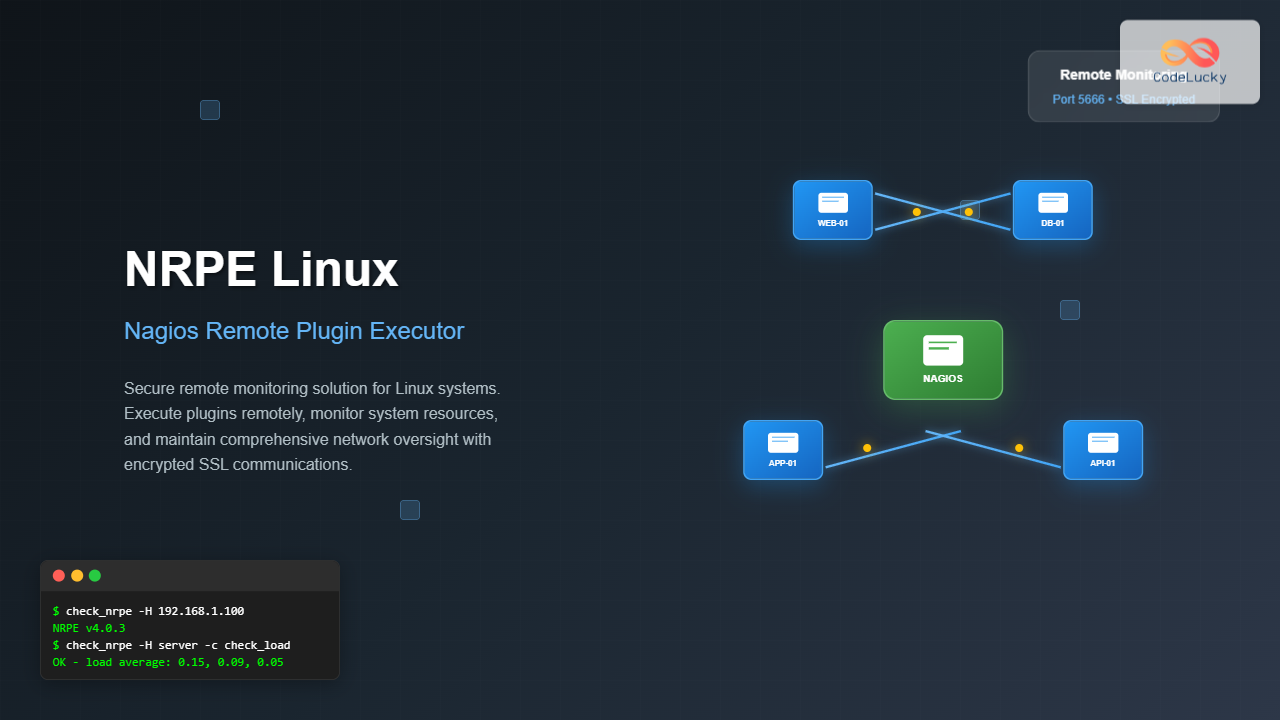
NRPE (Nagios Remote Plugin Executor) is a crucial component in the Nagios monitoring ecosystem that enables remote execution of monitoring plugins on Linux and Unix systems. This powerful tool allows system administrators to monitor remote hosts without requiring SNMP or other protocols, providing direct access to system resources and custom checks.
What is NRPE?
NRPE consists of two main components: the NRPE daemon that runs on remote hosts and the check_nrpe plugin that executes on the Nagios monitoring server. The daemon listens for requests from authorized monitoring servers, executes the requested plugins locally, and returns the results.
