The rkhunter (Rootkit Hunter) is a powerful Unix-based security scanner designed to detect rootkits, backdoors, and local exploits on Linux systems. This comprehensive tool helps system administrators maintain security by scanning for known rootkits, performing various security checks, and monitoring system integrity.
What is rkhunter?
Rkhunter is an open-source security tool that performs over 200 different security checks on your Linux system. It compares SHA-1 hashes of important files with known good ones in online databases, searches for default directories and permissions of rootkits, and looks for wrong file permissions, hidden files, and suspicious strings in kernel modules.
Key Features of rkhunter
- Rootkit Detection: Scans for known rootkits and malicious software
- File Integrity Checking: Monitors changes in critical system files
- Network Port Monitoring: Detects suspicious network activity
- System Command Verification: Checks for trojaned system binaries
- Startup File Analysis: Examines boot scripts and configuration files
- Log File Analysis: Reviews system logs for suspicious activities
Installing rkhunter
Installation methods vary depending on your Linux distribution:
Ubuntu/Debian Systems
sudo apt update
sudo apt install rkhunterCentOS/RHEL/Fedora Systems
# For CentOS/RHEL 7/8
sudo yum install rkhunter
# For Fedora
sudo dnf install rkhunterArch Linux
sudo pacman -S rkhunterManual Installation
# Download the latest version
wget https://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/rkhunter/rkhunter/1.4.6/rkhunter-1.4.6.tar.gz
# Extract and install
tar -xzf rkhunter-1.4.6.tar.gz
cd rkhunter-1.4.6
sudo ./installer.sh --layout default --installBasic rkhunter Usage
Initial Setup and Database Update
Before running your first scan, update the rkhunter database:
sudo rkhunter --updateSample Output:
[ Rootkit Hunter version 1.4.6 ]
Checking rkhunter data files...
Checking file mirrors.dat [ No update ]
Checking file programs_bad.dat [ Updated ]
Checking file backdoorports.dat [ No update ]
Checking file suspscan.dat [ Updated ]
Checking file i18n/cn [ No update ]
Checking file i18n/de [ No update ]
Checking file i18n/en [ No update ]Initialize the Properties Database
sudo rkhunter --propupdThis command creates a baseline of your system’s current state for future comparisons.
Running Security Scans
Basic System Scan
sudo rkhunter --checkThis performs a comprehensive system scan. You’ll be prompted to press Enter after each section completes.
Silent Scan with Report
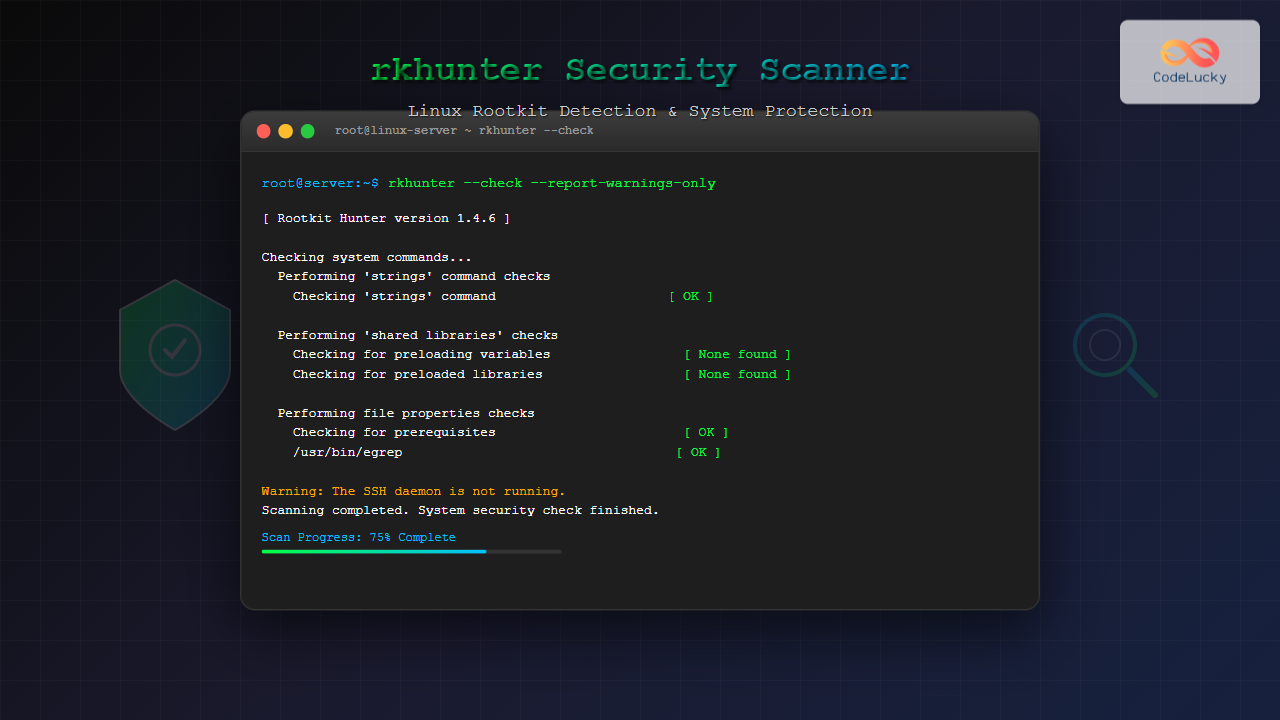
sudo rkhunter --check --skip-keypress --report-warnings-onlySample Output:
[ Rootkit Hunter version 1.4.6 ]
Checking system commands...
Performing 'strings' command checks
Checking 'strings' command [ OK ]
Performing 'shared libraries' checks
Checking for preloading variables [ None found ]
