wpa_supplicant is a crucial Linux daemon that handles WPA/WPA2 wireless authentication, making it possible to connect to secure wireless networks. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about configuring and using wpa_supplicant for reliable wireless connectivity.
What is wpa_supplicant?
wpa_supplicant is an IEEE 802.1X supplicant implementation that provides key negotiation with WPA authenticators and controls the roaming and IEEE 802.11 authentication/association processes. It supports various authentication methods including WPA-PSK, WPA-EAP, and WPA2.
Key Features
- WPA/WPA2 personal and enterprise support
- IEEE 802.11i/RSN (WPA2) pre-authentication
- IEEE 802.1X EAP methods
- Dynamic WEP keys with IEEE 802.1X
- Wireless Protected Setup (WPS)
- P2P (Wi-Fi Direct) support
Installation and Setup
Installing wpa_supplicant
On most Linux distributions, wpa_supplicant comes pre-installed. If not, install it using your package manager:
# Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt update
sudo apt install wpasupplicant
# CentOS/RHEL/Fedora
sudo yum install wpa_supplicant
# or
sudo dnf install wpa_supplicant
# Arch Linux
sudo pacman -S wpa_supplicantChecking Installation
$ wpa_supplicant -vExpected output:
wpa_supplicant v2.9
Copyright (c) 2003-2019, Jouni Malinen <[email protected]> and contributors
This software may be distributed under the terms of the BSD license.
See README for more details.Configuration File Structure
The main configuration file is typically located at /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf. The basic structure includes global parameters and network blocks.
Basic Configuration Template
# /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf
ctrl_interface=/run/wpa_supplicant
ctrl_interface_group=wheel
update_config=1
country=US
network={
ssid="YourNetworkName"
psk="YourPassword"
priority=1
}Configuration Parameters Explained
| Parameter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| ctrl_interface | Control interface socket path | /run/wpa_supplicant |
| ctrl_interface_group | Group allowed to use control interface | wheel |
| update_config | Allow configuration updates | 1 (enabled) |
| country | Country code for regulatory domain | US, GB, DE |
Network Configuration Examples
WPA2-PSK (Personal) Network
network={
ssid="HomeNetwork"
psk="MySecurePassword123"
key_mgmt=WPA-PSK
proto=WPA2
pairwise=CCMP
group=CCMP
priority=5
}WPA3-SAE Network
network={
ssid="WPA3Network"
sae_password="MyWPA3Password"
key_mgmt=SAE
ieee80211w=2
priority=10
}Hidden Network
network={
ssid="HiddenNetwork"
psk="HiddenPassword123"
scan_ssid=1
priority=3
}Open Network
network={
ssid="FreeWiFi"
key_mgmt=NONE
priority=1
}Enterprise WPA2-EAP
network={
ssid="CorpNetwork"
key_mgmt=WPA-EAP
eap=PEAP
identity="[email protected]"
password="password123"
phase2="auth=MSCHAPV2"
ca_cert="/etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificate.pem"
priority=8
}Running wpa_supplicant
Basic Command Structure
sudo wpa_supplicant -i <interface> -c <config_file> -BCommon Usage Examples
Start wpa_supplicant in Background
sudo wpa_supplicant -B -i wlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.confStart with Debug Output
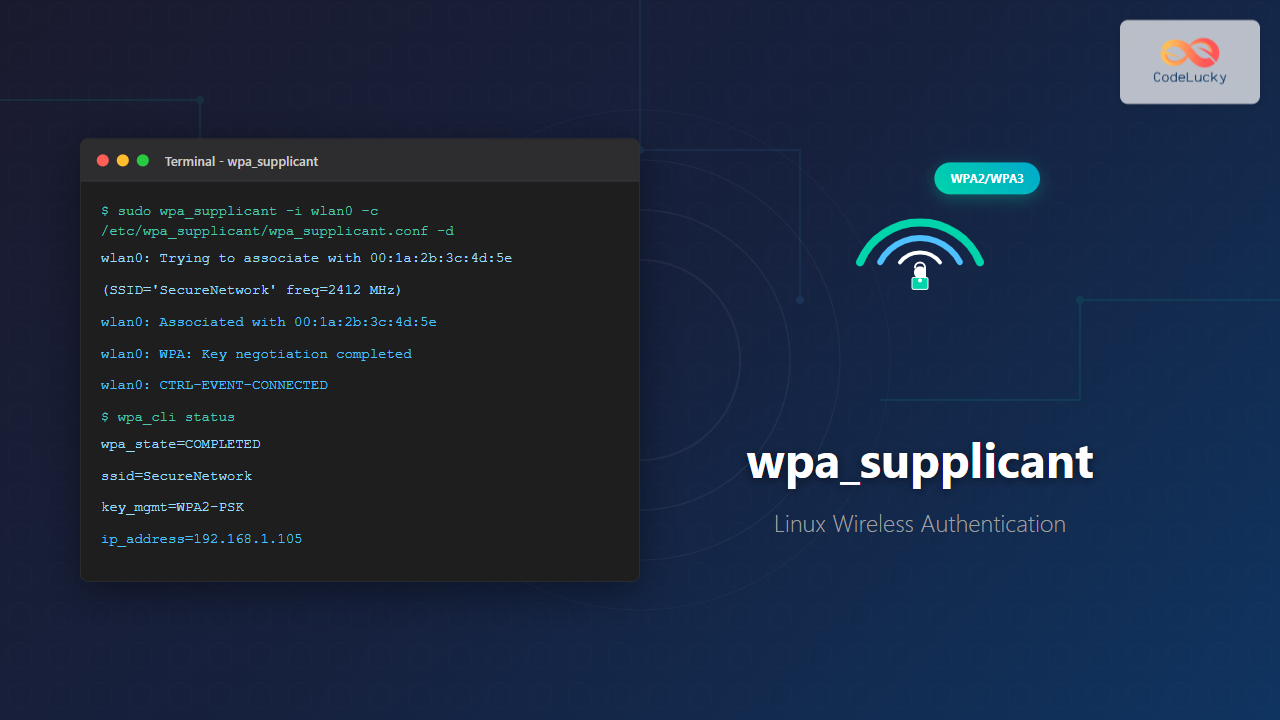
sudo wpa_supplicant -i wlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf -dDebug output example:
wlan0: Trying to associate with 00:1a:2b:3c:4d:5e (SSID='HomeNetwork' freq=2412 MHz)
wlan0: Associated with 00:1a:2b:3c:4d:5e
wlan0: WPA: Key negotiation completed with 00:1a:2b:3c:4d:5e [PTK=CCMP GTK=CCMP]
wlan0: CTRL-EVENT-CONNECTED - Connection to 00:1a:2b:3c:4d:5e completedStart with Specific Driver
sudo wpa_supplicant -D nl80211 -i wlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.confCommand-Line Options