- Direct system monitoring without SNMP overhead
- Custom plugin execution capabilities
- Secure SSL-encrypted communications
- Flexible configuration options
Installing NRPE on Linux
Ubuntu/Debian Installation
# Update package repository
sudo apt update
# Install NRPE daemon and plugins
sudo apt install nagios-nrpe-server nagios-plugins-basic nagios-plugins-standard
# Start and enable NRPE service
sudo systemctl start nagios-nrpe-server
sudo systemctl enable nagios-nrpe-serverCentOS/RHEL Installation
# Install EPEL repository
sudo yum install epel-release
# Install NRPE and plugins
sudo yum install nrpe nagios-plugins-all
# Start and enable NRPE service
sudo systemctl start nrpe
sudo systemctl enable nrpeSource Installation
For custom installations or latest versions:
# Create nagios user
sudo useradd nagios
# Download and compile NRPE
wget https://github.com/NagiosEnterprises/nrpe/archive/nrpe-4.0.3.tar.gz
tar -xzf nrpe-4.0.3.tar.gz
cd nrpe-nrpe-4.0.3/
# Configure and compile
./configure --enable-command-args --enable-ssl
make all
sudo make install-all
# Install systemd service
sudo make install-daemon-configNRPE Configuration
Main Configuration File
The primary configuration file is located at /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg:
# NRPE Configuration File
# Main server configuration
# Process ID file
pid_file=/var/run/nrpe/nrpe.pid
# Port number (default is 5666)
server_port=5666
# Address to bind to (0.0.0.0 for all interfaces)
server_address=0.0.0.0
# Allowed hosts (comma-separated list)
allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1,::1,10.0.1.100,192.168.1.50
# Don't blame NRPE for being insecure
dont_blame_nrpe=0
# Allow bash command substitution
allow_bash_command_substitution=0
# Command timeout
command_timeout=60
# Connection timeout
connection_timeout=300Command Definitions
Define custom commands in the configuration file:
# System load check
command[check_load]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_load -w 15,10,5 -c 30,25,20
# Disk usage check
command[check_disk]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_disk -w 20% -c 10% -p /
# Memory usage check
command[check_memory]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_mem.pl -f -w 80 -c 90
# Process count check
command[check_procs]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -w 250 -c 400 -s RSZDT
# Custom service check
command[check_apache]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -c 1:4 -C apache2
# Check specific log file
command[check_log]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_log -F /var/log/messages -O /tmp/messages.old -q "ERROR"SSL Configuration
Enable SSL encryption for secure communications:
# SSL configuration in nrpe.cfg
ssl_version=TLSv1.2+
ssl_use_adh=0
ssl_cert_file=/etc/ssl/certs/nrpe-cert.pem
ssl_privatekey_file=/etc/ssl/private/nrpe-key.pem
ssl_cacert_file=/etc/ssl/certs/ca-cert.pem
ssl_ciphers=ALL:!MD5:@STRENGTHGenerate SSL certificates:
# Generate private key and certificate
sudo openssl req -new -x509 -days 365 -nodes \
-out /etc/ssl/certs/nrpe-cert.pem \
-keyout /etc/ssl/private/nrpe-key.pem
# Set proper permissions
sudo chmod 600 /etc/ssl/private/nrpe-key.pem
sudo chown nagios:nagios /etc/ssl/private/nrpe-key.pemTesting NRPE Configuration
Local Testing
# Test NRPE daemon locally
/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_nrpe -H localhost
# Expected output:
NRPE v4.0.3# Test specific command
/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_nrpe -H localhost -c check_load
# Expected output:
OK - load average: 0.15, 0.09, 0.05|load1=0.150;15.000;30.000;0; load5=0.090;10.000;25.000;0; load15=0.050;5.000;20.000;0;Remote Testing
From the Nagios monitoring server:
# Test remote NRPE connection
/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_nrpe -H 192.168.1.100
# Test with specific command
/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_nrpe -H 192.168.1.100 -c check_diskAdvanced NRPE Usage
Command Arguments
Enable command arguments by setting dont_blame_nrpe=1:
# Configuration allowing arguments
command[check_disk_arg]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_disk -w $ARG1$ -c $ARG2$ -p $ARG3$
