The rdesktop command is a powerful Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) client for Linux systems that enables seamless connections to Windows machines and other RDP-enabled servers. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about using rdesktop effectively in your Linux environment.
What is rdesktop?
rdesktop is an open-source RDP client that allows Linux users to connect to Windows Terminal Services, Windows desktops, and other RDP-compatible servers. It provides a native way to access remote Windows systems without requiring additional virtualization software or complex configurations.
Key Features of rdesktop
- Full RDP protocol support (versions 4 and 5)
- Audio redirection capabilities
- File system sharing
- Clipboard synchronization
- Multiple display resolution options
- Encryption support
- Keyboard layout mapping
Installing rdesktop
Before using rdesktop, you need to install it on your Linux system. The installation process varies depending on your distribution:
Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt update
sudo apt install rdesktopCentOS/RHEL/Fedora
# For CentOS/RHEL
sudo yum install rdesktop
# For Fedora
sudo dnf install rdesktopArch Linux
sudo pacman -S rdesktopBasic rdesktop Syntax
The basic syntax for rdesktop follows this pattern:
rdesktop [options] server[:port]Where:
serveris the IP address or hostname of the target machineportis optional (default is 3389)optionsare various flags to customize the connection
Essential rdesktop Options
User Authentication Options
| Option | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
-u username |
Specify username | -u john |
-p password |
Specify password (not recommended) | -p mypass |
-d domain |
Specify domain | -d COMPANY |
Display and Resolution Options
| Option | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
-g geometry |
Set screen resolution | -g 1024x768 |
-f |
Full screen mode | -f |
-D |
Hide window decorations | -D |
-T title |
Set window title | -T "Remote Server" |
Basic Connection Examples
Simple Connection
Connect to a Windows machine with basic credentials:
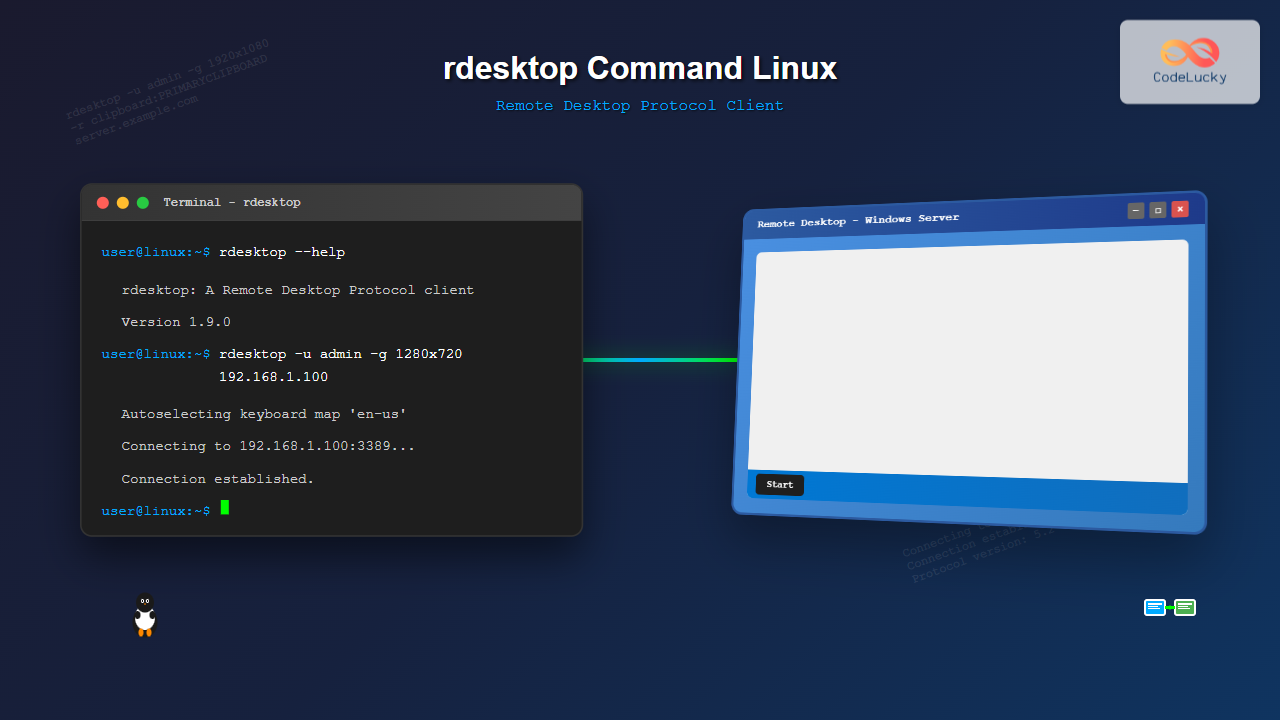
rdesktop -u administrator 192.168.1.100Expected Output:
Autoselecting keyboard map 'en-us' from locale
Connecting to 192.168.1.100:3389...
Connection established.
