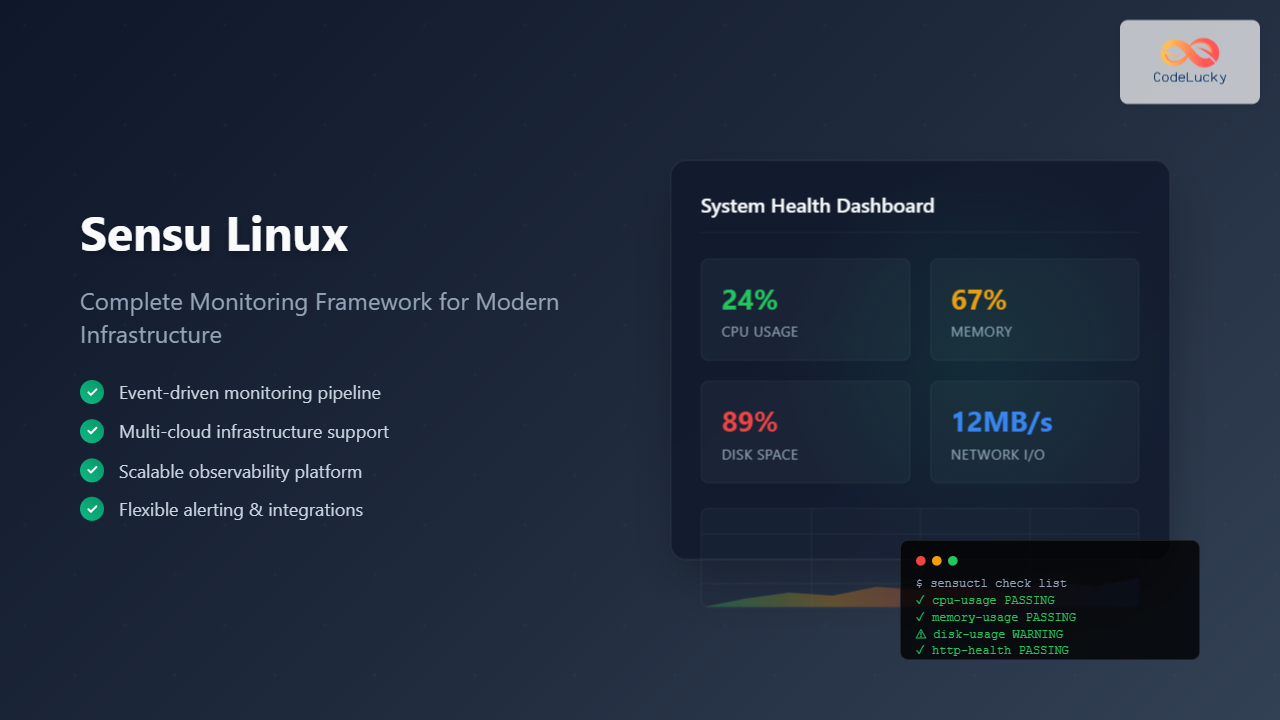
Sensu is a powerful, open-source monitoring framework designed to monitor servers, services, application health, and business KPIs. Built with modern infrastructure in mind, Sensu provides comprehensive observability for distributed systems and cloud-native environments.
What is Sensu Linux Monitoring Framework?
Sensu is a monitoring event pipeline that automates the monitoring workflow from check execution scheduling to alert handling. Unlike traditional monitoring solutions, Sensu focuses on being a monitoring router that can integrate with existing tools and workflows, making it highly flexible and adaptable to various environments.
