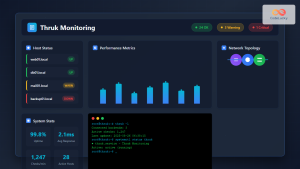
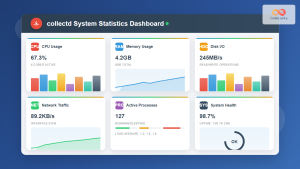
The Nagios Data Output Utilities (ndoutils) serve as a crucial bridge between your Nagios monitoring system and database storage, enabling persistent data retention and advanced reporting capabilities. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about implementing ndoutils on Linux systems.
What is ndoutils?
ndoutils is an addon for Nagios that allows you to store all of your Nagios configuration and event data in a database. Originally developed by Ethan Galstad, ndoutils consists of several components that work together to capture, process, and store Nagios data in MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Oracle databases.
Key Components of ndoutils
- ndomod.o – Event broker module that captures Nagios data
- ndo2db – Daemon that processes and stores data in the database
- file2sock – Utility for reading data from files and sending to sockets
- log2ndo – Tool for importing historical log data
Installation Prerequisites
Before installing ndoutils, ensure your Linux system meets these requirements:
System Requirements
# Check your system information
uname -a
cat /etc/os-release
# Ensure Nagios is installed and running
systemctl status nagios
# Verify database server is available
mysql --version
# or
postgresql --version
Required Dependencies
Install the necessary development packages:
# For CentOS/RHEL/Fedora
sudo yum install gcc mysql-devel mysql-server make
# For Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install build-essential mysql-server mysql-client libmysqlclient-dev
Installing ndoutils from Source
Step 1: Download and Extract
# Navigate to temporary directory
cd /tmp
# Download ndoutils (replace with latest version)
wget https://github.com/NagiosEnterprises/ndoutils/releases/download/ndoutils-2.1.3/ndoutils-2.1.3.tar.gz
# Extract the archive
tar -xzf ndoutils-2.1.3.tar.gz
cd ndoutils-2.1.3
Step 2: Compile and Install
# Configure the build
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nagios --enable-mysql --disable-pgsql
# Compile the source
make all
# Install binaries and configuration files
sudo make install
sudo make install-config
sudo make install-init
Step 3: Verify Installation
# Check installed files
ls -la /usr/local/nagios/bin/ndo*
ls -la /usr/local/nagios/etc/ndo*
# Expected output:
# -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 45632 Aug 26 06:30 /usr/local/nagios/bin/ndo2db
# -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 12456 Aug 26 06:30 /usr/local/nagios/bin/file2sock
# -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 89234 Aug 26 06:30 /usr/local/nagios/lib/ndomod.o
Database Setup
MySQL Database Configuration
# Log into MySQL as root
mysql -u root -p
# Create database and user
CREATE DATABASE nagios;
CREATE USER 'ndouser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'ndopassword';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON nagios.* TO 'ndouser'@'localhost';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
EXIT;
# Import database schema
mysql -u ndouser -p nagios < /usr/local/nagios/share/installdb.mysql
Verify Database Tables
# Check created tables
mysql -u ndouser -p nagios -e "SHOW TABLES;"
# Expected output showing tables like:
# +---------------------------+
# | Tables_in_nagios |
# +---------------------------+
# | nagios_acknowledgements |
# | nagios_commands |
# | nagios_configfiles |
# | nagios_contacts |
# | nagios_hosts |
# | nagios_services |
# | nagios_statehistory |
# +---------------------------+
Configuration Files
Configuring ndo2db.cfg
Edit the main ndo2db configuration file:
# Edit ndo2db configuration
sudo nano /usr/local/nagios/etc/ndo2db.cfg
