NetworkManager is a powerful network management service that provides automatic network detection and configuration for Linux systems. It simplifies network administration by handling complex networking tasks behind the scenes while offering both graphical and command-line interfaces for manual configuration.
What is NetworkManager?
NetworkManager is a daemon that manages network interfaces and connections on Linux systems. It automatically detects available networks, manages connection profiles, and handles network switching seamlessly. Unlike traditional network configuration methods that require manual editing of configuration files, NetworkManager provides dynamic network management with support for various connection types including Ethernet, Wi-Fi, mobile broadband, and VPN.
Key Features of NetworkManager
- Automatic Network Detection: Automatically discovers and connects to available networks
- Connection Profiles: Stores network configurations for easy switching
- Multiple Interface Support: Manages various connection types simultaneously
- Policy-based Routing: Intelligent routing decisions based on network policies
- VPN Integration: Built-in support for various VPN protocols
- Power Management: Optimizes network usage for battery-powered devices
Installing NetworkManager
Most modern Linux distributions come with NetworkManager pre-installed. However, if you need to install it manually, here are the commands for different distributions:
Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt update
sudo apt install network-manager network-manager-gnomeRed Hat/CentOS/Fedora
sudo dnf install NetworkManager NetworkManager-wifi
# For older versions using yum:
sudo yum install NetworkManager NetworkManager-wifiArch Linux
sudo pacman -S networkmanager networkmanager-openvpnNetworkManager Service Management
NetworkManager runs as a systemd service. Here are the essential service management commands:
Starting and Enabling NetworkManager
sudo systemctl start NetworkManager
sudo systemctl enable NetworkManagerChecking Service Status
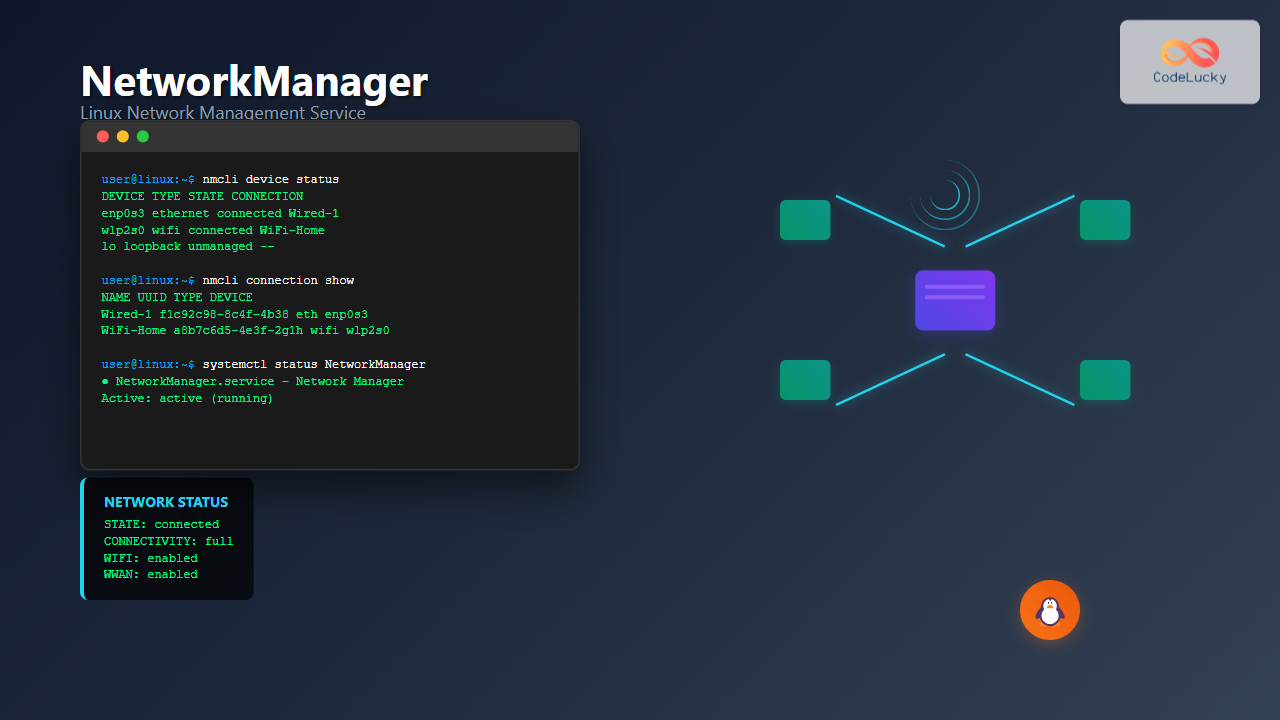
sudo systemctl status NetworkManagerExpected Output:
● NetworkManager.service - Network Manager
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/NetworkManager.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2025-08-26 02:08:15 IST; 2h 15min ago
Docs: man:NetworkManager(8)
Main PID: 1234 (NetworkManager)
Tasks: 3 (limit: 4915)
Memory: 15.2M
CPU: 2.345sRestarting NetworkManager
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManagerCommand Line Interface: nmcli
The nmcli (NetworkManager Command Line Interface) is the primary tool for managing NetworkManager from the terminal. It provides comprehensive control over network connections and settings.
Basic nmcli Syntax
nmcli [OPTIONS] OBJECT { COMMAND | help }Common nmcli Objects
general– NetworkManager general status and operationsnetworking– Overall networking controlradio– NetworkManager radio switchesconnection– NetworkManager connectionsdevice– Devices managed by NetworkManager
