The quotaon command is a powerful Linux utility that enables disk quota enforcement on file systems. It allows system administrators to control and monitor disk space usage by users and groups, preventing any single user from consuming excessive storage resources that could impact system performance or availability.
What is the quotaon Command?
The quotaon command activates disk quota checking and enforcement on specified file systems. When quotas are enabled, the kernel tracks disk usage for each user and group, enforcing the limits defined in quota files. This is essential for multi-user environments where resource management is critical.
Basic Syntax and Options
The basic syntax of the quotaon command is:
quotaon [options] filesystem
quotaon [options] -aCommon Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-a |
Turn on quotas for all file systems in /etc/fstab |
-u |
Turn on user quotas (default) |
-g |
Turn on group quotas |
-p |
Print state of quotas |
-f |
Force quota enabling |
-v |
Verbose output |
Prerequisites for Using quotaon
Before using the quotaon command, several prerequisites must be met:
1. Quota Support in Kernel
Verify quota support is compiled into your kernel:
cat /proc/filesystems | grep quota2. Quota Tools Installation
Install quota tools on your system:
# Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt-get install quota
# CentOS/RHEL/Fedora
sudo yum install quota
# or for newer versions
sudo dnf install quota3. File System Configuration
The file system must be mounted with quota options. Edit /etc/fstab:
# Example fstab entry
/dev/sda2 /home ext4 defaults,usrquota,grpquota 0 2Setting Up Disk Quotas
Step 1: Remount File System
After modifying fstab, remount the file system:
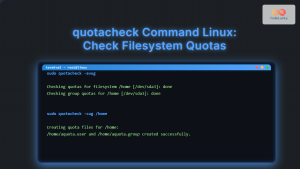
sudo mount -o remount /homeStep 2: Create Quota Files
Generate quota files for the file system:
sudo quotacheck -cum /homeThis creates:
aquota.user– User quota fileaquota.group– Group quota file
Step 3: Enable Quotas
Now activate quotas using quotaon:
sudo quotaon /homePractical Examples
Example 1: Enable User Quotas on Specific File System
sudo quotaon -u /homeOutput:
quotaon: /home: quotas turned onExample 2: Enable Group Quotas
sudo quotaon -g /homeOutput:
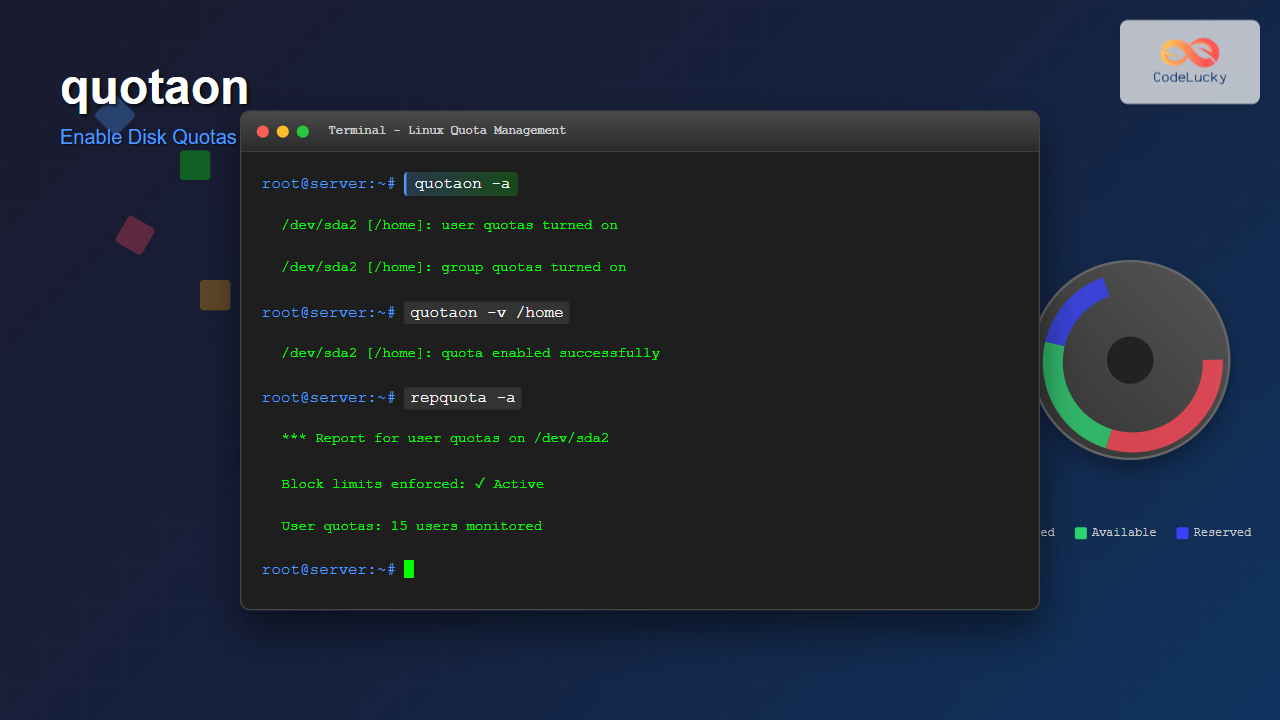
quotaon: /home: group quotas turned onExample 3: Enable All Quotas System-wide
sudo quotaon -aOutput:
/dev/sda2 [/home]: group quotas turned on
/dev/sda2 [/home]: user quotas turned onExample 4: Verbose Output
sudo quotaon -v /homeOutput:
/dev/sda2 [/home]: user quotas turned on
/dev/sda2 [/home]: group quotas turned onExample 5: Check Quota Status
sudo quotaon -p /homeOutput:
user quota on /home (/dev/sda2) is on
group quota on /home (/dev/sda2) is onSetting User and Group Limits
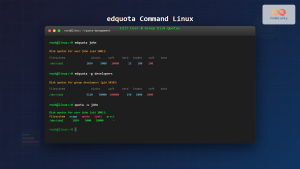
After enabling quotas, set limits using the edquota command:
Setting User Limits
sudo edquota -u usernameThis opens an editor where you can set:
- Soft limit – Warning threshold
- Hard limit – Maximum allowed usage
- Grace period – Time before soft limit becomes hard limit
Setting Group Limits
sudo edquota -g groupnameMonitoring Quota Usage
Check User Quota Usage
quota -u usernameSample Output:
Disk quotas for user john (uid 1001):
