The wget command is one of the most powerful and versatile tools in Linux for downloading files from the internet. Whether you’re downloading a single file, mirroring an entire website, or automating download tasks, wget provides extensive functionality that makes it indispensable for system administrators, developers, and Linux users alike.
What is wget Command?
wget (World Wide Web get) is a free command-line utility for downloading files from web servers using HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP protocols. It’s a non-interactive downloader, meaning it can work in the background without requiring user interaction, making it perfect for scripts and automated tasks.
Installing wget
Most Linux distributions come with wget pre-installed. However, if it’s not available on your system, you can install it using your distribution’s package manager:
# Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt update && sudo apt install wget
# CentOS/RHEL/Fedora
sudo yum install wget
# or for newer versions
sudo dnf install wget
# Arch Linux
sudo pacman -S wgetBasic wget Syntax
The basic syntax of wget is straightforward:
wget [OPTIONS] [URL]Simple File Download Examples
Download a Single File
The simplest use case is downloading a single file:
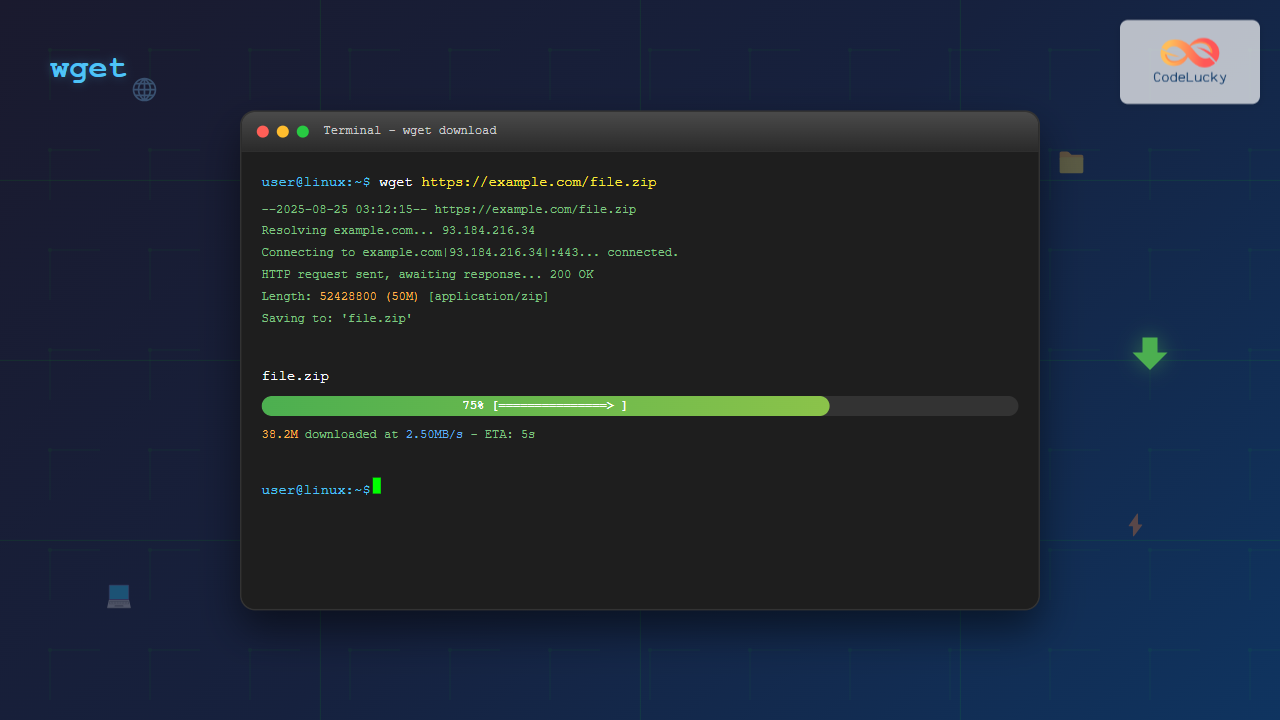
wget https://example.com/file.zipExpected Output:
--2025-08-25 03:11:42-- https://example.com/file.zip
Resolving example.com (example.com)... 93.184.216.34
Connecting to example.com (example.com)|93.184.216.34|:443... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 1048576 (1.0M) [application/zip]
Saving to: 'file.zip'
file.zip 100%[===================>] 1.00M 2.50MB/s in 0.4s
2025-08-25 03:11:43 (2.50 MB/s) - 'file.zip' saved [1048576/1048576]Download with Custom Filename
Use the -O option to specify a custom filename:
wget -O myfile.zip https://example.com/file.zipDownload to Specific Directory
Use the -P option to specify the download directory:
wget -P /home/user/downloads https://example.com/file.zipAdvanced Download Options
Resume Interrupted Downloads
One of wget’s most useful features is the ability to resume interrupted downloads:
wget -c https://example.com/largefile.isoThe -c option continues partial downloads, saving time and bandwidth when downloading large files.