Key Features of Sensu
- Event-driven architecture: Processes monitoring events through a flexible pipeline
- Multi-cloud support: Works across on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments
- Scalable design: Handles thousands of nodes and checks efficiently
- Rich integrations: Connects with popular tools like Slack, PagerDuty, and Grafana
- Flexible alerting: Sophisticated alert routing and filtering capabilities
Installing Sensu on Linux
Prerequisites
Before installing Sensu, ensure your system meets the following requirements:
- Linux distribution (Ubuntu 18.04+, CentOS 7+, or RHEL 7+)
- Minimum 2GB RAM and 2 CPU cores
- PostgreSQL database (for Sensu Go)
- Root or sudo privileges
Installing Sensu Go
Sensu Go is the latest version of Sensu. Here’s how to install it on Ubuntu:
# Add Sensu repository
curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/sensu/stable/script.deb.sh | sudo bash
# Update package list
sudo apt-get update
# Install Sensu Go backend and agent
sudo apt-get install sensu-go-backend sensu-go-agent sensu-go-cli
For CentOS/RHEL:
# Add Sensu repository
curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/sensu/stable/script.rpm.sh | sudo bash
# Install Sensu Go components
sudo yum install sensu-go-backend sensu-go-agent sensu-go-cli
Starting Sensu Services
# Start and enable Sensu backend
sudo systemctl start sensu-backend
sudo systemctl enable sensu-backend
# Start and enable Sensu agent
sudo systemctl start sensu-agent
sudo systemctl enable sensu-agent
# Check service status
sudo systemctl status sensu-backend
sudo systemctl status sensu-agent
Configuring Sensu Backend
Initial Backend Configuration
Create the initial configuration file for the Sensu backend:
# Create backend configuration directory
sudo mkdir -p /etc/sensu
# Create backend configuration file
sudo tee /etc/sensu/backend.yml << EOF
##
# Sensu Backend Configuration
##
state-dir: "/var/lib/sensu/sensu-backend"
cache-dir: "/var/cache/sensu/sensu-backend"
config-file: "/etc/sensu/backend.yml"
debug: false
##
# Backend store configuration
##
etcd-listen-client-urls: "http://127.0.0.1:2379"
etcd-listen-peer-urls: "http://127.0.0.1:2380"
etcd-initial-cluster: "default=http://127.0.0.1:2380"
etcd-initial-advertise-peer-urls: "http://127.0.0.1:2380"
etcd-initial-cluster-state: "new"
etcd-initial-cluster-token: ""
etcd-name: "default"
##
# Backend API configuration
##
api-listen-address: "[::]:8080"
api-url: "http://localhost:8080"
dashboard-host: "[::]"
dashboard-port: 3000
EOF
Initialize Sensu Backend
# Initialize the backend (creates admin user)
sudo sensu-backend init
# Start the backend service
sudo systemctl restart sensu-backend
Configuring Sensu Agent
Configure the Sensu agent to connect to the backend:
# Create agent configuration file
sudo tee /etc/sensu/agent.yml << EOF
##
# Sensu Agent Configuration
##
backend-url:
- "ws://127.0.0.1:8081"
cache-dir: "/var/cache/sensu/sensu-agent"
config-file: "/etc/sensu/agent.yml"
name: "$(hostname)"
namespace: "default"
subscriptions:
- "linux"
- "$(hostname)"
##
# Security configuration
##
trusted-ca-file: ""
insecure-skip-tls-verify: false
EOF
# Restart agent service
sudo systemctl restart sensu-agent
# Verify agent is connected
sudo journalctl -u sensu-agent -f
Using Sensu CLI (sensuctl)
Initial CLI Configuration
# Configure sensuctl to connect to backend
sensuctl configure -n \
--username 'admin' \
--password 'P@ssw0rd!' \
--namespace default \
--url 'http://127.0.0.1:8080'
Basic CLI Commands
# Check cluster health
sensuctl cluster health
# List all entities (agents)
sensuctl entity list
# View entity details
sensuctl entity info $(hostname)
# List all checks
sensuctl check list
# List all events
sensuctl event list
Example output:
$ sensuctl entity list
Name Class OS Subscriptions Last Seen
──────────── ─────────── ───────── ─────────────────────────── ──────────────────────────────
webserver01 agent linux linux,webserver01 2025-08-26 05:30:12 +0000 UTC
dbserver01 agent linux linux,dbserver01 2025-08-26 05:30:15 +0000 UTC
Creating Monitoring Checks
CPU Usage Check
Create a check to monitor CPU usage:
# Create CPU check configuration
cat << EOF | sensuctl create