# Key configuration parameters:
lock_file=/usr/local/nagios/var/ndo2db.lock
ndo2db_user=nagios
ndo2db_group=nagios
socket_type=unix
socket_name=/usr/local/nagios/var/ndo.sock
db_servertype=mysql
db_host=localhost
db_port=3306
db_name=nagios
db_prefix=nagios_
db_user=ndouser
db_pass=ndopassword
max_timedevents_age=1440
max_systemcommands_age=10080
max_servicechecks_age=10080
max_hostchecks_age=10080
max_eventhandlers_age=44640
Configuring ndomod.cfg
# Edit ndomod configuration
sudo nano /usr/local/nagios/etc/ndomod.cfg
# Essential settings:
instance_name=default
output_type=unixsocket
output=/usr/local/nagios/var/ndo.sock
tcp_port=5668
output_buffer_items=5000
buffer_file=/usr/local/nagios/var/ndomod.tmp
file_rotation_interval=14400
file_rotation_timeout=60
reconnect_interval=15
reconnect_warning_interval=900
data_processing_options=-1
config_output_options=2
Integrating with Nagios Configuration
Add ndoutils to your main Nagios configuration:
# Edit nagios.cfg
sudo nano /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
# Add broker module
broker_module=/usr/local/nagios/lib/ndomod.o config_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/ndomod.cfg
# Enable event broker
event_broker_options=-1
Starting and Managing Services
Service Management Commands
# Start ndo2db daemon
sudo systemctl start ndo2db
sudo systemctl enable ndo2db
# Check service status
sudo systemctl status ndo2db
# Expected output:
# ● ndo2db.service - Nagios Data Out Daemon
# Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/ndo2db.service; enabled)
# Active: active (running) since Tue 2025-08-26 06:31:02 IST
# Main PID: 12345 (ndo2db)
# Tasks: 1 (limit: 4915)
# Memory: 2.1M
# CGroup: /system.slice/ndo2db.service
# └─12345 /usr/local/nagios/bin/ndo2db -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/ndo2db.cfg
# Restart Nagios to load the module
sudo systemctl restart nagios
Verifying Socket Communication
# Check if socket exists
ls -la /usr/local/nagios/var/ndo.sock
# Test socket connectivity
echo "test" | nc -U /usr/local/nagios/var/ndo.sock
# Monitor ndo2db logs
sudo tail -f /usr/local/nagios/var/ndo2db.log
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Common Log Locations
# Main log files
/usr/local/nagios/var/ndo2db.log
/usr/local/nagios/var/nagios.log
/var/log/messages
/var/log/syslog
# Check for errors
sudo grep -i error /usr/local/nagios/var/ndo2db.log
sudo grep -i ndomod /usr/local/nagios/var/nagios.log
Database Monitoring Queries
# Check data insertion
mysql -u ndouser -p nagios -e "
SELECT COUNT(*) as total_hosts FROM nagios_hosts;
SELECT COUNT(*) as total_services FROM nagios_services;
SELECT COUNT(*) as recent_checks FROM nagios_statehistory
WHERE state_time > DATE_SUB(NOW(), INTERVAL 1 HOUR);"
# Monitor database size
mysql -u ndouser -p nagios -e "
SELECT
table_name,
ROUND(((data_length + index_length) / 1024 / 1024), 2) AS 'Size (MB)'
FROM information_schema.tables
WHERE table_schema = 'nagios'
ORDER BY (data_length + index_length) DESC;"
Performance Optimization
# Optimize database tables
mysql -u ndouser -p nagios -e "
OPTIMIZE TABLE nagios_statehistory;
OPTIMIZE TABLE nagios_logentries;
OPTIMIZE TABLE nagios_servicechecks;"
# Clean old data
mysql -u ndouser -p nagios -e "
DELETE FROM nagios_logentries
WHERE logentry_time < DATE_SUB(NOW(), INTERVAL 30 DAY);
DELETE FROM nagios_statehistory
WHERE state_time < DATE_SUB(NOW(), INTERVAL 90 DAY);"
Advanced Configuration
Multiple Instance Setup
# Configure multiple Nagios instances
# Instance 1 configuration
instance_name=production
output=/usr/local/nagios/var/ndo_prod.sock
# Instance 2 configuration
instance_name=development
output=/usr/local/nagios/var/ndo_dev.sock