Managing Network Connections
Viewing Available Connections
nmcli connection showSample Output:
NAME UUID TYPE DEVICE
Wired connection 1 f1c92c98-8c4f-4b38-9a5e-7f2d6c8b9e3a ethernet enp0s3
MyWiFi a8b7c6d5-4e3f-2g1h-9i8j-7k6l5m4n3o2p wifi wlp2s0
VPN Connection b9a8c7d6-5e4f-3g2h-1i9j-8k7l6m5n4o3p vpn --Viewing Connection Details
nmcli connection show "MyWiFi"Creating a New Ethernet Connection
nmcli connection add type ethernet con-name "Office-LAN" ifname enp0s3 \
ip4 192.168.1.100/24 gw4 192.168.1.1Creating a Wi-Fi Connection
nmcli connection add type wifi con-name "Home-WiFi" ifname wlp2s0 \
ssid "MyHomeNetwork" wifi-sec.key-mgmt wpa-psk wifi-sec.psk "mypassword"Device Management
Listing Network Devices
nmcli device statusExpected Output:
DEVICE TYPE STATE CONNECTION
enp0s3 ethernet connected Wired connection 1
wlp2s0 wifi connected MyWiFi
lo loopback unmanaged --Viewing Device Details
nmcli device show enp0s3Connecting and Disconnecting Devices
# Connect to a specific network
nmcli device connect wlp2s0
# Disconnect a device
nmcli device disconnect wlp2s0Wi-Fi Management
Scanning for Wi-Fi Networks
nmcli device wifi listSample Output:
BSSID SSID MODE CHAN RATE SIGNAL BARS SECURITY
aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff MyHomeNetwork Infra 6 130 Mbit/s 85 ▂▄▆█ WPA2
11:22:33:44:55:66 OfficeWiFi Infra 11 54 Mbit/s 65 ▂▄▆_ WPA2 WPS
77:88:99:aa:bb:cc PublicHotspot Infra 1 54 Mbit/s 45 ▂▄__ --Connecting to Wi-Fi Networks
# Connect to an open network
nmcli device wifi connect "PublicHotspot"
# Connect to a secured network
nmcli device wifi connect "MyHomeNetwork" password "mypassword"Connecting to Hidden Wi-Fi Networks
nmcli connection add type wifi con-name "HiddenNetwork" \
wifi.ssid "HiddenSSID" wifi-sec.key-mgmt wpa-psk \
wifi-sec.psk "password" wifi.hidden yesStatic IP Configuration
Configuring Static IP for Ethernet
nmcli connection modify "Wired connection 1" \
ipv4.addresses 192.168.1.100/24 \
ipv4.gateway 192.168.1.1 \
ipv4.dns 8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4 \
ipv4.method manualApplying Configuration Changes
nmcli connection up "Wired connection 1"Reverting to DHCP
nmcli connection modify "Wired connection 1" ipv4.method auto
nmcli connection up "Wired connection 1"VPN Configuration
Creating an OpenVPN Connection
nmcli connection add type vpn con-name "MyVPN" \
vpn-type openvpn \
vpn.data "remote=vpn.example.com,connection-type=tls,cert=/path/to/cert.pem,key=/path/to/key.pem,ca=/path/to/ca.pem"Connecting to VPN
nmcli connection up "MyVPN"Viewing VPN Status
nmcli connection show --activeNetwork Troubleshooting
Checking NetworkManager Status
nmcli general statusOutput Example:
STATE CONNECTIVITY WIFI-HW WIFI WWAN-HW WWAN
connected full enabled enabled enabled enabledMonitoring Network Activity
nmcli monitorReloading Network Configuration
sudo nmcli general reloadChecking DNS Configuration