Checking for preloaded libraries [ None found ]
Checking LD_LIBRARY_PATH variable [ Not found ]
Performing file properties checks
Checking for prerequisites [ OK ]
/usr/bin/egrep [ OK ]
/usr/bin/fgrep [ OK ]
/usr/bin/which [ OK ]
Warning: The SSH daemon is not running.
Warning: The command '/usr/bin/lwp-request' has been replaced by a script: /usr/bin/lwp-request: Perl script text executableCheck Specific Components
You can scan specific system components:
# Check only for rootkits
sudo rkhunter --check --enable rootkits
# Check system commands only
sudo rkhunter --check --enable system_commands
# Check network interfaces
sudo rkhunter --check --enable networkConfiguration and Customization
The main configuration file is located at /etc/rkhunter.conf. Here are important configuration options:
Email Notifications
# Enable email notifications
[email protected]
# Set mail command
MAIL_CMD=mail -s "[rkhunter] Warnings found for ${HOST_NAME}"Whitelisting
Add trusted applications and directories:
# Whitelist specific files
ALLOWHIDDENFILE=/etc/.java
ALLOWHIDDENFILE=/dev/.udev
# Allow specific processes
ALLOWPROCLIST=/usr/sbin/mysqldDisable Specific Tests
# Disable tests that may cause false positives
DISABLE_TESTS="suspscan hidden_procs deleted_files packet_cap_apps apps"Advanced rkhunter Commands
View Current Configuration
sudo rkhunter --config-checkList Available Tests
sudo rkhunter --listSample Output:
Available test names:
all
additional_rkts
apps
attributes
avail_modules
backdoorports
deleted_files
filesystem
group_accounts
group_changes
hashes
hidden_ports
hidden_procs
immutable
known_rkts
loaded_modules
local_host
malware
network
none
os_specific
packet_cap_apps
passwd_changes
ports
possible_rkt_files
possible_rkt_strings
promisc
properties
rootkits
running_procs
scripts
shared_libs
startup_files
startup_malware
suspscan
system_commands
system_configs
trojansGenerate Reports
# Generate detailed report
sudo rkhunter --check --report-warnings-only --logfile /var/log/rkhunter-scan.log
# View the report
sudo cat /var/log/rkhunter-scan.logVersion and Help Information
# Check version
rkhunter --version
# Display help
rkhunter --helpInterpreting Scan Results
Understanding Status Messages
- [OK] – Test passed successfully
- [Warning] – Potential issue found, requires investigation
- [Not found] – Expected file or process not found
- [None found] – No suspicious items detected
- [Skipped] – Test was skipped due to configuration
Common Warnings and Solutions
SSH Configuration Warning
Warning: The SSH daemon configuration may have some non-default settings:
SSH daemon is configured to use a non-standard port: 2222Solution: This is often intentional. Whitelist in configuration:
ALLOW_SSH_ROOT_USER=yes
ALLOW_SSH_PROT_V1=2File Properties Changed
Warning: The file properties have changed:
File: /usr/bin/curl
Current hash: SHA1:a1b2c3d4e5f6...