---
type: CheckConfig
api_version: core/v2
metadata:
name: cpu-usage
namespace: default
spec:
command: "check-cpu-usage -w 75 -c 90"
subscriptions:
- "linux"
interval: 30
publish: true
runtime_assets:
- "sensu/check-cpu-usage"
handlers:
- "email"
EOF
Memory Usage Check
# Create memory check
cat << EOF | sensuctl create
---
type: CheckConfig
api_version: core/v2
metadata:
name: memory-usage
namespace: default
spec:
command: "check-memory-usage -w 80 -c 95"
subscriptions:
- "linux"
interval: 60
publish: true
runtime_assets:
- "sensu/check-memory-usage"
handlers:
- "slack"
EOF
Disk Space Check
# Create disk space check
cat << EOF | sensuctl create
---
type: CheckConfig
api_version: core/v2
metadata:
name: disk-usage
namespace: default
spec:
command: "check-disk-usage -w 85 -c 95 -p /"
subscriptions:
- "linux"
interval: 300
publish: true
runtime_assets:
- "sensu/check-disk-usage"
handlers:
- "pagerduty"
EOF
Configuring Handlers and Alerts
Email Handler
# Create email handler
cat << EOF | sensuctl create
---
type: Handler
api_version: core/v2
metadata:
name: email
namespace: default
spec:
type: pipe
command: "sensu-email-handler -f [email protected] -t [email protected] -s localhost -u username -p password"
timeout: 30
runtime_assets:
- "sensu/sensu-email-handler"
filters:
- "is_incident"
EOF
Slack Handler
# Create Slack handler
cat << EOF | sensuctl create
---
type: Handler
api_version: core/v2
metadata:
name: slack
namespace: default
spec:
type: pipe
command: "sensu-slack-handler --webhook-url https://hooks.slack.com/services/YOUR/WEBHOOK/URL --channel '#alerts'"
timeout: 30
runtime_assets:
- "sensu/sensu-slack-handler"
filters:
- "is_incident"
EOF
Creating Filters
# Create incident filter
cat << EOF | sensuctl create
---
type: EventFilter
api_version: core/v2
metadata:
name: is_incident
namespace: default
spec:
action: allow
expressions:
- event.check.status != 0
EOF
Installing Runtime Assets
Runtime assets provide the check plugins and handlers:
# Install CPU check asset
sensuctl asset add sensu/check-cpu-usage:0.2.2
# Install memory check asset
sensuctl asset add sensu/check-memory-usage:0.1.1
# Install disk check asset
sensuctl asset add sensu/check-disk-usage:0.2.1
# Install email handler asset
sensuctl asset add sensu/sensu-email-handler:0.2.0
# Install Slack handler asset
sensuctl asset add sensu/sensu-slack-handler:1.0.3
# List installed assets
sensuctl asset list
Advanced Monitoring Configurations
Service Health Check
# Create HTTP service check
cat << EOF | sensuctl create
---
type: CheckConfig
api_version: core/v2
metadata:
name: webserver-health
namespace: default
spec:
command: "check-http -u http://localhost:80 -t 10"
subscriptions:
- "webserver"
interval: 30
publish: true
runtime_assets:
- "sensu/check-http"
handlers:
- "slack"
- "email"
EOF
Database Connection Check
# Create database connection check
cat << EOF | sensuctl create
---
type: CheckConfig
api_version: core/v2
metadata:
name: database-connection
namespace: default
spec:
command: "check-postgres-alive -h localhost -u postgres -d myapp"
subscriptions:
- "database"
interval: 60
publish: true
runtime_assets:
- "sensu/check-postgres-alive"
handlers:
- "pagerduty"
EOF
Process Monitoring
# Create process monitoring check
cat << EOF | sensuctl create
---
type: CheckConfig
api_version: core/v2
metadata:
name: nginx-process
namespace: default
spec:
command: "check-process -p nginx"
subscriptions:
- "webserver"
interval: 30
publish: true
runtime_assets:
- "sensu/check-process"
handlers:
- "slack"
EOF
Setting Up Multi-Tenant Environments
Creating Namespaces
# Create production namespace
sensuctl namespace create production
# Create staging namespace
sensuctl namespace create staging
# List namespaces
sensuctl namespace list
# Switch to production namespace
sensuctl config set-namespace production
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
# Create a role for read-only access
cat << EOF | sensuctl create
---
type: Role
api_version: core/v2
metadata:
name: readonly
namespace: production
spec:
rules:
- resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["get", "list"]
EOF
# Create a user
sensuctl user create alice --password 'AlicePass123!'