| Option | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| -i | Network interface | -i wlan0 |
| -c | Configuration file path | -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf |
| -B | Run in background (daemon mode) | -B |
| -D | Driver name | -D nl80211 |
| -d | Debug mode | -d |
| -P | PID file | -P /run/wpa_supplicant.pid |
Using wpa_cli (Interactive Control)
wpa_cli provides an interactive command-line interface for controlling wpa_supplicant.
Starting wpa_cli
$ sudo wpa_cli -i wlan0Interactive prompt:
wpa_cli v2.9
Copyright (c) 2004-2019, Jouni Malinen <[email protected]> and contributors
Interactive mode
>Common wpa_cli Commands
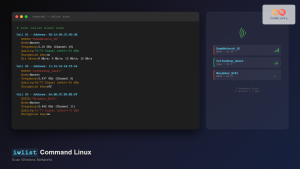
Scan for Networks
> scan
OK
> scan_results
bssid / frequency / signal level / flags / ssid
00:1a:2b:3c:4d:5e 2412 -45 [WPA2-PSK-CCMP][ESS] HomeNetwork
aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff 2437 -52 [WPA2-PSK-CCMP][WPS][ESS] NeighborWiFi
11:22:33:44:55:66 5180 -38 [WPA2-PSK-CCMP][ESS] Office5GAdd Network
> add_network
0
> set_network 0 ssid "NewNetwork"
OK
> set_network 0 psk "password123"
OK
> enable_network 0
OKCheck Status
> status
bssid=00:1a:2b:3c:4d:5e
freq=2412
ssid=HomeNetwork
id=0
mode=station
pairwise_cipher=CCMP
group_cipher=CCMP
key_mgmt=WPA2-PSK
wpa_state=COMPLETED
ip_address=192.168.1.105List Networks
> list_networks
network id / ssid / bssid / flags
0 HomeNetwork any [CURRENT]
1 Office5G any [DISABLED]
2 FreeWiFi any [DISABLED]Save Configuration
> save_config
OKSystemd Integration
Enable wpa_supplicant Service
# Enable for specific interface
sudo systemctl enable [email protected]
# Start the service
sudo systemctl start [email protected]
# Check status
sudo systemctl status [email protected]Status output example:
● [email protected] - WPA supplicant daemon (interface-specific version)
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/[email protected]; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2025-08-26 02:15:32 IST; 15min ago
Main PID: 1234 (wpa_supplicant)
Status: "wlan0: COMPLETED"
Tasks: 1 (limit: 4915)
CGroup: /system.slice/system-wpa_supplicant.slice/[email protected]
└─1234 /sbin/wpa_supplicant -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant-wlan0.conf -i wlan0Custom Service File
Create a custom service file at /etc/systemd/system/wpa_supplicant-custom.service:
[Unit]
Description=WPA supplicant
Before=network.target
After=dbus.service
Wants=network.target
IgnoreOnIsolate=true
[Service]
Type=dbus
BusName=fi.w1.wpa_supplicant1
ExecStart=/sbin/wpa_supplicant -u -s -O /run/wpa_supplicant
Restart=always
RestartSec=5
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetAdvanced Configuration
Multiple Network Priorities
# High priority home network
network={
ssid="HomeNetwork"
psk="homepassword"
priority=10
}
# Medium priority office network
network={
ssid="OfficeNetwork"
psk="officepassword"
priority=5
}
# Low priority public network
network={
ssid="PublicWiFi"
key_mgmt=NONE
priority=1
}MAC Address Randomization
# Global MAC randomization
mac_addr=1
preassoc_mac_addr=1
gas_rand_mac_addr=1
network={
ssid="PrivacyNetwork"
psk="password123"
mac_addr=1
}Country-Specific Configuration
# Country code for regulatory compliance
country=US
# Scan only allowed channels
freq_list=2412 2437 2462 5180 5200 5220
network={
ssid="USNetwork"
psk="password123"
scan_freq=2412 2437 2462
}Security Considerations
Protecting Configuration Files
# Set proper permissions
sudo chmod 600 /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf
sudo chown root:root /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.confUsing PSK Hash Instead of Plaintext
Generate PSK hash to avoid storing plaintext passwords:
