Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a cornerstone of network management, and net-snmp is the most widely used open-source implementation for Linux systems. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about net-snmp, from basic concepts to advanced configuration and practical usage scenarios.
What is net-snmp?
Net-SNMP is a suite of applications used to implement SNMP v1, v2c, and v3 using both IPv4 and IPv6. It provides tools and libraries for:
- SNMP Agent (snmpd) – Responds to SNMP requests
- Command-line tools – For querying and managing SNMP-enabled devices
- Trap daemon (snmptrapd) – Receives and processes SNMP traps
- Development libraries – For building SNMP-enabled applications
Installing net-snmp on Linux
Installation varies depending on your Linux distribution:
Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader snmpd
CentOS/RHEL/Fedora:
sudo yum install net-snmp net-snmp-utils
# or for newer versions
sudo dnf install net-snmp net-snmp-utils
Arch Linux:
sudo pacman -S net-snmp
Basic SNMP Concepts
Before diving into net-snmp commands, understanding these key concepts is essential:
- OID (Object Identifier) – Unique identifier for managed objects
- MIB (Management Information Base) – Database of manageable objects
- Community String – Authentication mechanism for SNMP v1/v2c
- Agent – Software running on managed devices
- Manager – System that monitors and controls agents
Essential net-snmp Commands
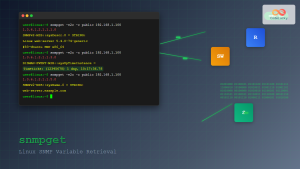
1. snmpget – Retrieve Single Values
The snmpget command retrieves a single SNMP object:
snmpget -v2c -c public localhost 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0
Expected Output:
SNMPv2-MIB::sysDescr.0 = STRING: Linux ubuntu 5.4.0-42-generic #46-Ubuntu SMP Fri Jul 10 00:24:02 UTC 2020 x86_64
Command breakdown:
-v2c– SNMP version 2c-c public– Community string “public”localhost– Target host1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0– OID for system description
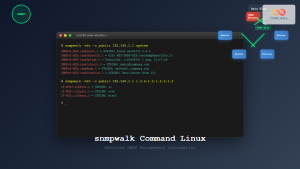
2. snmpwalk – Retrieve Multiple Values
Use snmpwalk to retrieve all objects under a specific OID:
snmpwalk -v2c -c public localhost 1.3.6.1.2.1.1
Sample Output:
SNMPv2-MIB::sysDescr.0 = STRING: Linux ubuntu 5.4.0-42-generic
SNMPv2-MIB::sysObjectID.0 = OID: NET-SNMP-MIB::netSnmpAgentOIDs.10
SNMPv2-MIB::sysUpTime.0 = Timeticks: (12345) 0:02:03.45
SNMPv2-MIB::sysContact.0 = STRING: root@localhost
SNMPv2-MIB::sysName.0 = STRING: ubuntu
SNMPv2-MIB::sysLocation.0 = STRING: Unknown
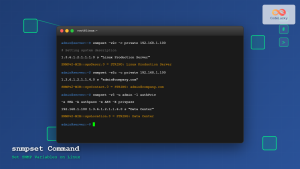
3. snmpset – Modify SNMP Values
The snmpset command modifies writable SNMP objects:
snmpset -v2c -c private localhost 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0 s "Data Center Room 101"
Output:
SNMPv2-MIB::sysLocation.0 = STRING: Data Center Room 101
4. snmptable – Display Tabular Data
View SNMP tables in a formatted manner:
snmptable -v2c -c public localhost 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2
Output Format:
SNMP table: IF-MIB::ifTable
ifIndex ifDescr ifType ifMtu ifSpeed ifPhysAddress ifAdminStatus ifOperStatus
1 lo 24 65536 10 "" up up
2 enp0s3 6 1500 1000000000 08:00:27:a4:b5:c6 up up
Configuring SNMP Agent (snmpd)
The main configuration file is typically located at /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf. Here’s a basic configuration:
# Basic community configuration
rocommunity public default
rwcommunity private localhost
# System information
syslocation "Server Room A"
syscontact "[email protected]"
sysdescr "Production Web Server"
# Access control
view systemview included 1.3.6.1.2.1.1
view systemview included 1.3.6.1.2.1.25.1.1
# Security settings
agentSecName internal
rouser internal noauth 1.3.6.1.2.1
rwuser internal noauth 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6
Starting and Managing snmpd Service
# Start the service
sudo systemctl start snmpd
# Enable auto-start
sudo systemctl enable snmpd
# Check status
sudo systemctl status snmpd
# Restart after configuration changes
sudo systemctl restart snmpd
SNMP Version 3 Configuration
SNMPv3 provides enhanced security with authentication and encryption:
Creating SNMPv3 Users
# Stop snmpd service first
sudo systemctl stop snmpd
# Create user with authentication
sudo net-snmp-create-v3-user -ro -a SHA -x AES -A "authpassword" -X "privpassword" snmpuser
# Start snmpd service
sudo systemctl start snmpd
Using SNMPv3 Commands
snmpget -v3 -u snmpuser -l authPriv -a SHA -A "authpassword" -x AES -X "privpassword" localhost 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0
Monitoring System Resources with SNMP
CPU Usage Monitoring
# Get CPU load averages
snmpwalk -v2c -c public localhost 1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.3
# Sample output
UCD-SNMP-MIB::laLoad.1 = STRING: 0.08
UCD-SNMP-MIB::laLoad.2 = STRING: 0.05