# Create role binding
cat << EOF | sensuctl create
---
type: RoleBinding
api_version: core/v2
metadata:
name: alice-readonly
namespace: production
spec:
subjects:
- type: User
name: alice
role_ref:
type: Role
name: readonly
EOF
Monitoring Best Practices
Check Naming Conventions
Use descriptive, consistent naming for checks:
cpu-usage– System resource checkswebserver-health– Service health checksdatabase-connection– Connectivity checksapp-response-time– Performance checks
Subscription Management
Organize agents using meaningful subscriptions:
# Agent configuration with multiple subscriptions
subscriptions:
- "linux"
- "webserver"
- "production"
- "critical"
Alert Fatigue Prevention
# Create fatigue check filter
cat << EOF | sensuctl create
---
type: EventFilter
api_version: core/v2
metadata:
name: fatigue_check
namespace: default
spec:
action: allow
expressions:
- event.check.occurrences == 1 || event.check.occurrences % 10 == 0
EOF
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Agent Connection Issues
# Check agent logs
sudo journalctl -u sensu-agent -n 50
# Test connectivity to backend
telnet localhost 8081
# Verify agent configuration
sensuctl entity info $(hostname)
Check Execution Problems
# Check recent events
sensuctl event list --format wide
# View specific event details
sensuctl event info webserver01 cpu-usage
# Test check manually
sudo -u sensu /usr/lib/sensu/plugins/check-cpu-usage -w 75 -c 90
Backend Performance Issues
# Check backend logs
sudo journalctl -u sensu-backend -n 100
# Monitor etcd performance
sensuctl cluster health
# Check resource usage
top -p $(pgrep sensu-backend)
Integration with External Tools
Grafana Integration
Sensu can send metrics to Grafana via InfluxDB:
# Create InfluxDB handler
cat << EOF | sensuctl create
---
type: Handler
api_version: core/v2
metadata:
name: influxdb
namespace: default
spec:
type: pipe
command: "sensu-influxdb-handler -d sensu"
timeout: 30
runtime_assets:
- "sensu/sensu-influxdb-handler"
EOF
Prometheus Integration
# Create Prometheus handler
cat << EOF | sensuctl create
---
type: Handler
api_version: core/v2
metadata:
name: prometheus
namespace: default
spec:
type: pipe
command: "sensu-prometheus-collector"
timeout: 30
runtime_assets:
- "sensu/sensu-prometheus-collector"
EOF
Backup and Recovery
Backing Up Sensu Configuration
# Export all resources
sensuctl dump all > sensu-backup-$(date +%Y%m%d).json
# Export specific resource types
sensuctl dump checks,handlers,filters > monitoring-config.json
# Create automated backup script
#!/bin/bash
BACKUP_DIR="/opt/sensu/backups"
DATE=$(date +%Y%m%d_%H%M%S)
mkdir -p $BACKUP_DIR
sensuctl dump all > $BACKUP_DIR/sensu-backup-$DATE.json
find $BACKUP_DIR -name "*.json" -mtime +7 -delete
Restoring Configuration
# Restore from backup
sensuctl create --file sensu-backup-20250826.json
# Validate restored configuration
sensuctl check list
sensuctl handler list
sensuctl filter list
Performance Optimization
Backend Tuning
# Optimize backend configuration
cat << EOF | sudo tee -a /etc/sensu/backend.yml
# Performance optimizations
etcd-quota-backend-bytes: 8589934592 # 8GB
max-request-bytes: 1572864 # 1.5MB
# Connection settings
etcd-heartbeat-interval: "100ms"
etcd-election-timeout: "1000ms"
EOF
Agent Optimization
# Optimize agent performance
cat << EOF | sudo tee -a /etc/sensu/agent.yml
# Agent performance settings
keepalive-interval: 20
keepalive-warning-timeout: 120
keepalive-critical-timeout: 180
EOF
Sensu provides a robust, scalable monitoring solution for modern infrastructure. Its event-driven architecture and extensive integration capabilities make it an excellent choice for organizations requiring comprehensive observability across diverse environments. By following the configurations and best practices outlined in this guide, you can build a reliable monitoring system that scales with your infrastructure needs.