# Usage from monitoring server
check_nrpe -H remote_host -c check_disk_arg -a 20% 10% /homeCustom Plugin Scripts
Create custom monitoring scripts:
#!/bin/bash
# /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_custom_service.sh
SERVICE_NAME="$1"
PROCESS_COUNT=$(ps aux | grep "$SERVICE_NAME" | grep -v grep | wc -l)
if [ $PROCESS_COUNT -gt 0 ]; then
echo "OK - $SERVICE_NAME is running ($PROCESS_COUNT processes)"
exit 0
else
echo "CRITICAL - $SERVICE_NAME is not running"
exit 2
fi# Make script executable
sudo chmod +x /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_custom_service.sh
# Add to NRPE configuration
command[check_custom]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_custom_service.sh $ARG1$NRPE Security Configuration
Firewall Configuration
# UFW (Ubuntu/Debian)
sudo ufw allow 5666/tcp
sudo ufw reload
# Firewalld (CentOS/RHEL)
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=5666/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
# iptables
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 5666 -s MONITORING_SERVER_IP -j ACCEPTSELinux Configuration (RHEL/CentOS)
# Allow NRPE network connections
sudo setsebool -P nagios_run_sudo 1
# Custom SELinux policy if needed
sudo semanage port -a -t nagios_port_t -p tcp 5666Troubleshooting NRPE
Common Issues and Solutions
# Check if NRPE is running
sudo systemctl status nrpe
# Verify port is listening
sudo netstat -tlnp | grep 5666
# Check firewall rules
sudo iptables -L | grep 5666# Increase timeout in nrpe.cfg
connection_timeout=300
# Check network connectivity
telnet remote_host 5666
# Verify allowed_hosts configuration
grep allowed_hosts /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfgDebug Mode
Run NRPE in debug mode for troubleshooting:
# Stop the service
sudo systemctl stop nrpe
# Run in debug mode
sudo /usr/bin/nrpe -c /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg -d
# Check log files
sudo tail -f /var/log/messages | grep nrpePerformance Optimization
Configuration Tuning
# Optimize for high-load environments
server_address=192.168.1.100 # Bind to specific interface
max_packet_age=30 # Packet age threshold
command_timeout=30 # Reduce command timeout
connection_timeout=60 # Reduce connection timeout
# Enable keep-alive
tcp_keepalive=1Resource Monitoring
# Monitor NRPE performance
command[check_nrpe_procs]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -C nrpe -c 1:5
# Monitor memory usage
command[check_nrpe_mem]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_proc_mem.sh nrpe 100 200Integration with Nagios Core
Host Configuration
Configure remote hosts in Nagios:
# /etc/nagios/conf.d/remote-host.cfg
define host {
use linux-server
host_name webserver-01
alias Web Server 01
address 192.168.1.100
check_command check-host-alive
max_check_attempts 5
notification_interval 30
notification_period 24x7
}Service Definitions
# Service checks using NRPE
define service {
use generic-service
host_name webserver-01
service_description Load Average
check_command check_nrpe!check_load
}
define service {
use generic-service
host_name webserver-01
service_description Disk Usage
check_command check_nrpe!check_disk
}Best Practices
- Use SSL encryption for all communications
- Restrict
allowed_hoststo specific monitoring servers - Disable command arguments unless absolutely necessary
- Regularly update NRPE and plugins
- Use strong SSL ciphers and disable weak protocols
- Set appropriate timeout values
- Use efficient plugin scripts
- Monitor NRPE daemon resource usage
- Implement proper logging and rotation
- Regular maintenance and cleanup
Conclusion
NRPE is an essential tool for comprehensive Linux system monitoring, providing secure and efficient remote plugin execution capabilities. By following the configuration guidelines and best practices outlined in this guide, you can implement a robust monitoring infrastructure that scales with your environment’s needs.
Remember to regularly update your NRPE installation, monitor its performance, and review your security configurations to maintain optimal monitoring capabilities across your Linux infrastructure.