The modinfo command is an essential Linux utility that displays detailed information about kernel modules. Whether you’re troubleshooting hardware issues, understanding module dependencies, or managing system resources, mastering modinfo is crucial for effective Linux system administration.
What is the modinfo Command?
The modinfo command extracts and displays information from Linux kernel module files. It reads module metadata including descriptions, author information, parameters, dependencies, and licensing details. This information is embedded within the module files during compilation and helps administrators understand module functionality and requirements.
Basic Syntax and Usage
The basic syntax of the modinfo command is:
modinfo [OPTIONS] MODULE_NAMEHere’s a simple example showing basic usage:
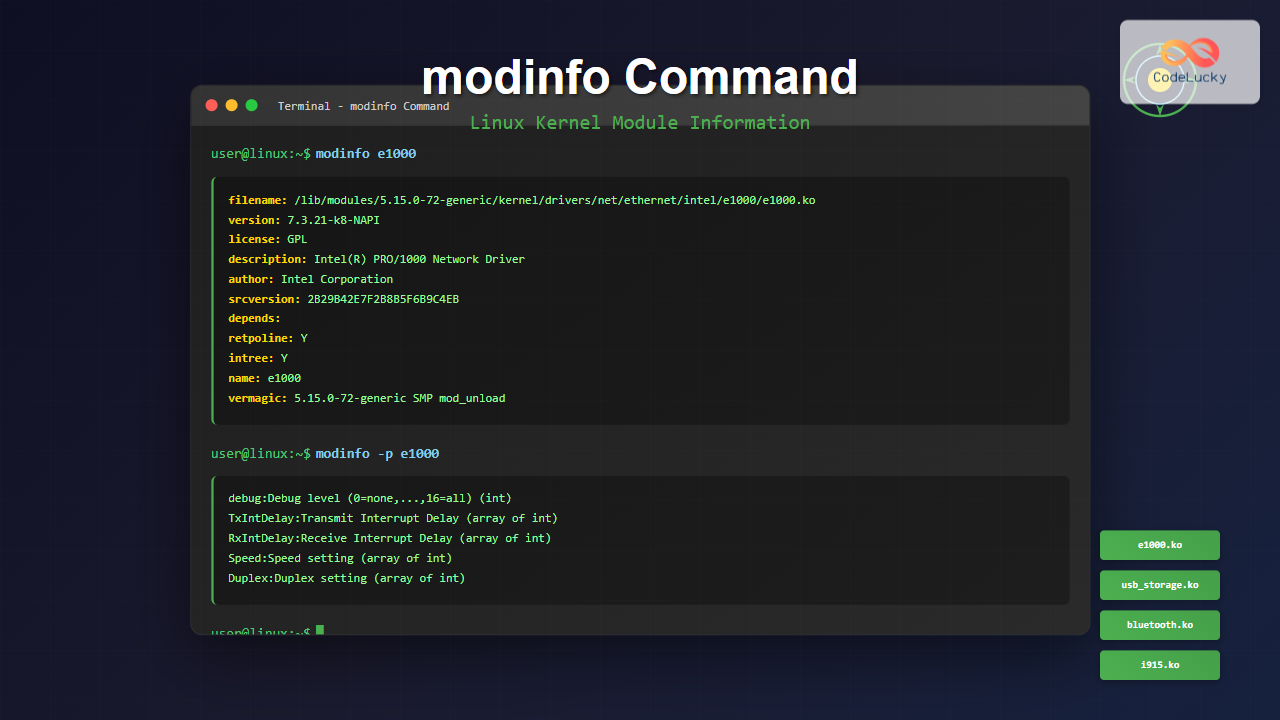
$ modinfo e1000
filename: /lib/modules/5.15.0-72-generic/kernel/drivers/net/ethernet/intel/e1000/e1000.ko
version: 7.3.21-k8-NAPI
license: GPL
description: Intel(R) PRO/1000 Network Driver
author: Intel Corporation, <[email protected]>
srcversion: 2B29B42E7F2B8B5F6B9C4EB
alias: pci:v00008086d00001026sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
alias: pci:v00008086d00001025sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
depends:
retpoline: Y
intree: Y
name: e1000
vermagic: 5.15.0-72-generic SMP mod_unload modversionsCommon Options and Parameters
Display Specific Fields
Use the -F or --field option to display specific information fields:
# Display only the description
$ modinfo -F description e1000
Intel(R) PRO/1000 Network Driver
# Display only the author
$ modinfo -F author e1000
Intel Corporation, <[email protected]>
# Display version information
$ modinfo -F version e1000
7.3.21-k8-NAPIList All Parameters
To view module parameters, use the -p option:
$ modinfo -p e1000
debug:Debug level (0=none,...,16=all) (int)
copybreak:Maximum size of packet that is copied to a new buffer on receive (uint)
TxIntDelay:Transmit Interrupt Delay (array of int)
TxAbsIntDelay:Transmit Absolute Interrupt Delay (array of int)
RxIntDelay:Receive Interrupt Delay (array of int)
RxAbsIntDelay:Receive Absolute Interrupt Delay (array of int)
Speed:Speed setting (array of int)
Duplex:Duplex setting (array of int)
AutoNeg:Advertised auto-negotiation setting (array of int)
FlowControl:Flow Control setting (array of int)
XsumRX:Disable or enable Receive Checksum offload (array of int)
TxDescriptors:Number of transmit descriptors (array of int)
RxDescriptors:Number of receive descriptors (array of int)
InterruptThrottleRate:Interrupt Throttling Rate (array of int)
SmartPowerDownEnable:Enable PHY smart power down (array of int)Display Module Dependencies
View what other modules a specific module depends on:
$ modinfo -F depends bluetooth
ecdh_generic,crc16
$ modinfo -F depends usb_storage
scsi_mod,usb_commonPractical Examples
Examining Graphics Drivers
Check information about graphics drivers:
$ modinfo i915
filename: /lib/modules/5.15.0-72-generic/kernel/drivers/gpu/drm/i915/i915.ko
license: GPL and additional rights
description: Intel Graphics
author: Intel Corporation
author: Tungsten Graphics, Inc.
srcversion: E8B02A03F1A7B3D9FB8C042
alias: pci:v00008086d0000A7A8sv*sd*bc03sc*i*
alias: pci:v00008086d0000A7A0sv*sd*bc03sc*i*
depends: drm_kms_helper,drm,i2c_algo_bit,video,button
retpoline: Y
intree: Y
name: i915
vermagic: 5.15.0-72-generic SMP mod_unload modversions
parm: modeset:Use kernel modesetting [KMS] (0=disable, 1=on, -1=force vga console preference) (int)
parm: panel_ignore_lid:Override lid status (0=autodetect, 1=autodetect disabled [default], -1=force lid closed) (int)
parm: enable_dc:Enable power-saving display C-states. (-1=auto [default]; 0=disable; 1=up to DC5; 2=up to DC6) (int)Network Module Information
Examine network interface modules:
$ modinfo -F description r8169
RealTek RTL-8169 Gigabit Ethernet driver
$ modinfo -F license r8169
GPL
$ modinfo -p r8169
use_dac:Enable PCI DAC. Unsafe on 32 bit PCI slot. (array of int)
debug:Debug verbosity level (0=none, ..., 16=all) (int)Sound System Modules
Check audio-related module information:
$ modinfo snd_hda_intel
filename: /lib/modules/5.15.0-72-generic/kernel/sound/pci/hda/snd-hda-intel.ko
description: Intel HDA driver
license: GPL
srcversion: A1B2C3D4E5F6789ABCDEF01
depends: snd_hda_codec,snd_hda_core,snd,snd_pcm
retpoline: Y
intree: Y
name: snd_hda_intel
vermagic: 5.15.0-72-generic SMP mod_unload modversions
parm: index:Index value for Intel HD audio interface. (array of int)
parm: id:ID string for Intel HD audio interface. (array of charp)
parm: model:Use the given board model. (array of charp)
parm: position_fix:DMA pointer read method.(0 = auto, 1 = LPIB, 2 = POSBUF, 3 = VIACOMBO, 4 = COMBO, 5 = SKL+, 6 = FIFO) (array of int)Advanced Usage Scenarios
Module Path Information
Find the exact location of module files:
$ modinfo -F filename usbcore
/lib/modules/5.15.0-72-generic/kernel/drivers/usb/core/usbcore.ko
$ modinfo -F filename ext4
/lib/modules/5.15.0-72-generic/kernel/fs/ext4/ext4.koChecking Module Signatures
View signature information for security validation:
$ modinfo -F sig_key e1000
$ modinfo -F sig_hashalgo e1000
$ modinfo -F signature e1000Listing Module Aliases
Display device aliases supported by a module:
$ modinfo -F alias e1000 | head -5
pci:v00008086d00001026sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
pci:v00008086d00001025sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
pci:v00008086d00001024sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
pci:v00008086d00001023sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
pci:v00008086d00001022sv*sd*bc*sc*i*Troubleshooting with modinfo
Diagnosing Module Issues
When experiencing hardware problems, use modinfo to verify module availability and configuration:
# Check if a module exists
$ modinfo nonexistent_module
modinfo: ERROR: Module nonexistent_module not found.