Stored hash: SHA1:f6e5d4c3b2a1...Solution: If legitimate update occurred, refresh the database:
sudo rkhunter --propupdAutomating rkhunter Scans
Creating Scheduled Scans with Cron
Add to crontab for daily scans:
# Edit root crontab
sudo crontab -e
# Add daily scan at 2 AM
0 2 * * * /usr/bin/rkhunter --cronjob --update --quietWeekly Comprehensive Scan Script
Create a script for detailed weekly scans:
#!/bin/bash
# /usr/local/bin/rkhunter_weekly.sh
# Update database
/usr/bin/rkhunter --update --quiet
# Perform comprehensive scan
/usr/bin/rkhunter --cronjob --report-warnings-only --logfile /var/log/rkhunter-weekly.log
# Email results if warnings found
if [ -s /var/log/rkhunter-weekly.log ]; then
mail -s "rkhunter Weekly Scan - Warnings Found" [email protected] < /var/log/rkhunter-weekly.log
fiMake executable and add to cron:
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/rkhunter_weekly.sh
# Add to crontab for Sunday at 3 AM
0 3 * * 0 /usr/local/bin/rkhunter_weekly.shIntegration with System Monitoring
Log File Locations
Rkhunter logs are typically stored in:
/var/log/rkhunter.log– Main log file/var/lib/rkhunter/db/rkhunter.dat– Properties database/var/lib/rkhunter/tmp/– Temporary files during scans
Monitoring with journalctl
# View rkhunter systemd logs
sudo journalctl -u rkhunter
# Follow real-time logs
sudo journalctl -u rkhunter -fTroubleshooting Common Issues
Database Update Failures
If updates fail due to network issues:
# Check connectivity
ping -c 4 rkhunter.sourceforge.net
# Manual database download
sudo rkhunter --update --debugFalse Positives
To handle false positives effectively:
- Verify the warning is legitimate
- Check system logs for corresponding activities
- Update whitelist in configuration if appropriate
- Refresh properties database after legitimate changes
Performance Optimization
For systems with performance concerns:
# Disable resource-intensive tests
DISABLE_TESTS="suspscan apps"
# Limit scan depth
SCANROOTKITMODE=1Security Best Practices
Regular Maintenance
- Update rkhunter database weekly
- Review scan logs regularly
- Keep the rkhunter software updated
- Maintain system patches and updates
Complementary Security Tools
Use rkhunter alongside other security tools:
- ClamAV for virus scanning
- AIDE/Tripwire for file integrity monitoring
- fail2ban for intrusion prevention
- chkrootkit as secondary rootkit scanner
Conclusion
The rkhunter command is an essential tool for Linux system security, providing comprehensive rootkit detection and system integrity monitoring. Regular use of rkhunter, combined with proper configuration and automation, significantly enhances your system’s security posture. Remember to keep the tool updated, review scan results carefully, and integrate it with your broader security monitoring strategy.
By implementing the practices and commands covered in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to detect and respond to potential security threats on your Linux systems. Regular scanning with rkhunter should be part of every system administrator’s security toolkit.