The repquota command is an essential Linux system administration tool used to report disk quota usage for users and groups on filesystems with quota enforcement enabled. This comprehensive guide will help you understand and master the repquota command for effective storage management.
What is the repquota Command?
The repquota command displays quota usage and limits for all users and groups on specified filesystems. It provides detailed information about current disk usage, allocated quotas, and helps administrators monitor storage consumption patterns.
Key Features:
- Reports user and group quota usage
- Displays soft and hard limits
- Shows grace periods for exceeded quotas
- Supports multiple filesystem types
- Provides detailed usage statistics
Basic Syntax
repquota [options] filesystemThe basic syntax requires specifying the filesystem path where quota reporting is needed.
Common Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-a |
Report on all filesystems with quotas |
-u |
Report user quotas (default) |
-g |
Report group quotas |
-v |
Verbose output with additional details |
-n |
Skip username/groupname resolution |
-t |
Truncate usernames to fit column width |
-s |
Use human-readable format (KB, MB, GB) |
Prerequisites
Before using repquota, ensure:
- Quotas are enabled on the filesystem
- You have root privileges or appropriate permissions
- The filesystem supports quota functionality
- Quota database files exist and are accessible
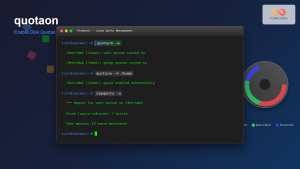
Enabling Quotas (Quick Setup)
# Edit /etc/fstab to add quota options
/dev/sda1 /home ext4 defaults,usrquota,grpquota 0 2
# Remount filesystem
mount -o remount /home
# Initialize quota database
quotacheck -cug /home
quotaon /homeBasic Examples
1. Report Quotas on Specific Filesystem
sudo repquota /homeSample Output:
*** Report for user quotas on device /dev/sda1
Block grace time: 7days; Inode grace time: 7days
Block limits File limits
User used soft hard grace used soft hard grace
----------------------------------------------------------------------
root -- 0 0 0 2 0 0
john -- 51200 102400 153600 1024 2000 3000
alice +- 204800 102400 153600 6days 1500 2000 3000
bob -- 76800 102400 153600 800 2000 3000 2. Report All Filesystems with Quotas
sudo repquota -aThis command reports quota usage across all mounted filesystems that have quotas enabled.
3. Report Group Quotas
sudo repquota -g /homeSample Output:
*** Report for group quotas on device /dev/sda1
Block grace time: 7days; Inode grace time: 7days
Block limits File limits
Group used soft hard grace used soft hard grace
----------------------------------------------------------------------
root -- 0 0 0 2 0 0
users -- 256000 512000 768000 3200 5000 7500
developers+- 409600 512000 768000 5days 4800 5000 7500 Advanced Usage Examples
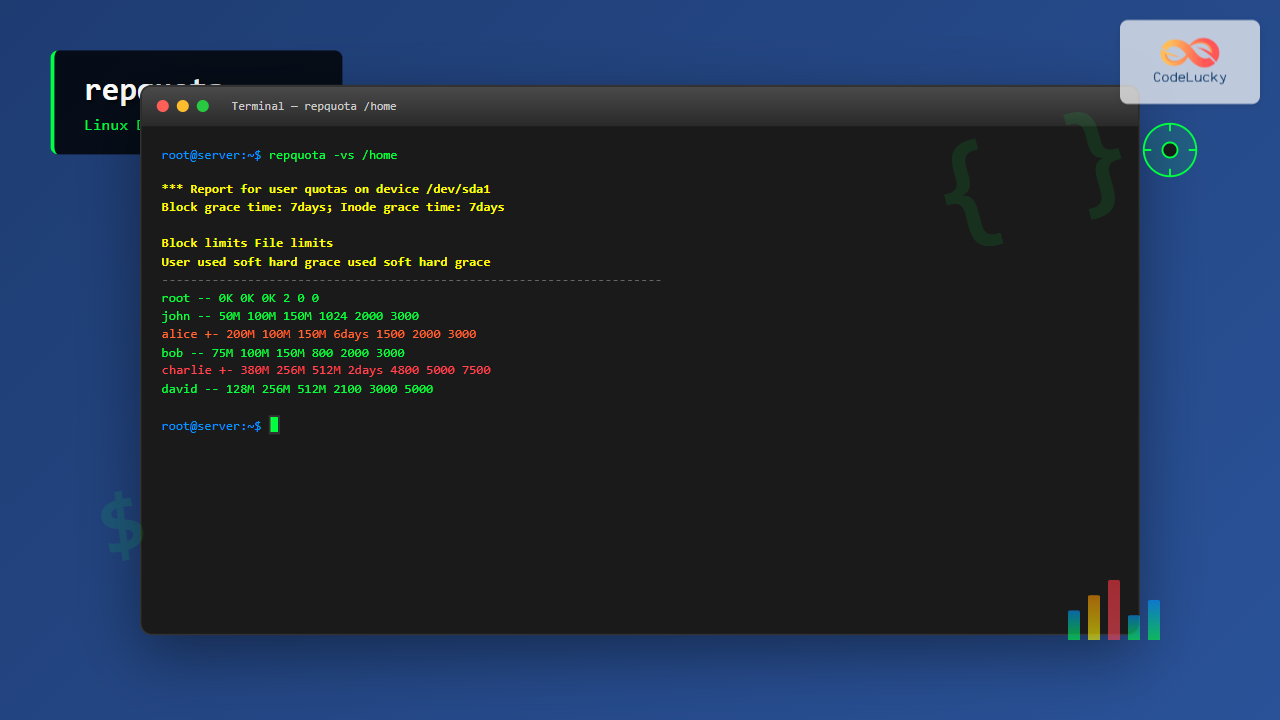
4. Verbose Output with Human-Readable Format
sudo repquota -vs /homeSample Output:
*** Report for user quotas on device /dev/sda1
Block grace time: 7days; Inode grace time: 7days
Block limits File limits
User used soft hard grace used soft hard grace
----------------------------------------------------------------------
root -- 0K 0K 0K 2 0 0
john -- 50M 100M 150M 1024 2000 3000
alice +- 200M 100M 150M 6days 1500 2000 3000
bob -- 75M 100M 150M 800 2000 3000 5. Skip Name Resolution for Performance
sudo repquota -n /homeThis option displays user/group IDs instead of names, improving performance on systems with many users.
