
Black Screen After Login
# Fix PolicyKit authentication
sudo nano /etc/polkit-1/localauthority/50-local.d/45-allow-colord.pkla
[Allow Colord all Users]
Identity=unix-user:*
Action=org.freedesktop.color-manager.create-device;org.freedesktop.color-manager.create-profile;org.freedesktop.color-manager.delete-device;org.freedesktop.color-manager.delete-profile;org.freedesktop.color-manager.modify-device;org.freedesktop.color-manager.modify-profile
ResultAny=no
ResultInactive=no
ResultActive=yes
Connection Refused Error
# Check if services are running
sudo systemctl status xrdp
sudo systemctl status xrdp-sesman
# Restart both services
sudo systemctl restart xrdp
sudo systemctl restart xrdp-sesman
# Check firewall status
sudo ufw status
Monitoring xrdp Performance
Real-time Monitoring
# Monitor active connections
sudo netstat -an | grep 3389
# Check process status
ps aux | grep xrdp
# Monitor system resources
htop -p $(pgrep xrdp)
# View connection statistics
sudo ss -tulpn | grep 3389
Log Analysis
# Analyze connection patterns
sudo grep "connection ok" /var/log/xrdp.log | tail -10
# Check failed login attempts
sudo grep "login failed" /var/log/xrdp-sesman.log
# Monitor session activities
sudo grep "session start" /var/log/xrdp-sesman.log
Security Best Practices
Access Control Configuration
# Restrict access by IP
sudo nano /etc/hosts.allow
# Add: sshd: 192.168.1.0/24
sudo nano /etc/hosts.deny
# Add: ALL: ALL
# Configure fail2ban for xrdp
sudo nano /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
Enhanced Security Settings
[xrdp]
enabled = true
port = 3389
filter = xrdp
logpath = /var/log/xrdp-sesman.log
maxretry = 3
findtime = 300
bantime = 600
Automation and Scripting
xrdp Installation Script
#!/bin/bash
# xrdp-setup.sh - Automated xrdp installation and configuration
echo "Installing xrdp..."
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y xrdp
echo "Configuring firewall..."
sudo ufw allow 3389/tcp
echo "Starting services..."
sudo systemctl enable xrdp
sudo systemctl start xrdp
echo "Creating SSL certificate..."
sudo openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes \
-keyout /etc/xrdp/key.pem \
-out /etc/xrdp/cert.pem \
-days 365 -batch
sudo chmod 400 /etc/xrdp/key.pem
sudo chmod 444 /etc/xrdp/cert.pem
echo "xrdp installation completed successfully!"
echo "Connect using: $(hostname -I | awk '{print $1}'):3389"
Connection Testing Script
#!/bin/bash
# test-xrdp.sh - Test xrdp connectivity
HOST=${1:-localhost}
PORT=${2:-3389}
echo "Testing xrdp connection to $HOST:$PORT..."
# Test port connectivity
if timeout 5 bash -c "Integration with Desktop Environments
GNOME Configuration
# Configure GNOME for xrdp
sudo nano /etc/xrdp/startwm.sh
# Add before the last line:
unset DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS
unset XDG_RUNTIME_DIR
gnome-session
XFCE Configuration
# Install XFCE desktop
sudo apt install xfce4 xfce4-goodies
# Configure for xrdp
echo "startxfce4" > ~/.xsession
chmod +x ~/.xsession
Conclusion
The xrdp command provides a robust solution for remote desktop access on Linux systems. By following this comprehensive guide, you can successfully install, configure, and optimize xrdp for your specific needs. Remember to implement proper security measures, monitor performance regularly, and keep your xrdp installation updated for the best experience.
Whether you’re managing a single Linux workstation or deploying xrdp across multiple servers, understanding these commands and configurations will help you maintain reliable remote desktop connectivity while ensuring security and performance standards.