rsyslog is one of the most powerful and widely used system logging tools in Linux. It stands for “rocket-fast syslog” and offers high-performance, scalable log processing. From collecting logs locally to forwarding them over the network, rsyslog empowers administrators to manage system and application logs efficiently. In this article, we’ll explore the rsyslog command in Linux, its configuration, and practical examples you can apply immediately on your systems.
What is rsyslog?
rsyslog is a robust logging daemon for Unix-like operating systems designed to collect, filter, store, and forward log data. It supports:
- Centralized log collection with TCP/UDP or RELP protocols.
- Advanced filtering rules based on log severity, program, or content.
- Custom output formats and storage options.
- High throughput and modular plugins.
Installing rsyslog on Linux
Most Linux distributions come with rsyslog pre-installed. To ensure it is installed, you can run:
# On Debian/Ubuntu
sudo apt update
sudo apt install rsyslog
# On RHEL/CentOS
sudo yum install rsyslog
After installation, enable and start the service:
sudo systemctl enable rsyslog
sudo systemctl start rsyslog
rsyslog Service Management
Manage the rsyslog service on systemd-based systems:
# Check service status
sudo systemctl status rsyslog
# Restart rsyslog
sudo systemctl restart rsyslog
Example output of status command:
● rsyslog.service - System Logging Service Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/rsyslog.service; enabled) Active: active (running) since Mon 2025-08-25 06:00:01 IST Main PID: 1275 (rsyslogd)
Location of rsyslog Configuration File
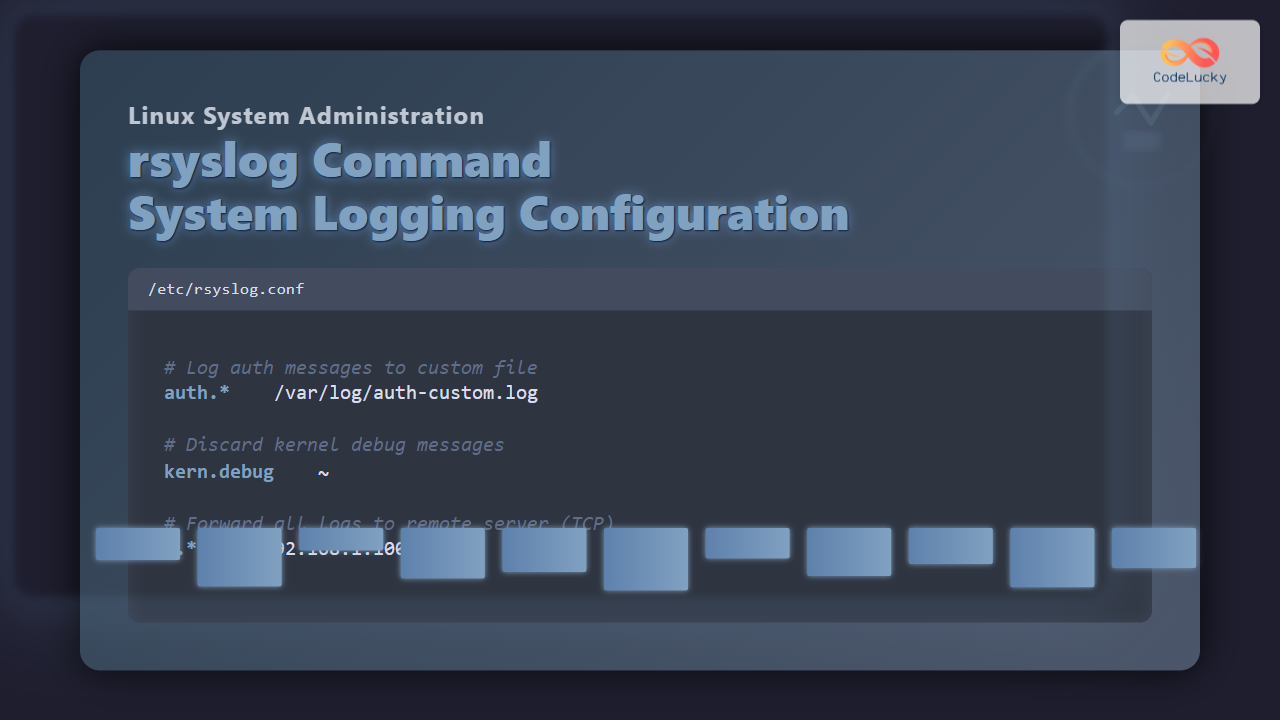
Configuration files for rsyslog are stored under:
/etc/rsyslog.conf– main configuration file./etc/rsyslog.d/– directory for modular custom configuration snippets.
rsyslog Configuration Syntax
The general syntax in /etc/rsyslog.conf uses facility.priority action format:
facility.priority action
Facility: Defines the category of message (e.g., auth, cron, daemon, kernel).
Priority: Defines the severity level (debug, info, notice, warn, err, crit, alert, emerg).
Action: Defines where the log should go (file, user terminal, or remote host).
Examples of rsyslog Configuration
1. Log Messages to a File
To send all authentication logs to a custom file:
auth.* /var/log/auth-custom.log
2. Log Only Errors and Higher Severity
To log only error (err) and above messages from the mail facility:
mail.err /var/log/mail-errors.log
3. Discard Certain Messages
To ignore kernel debug messages:
kern.debug ~
The ~ symbol discards the message.
4. Forward Logs to Remote Server
Centralized logging is one of the key strengths of rsyslog. To forward logs to a remote server 192.168.1.100 on UDP port 514:
*.* @192.168.1.100:514
For TCP instead of UDP:
*.* @@192.168.1.100:514
Note: Double @ (@@) indicates TCP and single @ indicates UDP.
5. Send Logs to User Terminal
Send critical alerts directly to a logged-in user’s terminal:
*.crit root
Viewing rsyslog Logs in Action
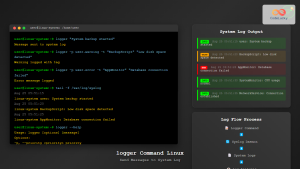
You can test log messages with the logger command:
logger "Test log from rsyslog configuration"
The message will be recorded in /var/log/syslog or /var/log/messages depending on your distribution.
Aug 25 06:05:12 server1 user[1556]: Test log from rsyslog configuration
Interactive Example: Filtering Logs in Real-Time
You can watch logs as they arrive using tail -f:
sudo tail -f /var/log/syslog
Then trigger a message:
logger -p local0.notice "Hello from rsyslog test"
You’ll see it instantly in the terminal output.
Useful Tips for rsyslog
- Always back up configuration files before editing them.
- Use
rsyslogd -N1to check configuration syntax after making changes. - Restart
rsyslogservice whenever configuration is updated. - Set proper file permissions for log files to maintain security.
Conclusion
The rsyslog command in Linux is an essential tool for system administrators who want efficient, customizable, and scalable logging. With its ability to filter logs, store them in various formats, and forward them across networks, rsyslog enables robust log management. Whether you are troubleshooting, monitoring, or building a centralized log server, mastering rsyslog is a must for Linux professionals.