6. Combined User and Group Report
sudo repquota -ug /homeReports both user and group quotas simultaneously.
Understanding Output Format
Column Explanations:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| User/Group | Username or group name |
| used (blocks) | Current disk space usage in KB |
| soft (blocks) | Soft limit for disk space |
| hard (blocks) | Hard limit for disk space |
| grace | Grace period remaining for soft limit |
| used (files) | Number of files/inodes used |
| soft (files) | Soft limit for file count |
| hard (files) | Hard limit for file count |
Status Indicators:
--: Within all limits+-: Soft limit exceeded, within grace period-+: Hard limit exceeded (rare, usually prevents further writes)++: Both soft and hard limits exceeded
Practical Use Cases
1. System Monitoring Script
#!/bin/bash
# Check quota usage and alert on high usage
THRESHOLD=80
repquota -a | awk '
/^[^-#*]/ {
if ($3 > 0 && $4 > 0) {
usage = ($3 / $4) * 100
if (usage > '$THRESHOLD') {
print "Warning: User " $1 " at " usage "% usage"
}
}
}'2. Generate Quota Report for Management
#!/bin/bash
# Generate formatted quota report
echo "Disk Quota Report - $(date)"
echo "=================================="
repquota -vs /home | awk '
BEGIN {
printf "%-15s %10s %10s %10s %8s\n", "User", "Used", "Soft", "Hard", "Usage%"
printf "%-15s %10s %10s %10s %8s\n", "----", "----", "----", "----", "------"
}
/^[^-#*]/ && $3 > 0 {
if ($4 > 0) {
usage = ($3 / $4) * 100
printf "%-15s %10s %10s %10s %7.1f%%\n", $1, $3, $4, $5, usage
}
}'3. Find Users Exceeding Quotas
sudo repquota /home | grep '+' | awk '{
print "User: " $1 " - Usage: " $3 "KB, Limit: " $4 "KB, Grace: " $6
}'Troubleshooting Common Issues
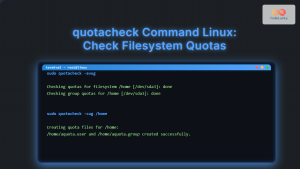
1. “repquota: Cannot open quotas on device”
Solution:
- Verify quotas are enabled on the filesystem
- Check if quota database files exist
- Run
quotacheckto rebuild quota database
sudo quotacheck -cug /home
sudo quotaon /home2. “Permission denied” Error
Solution:
- Run command with sudo privileges
- Verify user has quota administration permissions
- Check file permissions on quota database files
3. Inconsistent Quota Information
Solution:
# Turn off quotas
sudo quotaoff /home
# Rebuild quota database
sudo quotacheck -cug /home
# Turn quotas back on
sudo quotaon /homeBest Practices
- Regular Monitoring: Schedule periodic quota reports to prevent storage issues
- Automated Alerts: Set up scripts to notify administrators when quotas approach limits
- Grace Period Management: Monitor grace periods and take action before they expire
- Documentation: Keep records of quota policies and user allocations
- Performance: Use
-noption for large user bases to improve performance
Integration with Other Commands
Combining with Other Quota Tools:
# Check specific user quota
quota -u john
# Set user quota
edquota -u alice
# View quota report and set new limits
repquota /home
edquota -u bobUsing with System Monitoring:
# Create daily quota report
repquota -vs /home > /var/log/daily-quota-$(date +%Y%m%d).log
# Email quota violations
repquota /home | grep '+' | mail -s "Quota Violations" [email protected]Security Considerations
- Access Control: Restrict repquota access to authorized administrators only
- Log Monitoring: Monitor quota command usage in system logs
- Data Protection: Protect quota database files from unauthorized modification
- Regular Audits: Periodically review quota configurations and usage patterns
Conclusion
The repquota command is an indispensable tool for Linux system administrators managing disk quotas. By understanding its various options and output format, you can effectively monitor storage usage, identify potential issues, and maintain optimal system performance. Regular quota reporting helps prevent storage-related problems and ensures fair resource allocation across users and groups.
Whether you’re managing a small server or large enterprise environment, mastering repquota will significantly improve your storage management capabilities and help maintain system stability.