# Verify module dependencies are met
$ modinfo -F depends wifi_module
cfg80211,mac80211Parameter Validation
Before setting module parameters, check available options:
$ modinfo -p iwlwifi
debug:debug output mask (uint)
swcrypto:using crypto in software (default 0 [hardware]) (int)
11n_disable:disable 11n functionality, bitmap: 1: full, 2: disable agg TX, 4: disable agg RX, 8 enable agg TX (uint)
amsdu_size:amsdu size 0: 12K for multi Rx queue devices, 4K for other devices, 1:4K, 2:8K, 3:12K (default 0) (uint)
fw_restart:restart firmware in case of error (default true) (bool)
antenna_coupling:specify antenna coupling in dB (default: 0 dB) (int)
nvm_file:NVM file name (charp)
uapsd_disable:disable U-APSD functionality bitmap 1: BSS 2: P2P Client (default: 3) (uint)Integration with System Management
Scripting with modinfo
Create scripts to automate module information gathering:
#!/bin/bash
# Script to check network module information
MODULES=("e1000" "r8169" "iwlwifi")
for module in "${MODULES[@]}"; do
echo "=== $module ==="
if modinfo "$module" &>/dev/null; then
echo "Description: $(modinfo -F description "$module")"
echo "Version: $(modinfo -F version "$module")"
echo "Dependencies: $(modinfo -F depends "$module")"
else
echo "Module not found"
fi
echo
doneMonitoring Module Changes
Compare module information across different kernel versions:
# Check module version for different kernels
$ modinfo -k 5.15.0-72-generic -F version nvidia
$ modinfo -k 5.15.0-75-generic -F version nvidiaCommon Use Cases
Hardware Compatibility Verification
Before purchasing hardware, check if drivers are available:
# Check wireless chipset support
$ modinfo ath10k_pci
$ modinfo iwlwifi
$ modinfo rtw88_pciPerformance Tuning
Identify tunable parameters for optimization:
$ modinfo -p nvidia
NVreg_Mobile:int
NVreg_ResmanDebugLevel:int
NVreg_RmLogonRC:int
NVreg_ModifyDeviceFiles:int
NVreg_DeviceFileUID:int
NVreg_DeviceFileGID:int
NVreg_DeviceFileMode:int
NVreg_InitializeSystemMemoryAllocations:int
NVreg_UsePageAttributeTable:int
NVreg_EnableMSI:intBest Practices
Documentation and Maintenance
- Always verify module information before making system changes
- Document custom parameters used in your environment
- Check dependencies before removing modules
- Monitor parameter changes across kernel updates
Security Considerations
- Verify module signatures in secure environments
- Check module sources and licensing information
- Monitor for unsigned modules that could indicate security risks
Conclusion
The modinfo command is an invaluable tool for Linux system administrators and users who need to understand kernel module behavior and configuration. From basic information display to advanced troubleshooting scenarios, modinfo provides comprehensive insights into your system’s kernel modules.
By mastering the various options and use cases covered in this guide, you’ll be equipped to effectively manage kernel modules, troubleshoot hardware issues, and optimize system performance. Regular use of modinfo as part of your system administration toolkit will enhance your understanding of Linux kernel module management and improve your overall system administration skills.
Remember to always consult module documentation and test changes in non-production environments before applying them to critical systems. The information provided by modinfo serves as your roadmap for safe and effective kernel module management.