UCD-SNMP-MIB::laLoad.3 = STRING: 0.01
Memory Usage Monitoring
# Get memory information
snmpwalk -v2c -c public localhost 1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4
# Key OIDs for memory
# Total RAM: 1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.5.0
# Available RAM: 1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.6.0
# Used RAM: 1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.14.0
Disk Usage Monitoring
# Monitor disk usage
snmptable -v2c -c public localhost 1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.9
# Output shows filesystem, size, used, available space
Network Interface Monitoring
Monitor network interfaces and traffic statistics:
# Get interface statistics
snmpwalk -v2c -c public localhost 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.10
# Interface names
snmpwalk -v2c -c public localhost 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2
# Interface speeds
snmpwalk -v2c -c public localhost 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5
SNMP Traps Configuration
Configure SNMP traps to receive notifications:
snmptrapd Configuration
Edit /etc/snmp/snmptrapd.conf:
# Authentication settings
authCommunity log,execute,net public
# Trap destinations
trap2sink localhost public
informsink localhost public
# Logging
logoption f /var/log/snmptrapd.log
Starting snmptrapd
sudo systemctl start snmptrapd
sudo systemctl enable snmptrapd
Sending Test Traps
snmptrap -v2c -c public localhost '' 1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.251.1 1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.251.1 s "Test trap message"
Advanced net-snmp Features
Custom OID Extensions
Extend SNMP functionality with custom scripts in snmpd.conf:
# Execute script and return result
exec .1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.50 diskfree /usr/local/bin/diskfree.sh
# Extend with shell command
extend .1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.51 temperature /usr/local/bin/get_temperature.sh
Pass-through Extensions
# Pass OID handling to external script
pass .1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.255 /usr/local/bin/custom_snmp_handler.sh
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Connection Issues
# Test connectivity
snmpget -v2c -c public -t 10 target_host 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0
# Debug mode for detailed output
snmpget -v2c -c public -d target_host 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0
Permission Problems
# Check snmpd process
ps aux | grep snmpd
# Verify configuration syntax
snmpd -Dread_config -f -Lo
Firewall Configuration
# Allow SNMP traffic (port 161)
sudo ufw allow 161/udp
# For SNMP traps (port 162)
sudo ufw allow 162/udp
Performance Optimization
Optimizing snmpd.conf
# Reduce MIB loading time
mibs +ALL
# Optimize access controls
view restricted included 1.3.6.1.2.1.1
view restricted included 1.3.6.1.2.1.2
view restricted excluded 1.3.6.1.2.1.3
# Set appropriate cache values
cachesize 1000
Monitoring Performance
# Check SNMP response times
time snmpget -v2c -c public localhost 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0
# Monitor snmpd resource usage
top -p $(pidof snmpd)
Integration with Monitoring Tools
Net-SNMP integrates seamlessly with popular monitoring solutions:
- Nagios/Icinga – Use check_snmp plugin
- Zabbix – Native SNMP monitoring support
- Cacti – RRD-based graphing with SNMP
- PRTG – Windows-based SNMP monitoring
Security Best Practices
- Use SNMPv3 whenever possible for authentication and encryption
- Change default community strings from “public” and “private”
- Implement access controls using view and access directives
- Restrict SNMP access to specific IP addresses or networks
- Monitor SNMP logs regularly for unauthorized access attempts
- Keep net-snmp updated to latest security patches
Conclusion
Net-SNMP is a powerful and flexible tool for network management on Linux systems. From basic monitoring to complex enterprise deployments, understanding its configuration and commands enables effective network administration. Start with simple configurations and gradually implement advanced features like SNMPv3 security and custom extensions as your requirements grow.
Regular practice with the command-line tools and proper configuration management will help you leverage net-snmp’s full potential for comprehensive network monitoring and management tasks.
- What is net-snmp?
- Installing net-snmp on Linux
- Basic SNMP Concepts
- Essential net-snmp Commands
- Configuring SNMP Agent (snmpd)
- SNMP Version 3 Configuration
- Monitoring System Resources with SNMP
- Network Interface Monitoring
- SNMP Traps Configuration
- Advanced net-snmp Features
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Performance Optimization
- Integration with Monitoring Tools
- Security Best Practices
- Conclusion