# Corresponding ndo2db instances
socket_name=/usr/local/nagios/var/ndo_prod.sock
socket_name=/usr/local/nagios/var/ndo_dev.sock
SSL/TLS Configuration
# Enable SSL in ndo2db.cfg
use_ssl=1
ssl_cert_file=/path/to/certificate.crt
ssl_key_file=/path/to/private.key
ssl_ca_file=/path/to/ca.crt
# Corresponding ndomod.cfg settings
output_type=tcpsocket
tcp_port=5668
use_ssl=1
Maintenance and Best Practices
Regular Maintenance Script
#!/bin/bash
# ndoutils_maintenance.sh
# Database cleanup
mysql -u ndouser -p'ndopassword' nagios << EOF
DELETE FROM nagios_logentries WHERE logentry_time < DATE_SUB(NOW(), INTERVAL 30 DAY);
DELETE FROM nagios_statehistory WHERE state_time < DATE_SUB(NOW(), INTERVAL 90 DAY);
OPTIMIZE TABLE nagios_logentries;
OPTIMIZE TABLE nagios_statehistory;
EOF
# Log rotation
/usr/sbin/logrotate /etc/logrotate.d/ndo2db
# Check service health
systemctl is-active ndo2db || systemctl restart ndo2db
echo "ndoutils maintenance completed: $(date)"
Monitoring Script
#!/bin/bash
# ndoutils_health_check.sh
# Check service status
if ! systemctl is-active --quiet ndo2db; then
echo "CRITICAL: ndo2db service is not running"
exit 2
fi
# Check socket connectivity
if [ ! -S /usr/local/nagios/var/ndo.sock ]; then
echo "CRITICAL: ndo socket not available"
exit 2
fi
# Check recent data
RECENT_DATA=$(mysql -u ndouser -p'ndopassword' nagios -se "
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM nagios_statehistory
WHERE state_time > DATE_SUB(NOW(), INTERVAL 5 MINUTE);")
if [ "$RECENT_DATA" -eq 0 ]; then
echo "WARNING: No recent data in database"
exit 1
fi
echo "OK: ndoutils is functioning properly"
exit 0
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Permission Issues
# Fix file permissions
sudo chown -R nagios:nagios /usr/local/nagios/var/
sudo chmod 755 /usr/local/nagios/var/
sudo chmod 664 /usr/local/nagios/var/ndo.sock
# SELinux context (if applicable)
sudo setsebool -P nagios_run_sudo 1
sudo semanage fcontext -a -t nagios_exec_t "/usr/local/nagios/bin/ndo2db"
sudo restorecon -R /usr/local/nagios/
Database Connection Issues
# Test database connectivity
mysql -u ndouser -p'ndopassword' -h localhost nagios -e "SELECT NOW();"
# Check MySQL configuration
sudo nano /etc/mysql/my.cnf
# Ensure bind-address allows connections
# Restart MySQL if needed
sudo systemctl restart mysql
Integration with Reporting Tools
Nagvis Integration
# Sample Nagvis backend configuration
[backend_ndomy]
backendtype=ndomy_1
dbhost=localhost
dbport=3306
dbname=nagios
dbuser=ndouser
dbpass=ndopassword
dbprefix=nagios_
dbinstancename=default
Custom Reporting Queries
# Host availability report
SELECT
h.display_name,
ROUND(AVG(CASE WHEN hs.current_state = 0 THEN 100 ELSE 0 END), 2) as uptime_percentage
FROM nagios_hosts h
JOIN nagios_hoststatus hs ON h.host_id = hs.host_object_id
WHERE h.is_active = 1
GROUP BY h.host_id, h.display_name
ORDER BY uptime_percentage DESC;
# Service performance summary
SELECT
s.display_name,
COUNT(*) as total_checks,
AVG(sc.execution_time) as avg_execution_time,
MAX(sc.execution_time) as max_execution_time
FROM nagios_services s
JOIN nagios_servicechecks sc ON s.service_id = sc.service_object_id
WHERE sc.start_time > DATE_SUB(NOW(), INTERVAL 24 HOUR)
GROUP BY s.service_id
ORDER BY avg_execution_time DESC;
ndoutils provides a powerful foundation for Nagios data persistence and advanced monitoring capabilities. By following this comprehensive guide, you’ll have a robust monitoring data storage system that enables detailed reporting, trend analysis, and integration with third-party tools. Regular maintenance and monitoring of your ndoutils installation will ensure optimal performance and data integrity for your monitoring infrastructure.