Protocol version negotiated: 5.2
Connection with Custom Resolution
Connect with a specific screen resolution:
rdesktop -u john -g 1280x1024 -T "Development Server" 10.0.0.50Full Screen Connection
Launch rdesktop in full screen mode:
rdesktop -u admin -f -D server.example.comAdvanced Configuration Options
Audio Redirection
Enable audio redirection to hear sounds from the remote desktop:
rdesktop -u user -r sound:local 192.168.1.50Clipboard Sharing
Enable clipboard synchronization between local and remote systems:
rdesktop -u user -r clipboard:PRIMARYCLIPBOARD 192.168.1.50Drive Mapping
Share local directories with the remote desktop:
rdesktop -u user -r disk:share=/home/user/shared 192.168.1.50Serial Port Redirection
Redirect serial ports for device communication:
rdesktop -u user -r comport:COM1=/dev/ttyS0 192.168.1.50Security and Encryption
Enabling Encryption
Use RDP encryption for secure connections:
rdesktop -u user -E -K 192.168.1.50Where:
-Eenables encryption-Kkeeps the window manager key bindings
Network Level Authentication
For Windows Vista and later with NLA enabled:
rdesktop -u user -N 192.168.1.50Practical Usage Scenarios
Connecting to Windows Server
Complete example for connecting to a Windows Server with domain authentication:
rdesktop -u administrator -d COMPANY -g 1440x900 -r clipboard:PRIMARYCLIPBOARD -r sound:local -T "Windows Server 2019" server.company.comDevelopment Environment Setup
Connect to a development server with shared folders:
rdesktop -u developer -g 1920x1080 -r disk:projects=/home/user/projects -r disk:tools=/opt/devtools dev-server.localKeyboard Layout Configuration
Setting Keyboard Layout
Specify a specific keyboard layout:
rdesktop -u user -k de 192.168.1.50Available Keyboard Layouts
Check available keyboard layouts:
ls /usr/share/rdesktop/keymaps/Common layouts include:
en-us– US Englishen-gb– UK Englishde– Germanfr– Frenches– Spanish
Connection Management
Saving Connection Settings
Create a shell script for frequently used connections:
#!/bin/bash
# save as connect-server.sh
rdesktop -u administrator \
-d COMPANY \
-g 1600x1200 \
-r clipboard:PRIMARYCLIPBOARD \
-r sound:local \
-T "Production Server" \
prod-server.company.comUsing Configuration Files
Create a configuration file approach:
# Create ~/.rdesktop/default.conf
username=john
domain=COMPANY
geometry=1920x1080
fullscreen=false
sound=localTroubleshooting Common Issues
Connection Refused
If you encounter connection refused errors:
- Verify the target server has RDP enabled
- Check Windows Firewall settings
- Ensure the correct port (default 3389) is open
- Test connectivity with
telnet server 3389
Authentication Failures
For authentication issues:
# Test with explicit domain specification
rdesktop -u username -d . 192.168.1.50 # Local account
# For domain accounts
rdesktop -u username -d DOMAIN 192.168.1.50Display Issues
If experiencing display problems:
- Try different color depths:
-a 16or-a 24 - Adjust resolution:
-g 1024x768 - Use windowed mode instead of fullscreen
Performance Optimization
Bandwidth Optimization
For slow connections, optimize bandwidth usage:
rdesktop -u user -x l -a 16 -z 192.168.1.50Where:
-x lsets LAN connection speed-a 16uses 16-bit color depth-zenables RDP compression
Connection Speed Settings
| Option | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
-x m |
Modem (56K) | Very slow connections |
-x b |
Broadband | DSL/Cable connections |
-x l |
LAN | Local network connections |
Security Best Practices
Secure Connection Guidelines
- Avoid password on command line:
# Instead of: rdesktop -u user -p password server # Use: rdesktop -u user server # Will prompt for password - Use VPN for remote connections:
# Connect through VPN first, then use rdesktop - Enable encryption:
rdesktop -u user -E -K server - Limit connection duration:
# Set session timeout in RDP server settings
Alternative RDP Clients
While rdesktop is powerful, consider these alternatives:
FreeRDP (xfreerdp)
# More modern RDP client
xfreerdp /u:username /v:server /size:1920x1080Remmina (GUI)
Remmina provides a graphical interface for RDP connections with easy profile management.
Scripting and Automation
Automated Connection Script
Create an interactive connection script:
#!/bin/bash
echo "RDP Connection Manager"
echo "1. Production Server"
echo "2. Development Server"
echo "3. Test Environment"
read -p "Select option: " choice
case $choice in
1)
rdesktop -u admin -g 1920x1080 prod-server.com
;;
2)
rdesktop -u developer -g 1600x1200 dev-server.local
;;
3)
rdesktop -u testuser -g 1280x1024 test.internal
;;
*)
echo "Invalid option"
;;
esacMonitoring and Logging
Enable Verbose Logging
For troubleshooting, enable detailed logging:
rdesktop -u user -v 192.168.1.50 2>&1 | tee rdesktop.logConnection Statistics
Monitor connection performance:
# Use system tools to monitor network usage
iftop -i eth0
netstat -iConclusion
The rdesktop command is an essential tool for Linux administrators and users who need reliable access to Windows systems. By mastering its various options and configurations, you can create efficient, secure, and optimized remote desktop connections tailored to your specific needs.
Whether you’re managing servers, accessing development environments, or providing remote support, rdesktop provides the flexibility and control necessary for professional RDP connectivity from Linux systems. Remember to always prioritize security by using encryption, avoiding command-line passwords, and implementing proper network security measures.
Practice with different options and configurations to find the setup that works best for your environment, and consider creating scripted solutions for frequently used connections to streamline your workflow.