$ wpa_passphrase "NetworkName" "password123"Output:
network={
ssid="NetworkName"
#psk="password123"
psk=a1b2c3d4e5f6789012345678901234567890abcdef1234567890abcdef123456
}Troubleshooting
Common Issues and Solutions
Authentication Failures
# Check logs for authentication errors
journalctl -u wpa_supplicant@wlan0 -f
# Common error patterns:
# CTRL-EVENT-SSID-TEMP-DISABLED - Wrong password
# CTRL-EVENT-SCAN-FAILED - Driver issues
# CTRL-EVENT-ASSOC-REJECT - Network rejectionInterface Not Found
# Check available interfaces
ip link show
# Bring interface up
sudo ip link set wlan0 up
# Check interface state
iwconfig wlan0Driver Issues
# List available drivers
wpa_supplicant -h
# Try different driver
sudo wpa_supplicant -D wext -i wlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.confDebug Mode Analysis
# Run with maximum debug output
sudo wpa_supplicant -i wlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf -dddDebug output analysis:
# Successful connection stages:
1. CTRL-EVENT-SCAN-STARTED
2. CTRL-EVENT-SCAN-RESULTS
3. Trying to associate with [BSSID]
4. Associated with [BSSID]
5. WPA: Key negotiation completed
6. CTRL-EVENT-CONNECTEDPerformance Optimization
Roaming Configuration
network={
ssid="EnterpriseNetwork"
psk="password123"
# Fast roaming settings
bgscan="simple:30:-45:300"
scan_freq=2412 2437 2462 5180 5200
}Power Management
# Disable power saving for better performance
iwconfig wlan0 power off
# Or configure in wpa_supplicant
network={
ssid="NetworkName"
psk="password123"
# Disable power save
disable_ht=1
disable_vht=1
}Integration with Network Managers
Working with NetworkManager
If using NetworkManager, stop it before using wpa_supplicant directly:
# Stop NetworkManager
sudo systemctl stop NetworkManager
# Disable NetworkManager management for interface
echo 'SUBSYSTEM=="net", ACTION=="add", DRIVERS=="?*", ATTR{address}=="aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff", ATTR{dev_id}=="0x0", ATTR{type}=="1", NAME="wlan0"' | sudo tee /etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rulesUsing with netplan (Ubuntu 18+)
# /etc/netplan/01-network-config.yaml
network:
version: 2
wifis:
wlan0:
dhcp4: yes
access-points:
"NetworkName":
password: "password123"Best Practices
Configuration Management
- Keep configuration files secure with proper permissions
- Use PSK hashes instead of plaintext passwords
- Regularly update country codes for compliance
- Set appropriate network priorities
- Monitor logs for security events
Monitoring and Maintenance
# Create monitoring script
#!/bin/bash
# monitor-wifi.sh
while true; do
STATUS=$(wpa_cli -i wlan0 status | grep wpa_state)
if [[ "$STATUS" != *"COMPLETED"* ]]; then
echo "$(date): WiFi disconnected, attempting reconnection"
wpa_cli -i wlan0 reassociate
fi
sleep 30
doneConclusion
wpa_supplicant is a powerful and flexible tool for managing wireless connections on Linux systems. By understanding its configuration options, command-line usage, and troubleshooting techniques, you can ensure reliable and secure wireless connectivity. Whether you’re managing a single device or deploying across multiple systems, wpa_supplicant provides the foundation for robust wireless network authentication.
Remember to regularly update your configurations, monitor connection stability, and follow security best practices to maintain optimal wireless connectivity performance.
- What is wpa_supplicant?
- Installation and Setup
- Configuration File Structure
- Network Configuration Examples
- Running wpa_supplicant
- Using wpa_cli (Interactive Control)
- Systemd Integration
- Advanced Configuration
- Security Considerations
- Troubleshooting
- Performance Optimization
- Integration with Network Managers
- Best Practices
- Conclusion