Filesystem blocks quota limit grace files quota limit grace
/dev/sda2 156 5000 10000 28 100 200System-wide Quota Report
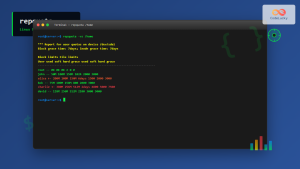
sudo repquota /homeSample Output:
*** Report for user quotas on device /dev/sda2
Block grace time: 7days; Inode grace time: 7days
Block limits File limits
User used soft hard grace used soft hard grace
----------------------------------------------------------------------
root -- 0 0 0 3 0 0
john -- 156 5000 10000 28 100 200
mary -- 892 3000 5000 45 80 120Advanced quotaon Usage
Force Enable Quotas
Sometimes you may need to force quota enabling:
sudo quotaon -f /homeEnable Quotas for Multiple File Systems
sudo quotaon /home /var /tmpTroubleshooting Common Issues
Issue 1: “quotaon: cannot find //aquota.user”
Solution: Run quotacheck to create quota files:
sudo quotacheck -cug /homeIssue 2: “quotaon: using //quota.user on //dev/sda2: No such file or directory”
Solution: Ensure the file system is mounted with quota options and quota files exist.
Issue 3: Permission Denied
Solution: Ensure you have root privileges:
sudo quotaon /homeBest Practices
1. Regular Monitoring
Set up automated scripts to monitor quota usage:
#!/bin/bash
# Check quota usage daily
repquota -a | mail -s "Daily Quota Report" [email protected]2. Grace Period Configuration
Set appropriate grace periods:
sudo edquota -t3. Backup Quota Files
Regularly backup quota databases:
sudo cp /home/aquota.user /backup/Integration with System Services
Automatic Quota Enabling at Boot
Create a systemd service to enable quotas at startup:
# /etc/systemd/system/quota.service
[Unit]
Description=Enable disk quotas
After=local-fs.target
[Service]
Type=oneshot
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/quotaon -a
RemainAfterExit=yes
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetEnable the service:
sudo systemctl enable quota.serviceSecurity Considerations
- File Permissions: Quota files should be readable only by root
- Regular Audits: Monitor quota violations and adjust limits accordingly
- Backup Strategy: Include quota files in system backups
Related Commands
quotaoff– Disable disk quotasquotacheck– Check and repair quota filesedquota– Edit user/group quotasrepquota– Display quota usage reportquota– Display user quota information
Conclusion
The quotaon command is an essential tool for Linux system administrators managing multi-user environments. By properly implementing disk quotas, you can prevent resource abuse, ensure fair usage, and maintain system stability. Regular monitoring and appropriate limit setting are key to effective quota management.
Remember to always test quota implementations in a non-production environment first, and maintain regular backups of your quota configuration files. With proper setup and monitoring, disk quotas become a powerful tool for system resource management.
- What is the quotaon Command?
- Basic Syntax and Options
- Prerequisites for Using quotaon
- Setting Up Disk Quotas
- Practical Examples
- Setting User and Group Limits
- Monitoring Quota Usage
- Advanced quotaon Usage
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Best Practices
- Integration with System Services
- Security Considerations
- Related Commands
- Conclusion