Limit Download Speed
Control bandwidth usage by limiting download speed:
# Limit to 200KB/s
wget --limit-rate=200k https://example.com/file.zip
# Limit to 1MB/s
wget --limit-rate=1m https://example.com/file.zipDownload Multiple Files
Download multiple files by listing URLs in a text file:
# Create a file with URLs
echo "https://example.com/file1.zip" > urls.txt
echo "https://example.com/file2.zip" >> urls.txt
echo "https://example.com/file3.zip" >> urls.txt
# Download all files
wget -i urls.txtBackground Downloads
Run wget in the background and log output to a file:
wget -b https://example.com/largefile.isoCheck the progress by viewing the log file:
tail -f wget-logAuthentication and Headers
HTTP Authentication
For password-protected resources:
# Basic authentication
wget --user=username --password=password https://example.com/protected/file.zip
# Or use --ask-password for interactive password input
wget --user=username --ask-password https://example.com/protected/file.zipCustom Headers
Add custom headers to your requests:
wget --header="User-Agent: Custom-Agent/1.0" https://example.com/file.zip
wget --header="Authorization: Bearer token123" https://api.example.com/file.zipWebsite Mirroring and Recursive Downloads
Download Entire Website
Mirror a complete website for offline browsing:
wget -m -k -K -E https://example.comOptions explained:
-m: Mirror (equivalent to -r -N -l inf –no-remove-listing)-k: Convert links for local viewing-K: Keep backup of original files-E: Adjust extension of HTML files
Recursive Download with Depth Limit
Download files recursively with a maximum depth:
wget -r -l 2 https://example.comThe -l 2 option limits recursion to 2 levels deep.
Download Specific File Types
Download only specific file types from a website:
# Download only PDF files
wget -r -A "*.pdf" https://example.com
# Download images only
wget -r -A "*.jpg,*.png,*.gif" https://example.comFTP Downloads
Anonymous FTP
wget ftp://ftp.example.com/path/to/file.zipFTP with Authentication
wget --ftp-user=username --ftp-password=password ftp://ftp.example.com/file.zipAdvanced Configuration Options
Retry and Timeout Settings
# Set number of retries
wget --tries=5 https://example.com/file.zip
# Set timeout values
wget --timeout=30 --dns-timeout=10 --connect-timeout=15 https://example.com/file.zipUser Agent Customization
Some servers block requests from wget’s default user agent. Customize it:
wget --user-agent="Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36" https://example.com/file.zipCookie Handling
# Save cookies to file
wget --save-cookies cookies.txt https://example.com/login
# Load cookies from file
wget --load-cookies cookies.txt https://example.com/protected-areaOutput and Logging Options
Quiet and Verbose Modes
# Quiet mode (minimal output)
wget -q https://example.com/file.zip
# Verbose mode (detailed output)
wget -v https://example.com/file.zip
# Debug mode (maximum detail)
wget -d https://example.com/file.zipCustom Log Files
# Log to specific file
wget -o download.log https://example.com/file.zip
# Append to log file
wget -a download.log https://example.com/file.zipPractical Use Cases and Scripts
Automated Backup Script
#!/bin/bash
# Daily backup download script
DATE=$(date +%Y%m%d)
LOG_FILE="/var/log/backup_download_$DATE.log"
wget -o $LOG_FILE \
--timeout=300 \
--tries=3 \
-P /backup/daily \
https://backup.example.com/daily/backup_$DATE.tar.gz
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
echo "Backup downloaded successfully" >> $LOG_FILE
else
echo "Backup download failed" >> $LOG_FILE
exit 1
fiBulk File Download with Progress
#!/bin/bash
# Download multiple files with progress tracking
urls=(
"https://example.com/file1.zip"
"https://example.com/file2.zip"
"https://example.com/file3.zip"
)
total=${#urls[@]}
current=0
for url in "${urls[@]}"; do
((current++))
echo "Downloading file $current of $total: $url"
wget --progress=bar:force -P downloads "$url"
echo "Completed $current/$total downloads"
doneCommon wget Options Reference
| Option | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
-O |
Output filename | wget -O file.zip URL |
-P |
Directory prefix | wget -P /downloads URL |
-c |
Continue partial download | wget -c URL |
-b |
Background download | wget -b URL |
-t |
Number of retries | wget -t 5 URL |
-T |
Timeout in seconds | wget -T 30 URL |
-r |
Recursive download | wget -r URL |
-l |
Maximum recursion depth | wget -r -l 2 URL |
Troubleshooting Common Issues
SSL Certificate Errors
For sites with SSL certificate issues:
# Skip certificate check (use cautiously)
wget --no-check-certificate https://example.com/file.zip
# Specify CA certificate bundle
wget --ca-certificate=/path/to/ca-bundle.crt https://example.com/file.zipConnection Refused or Timeout
# Increase timeout and retry values
wget --timeout=60 --tries=10 --retry-connrefused https://example.com/file.zipServer Blocking wget
# Use a different user agent
wget --user-agent="Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Googlebot/2.1)" https://example.com/file.zipSecurity Considerations
When using wget, keep these security aspects in mind:
- Avoid plaintext passwords: Use
--ask-passwordinstead of--password - Validate certificates: Don’t use
--no-check-certificateunless absolutely necessary - Limit recursion: Always set depth limits when using recursive downloads
- Check file integrity: Verify checksums when available
Performance Optimization Tips
- Use parallel downloads: Run multiple wget instances for different files
- Optimize connection settings: Adjust timeout values based on your network
- Resume interrupted downloads: Always use
-cfor large files - Limit bandwidth: Use
--limit-rateto avoid overwhelming your connection
Conclusion
The wget command is an incredibly powerful tool for downloading files and content from the internet. From simple file downloads to complex website mirroring operations, wget provides the flexibility and reliability needed for both interactive use and automated scripts. By mastering the various options and techniques covered in this guide, you’ll be able to handle virtually any download scenario efficiently and effectively.
Remember to always respect website robots.txt files and terms of service when using wget, especially for recursive downloads and website mirroring. With great power comes great responsibility, and wget certainly provides great power for managing internet downloads in Linux environments.
- What is wget Command?
- Installing wget
- Basic wget Syntax
- Simple File Download Examples
- Advanced Download Options
- Authentication and Headers
- Website Mirroring and Recursive Downloads
- FTP Downloads
- Advanced Configuration Options
- Output and Logging Options
- Practical Use Cases and Scripts
- Common wget Options Reference
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Security Considerations
- Performance Optimization Tips
- Conclusion