nmcli device show | grep DNSConfiguration Files and Locations
Main Configuration File
NetworkManager’s main configuration is stored in:
/etc/NetworkManager/NetworkManager.confConnection Profiles
Individual connection profiles are stored in:
/etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/Sample Configuration File Structure
[main]
plugins=keyfile,ifupdown
[ifupdown]
managed=false
[device]
wifi.scan-rand-mac-address=noGUI Management Tools
GNOME Network Settings
For GNOME desktop environments, access network settings through:
gnome-control-center networkNetworkManager Applet
The system tray applet provides quick access to network connections:
nm-appletAdvanced NetworkManager Features
Connection Priorities
# Set connection priority (higher numbers = higher priority)
nmcli connection modify "MyWiFi" connection.autoconnect-priority 10MAC Address Randomization
nmcli connection modify "MyWiFi" wifi.cloned-mac-address randomConnection Zones (Firewalld Integration)
nmcli connection modify "Office-LAN" connection.zone workPerformance Optimization
Disabling Unused Interfaces
# Disable Wi-Fi if not needed
nmcli radio wifi off
# Disable WWAN
nmcli radio wwan offConnection Timeout Settings
nmcli connection modify "MyConnection" \
ipv4.dhcp-timeout 30 \
connection.autoconnect-retries 3Security Best Practices
Setting Connection Permissions
# Restrict connection to specific users
nmcli connection modify "SecureWiFi" \
connection.permissions user:admin:usernameCertificate-based Authentication
nmcli connection add type wifi con-name "Enterprise-WiFi" \
wifi.ssid "CorpNetwork" \
wifi-sec.key-mgmt wpa-eap \
802-1x.eap tls \
802-1x.identity "username" \
802-1x.client-cert "/path/to/client.crt" \
802-1x.private-key "/path/to/private.key"Common Issues and Solutions
NetworkManager Not Starting
# Check for conflicting services
sudo systemctl disable networking
sudo systemctl stop networking
sudo systemctl start NetworkManagerDNS Resolution Problems
# Reset DNS configuration
sudo systemctl restart systemd-resolved
nmcli general reloadWi-Fi Connection Issues
# Reset Wi-Fi interface
sudo nmcli radio wifi off
sudo nmcli radio wifi on
nmcli device wifi rescanConclusion
NetworkManager provides a comprehensive solution for network management in Linux environments. Its combination of automatic configuration capabilities and extensive manual control options makes it suitable for both desktop users and system administrators. Whether you’re managing a single laptop or multiple servers, understanding NetworkManager’s features and commands will significantly improve your network administration efficiency.
The key to mastering NetworkManager lies in understanding its layered approach: the service manages devices and connections, while tools like nmcli provide the interface for configuration and monitoring. Regular practice with the command-line tools, combined with knowledge of the configuration files, will give you complete control over your Linux network infrastructure.