Memcached is a high-performance, distributed memory object caching system that dramatically improves application performance by storing frequently accessed data in RAM. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about implementing and managing memcached on Linux systems.
What is Memcached?
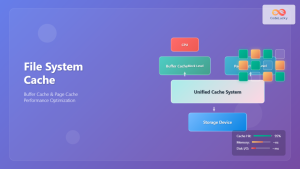
Memcached is an open-source, distributed memory caching system designed to speed up dynamic web applications by alleviating database load. It stores data and objects in RAM to reduce the number of times an external data source must be read, making it an essential tool for high-traffic websites and applications.
Key Features of Memcached
- High Performance: Operates entirely in memory for lightning-fast data retrieval
- Distributed Architecture: Scales horizontally across multiple servers
- Simple Protocol: Easy-to-understand text-based protocol
- Language Agnostic: Supports multiple programming languages
- Thread-Safe: Handles concurrent requests efficiently
Installing Memcached on Linux
Ubuntu/Debian Installation
Install memcached and development libraries:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install memcached libmemcached-toolsCentOS/RHEL/Fedora Installation
For RPM-based distributions:
# CentOS/RHEL 7/8
sudo yum install memcached libmemcached
# Fedora/CentOS 8+
sudo dnf install memcached libmemcachedCompiling from Source
For the latest version or custom configurations:
wget http://memcached.org/latest
tar -zxvf memcached-1.x.x.tar.gz
cd memcached-1.x.x
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/memcached
make && sudo make installConfiguring Memcached
Main Configuration File
The primary configuration file is located at /etc/memcached.conf:
# Memory allocation (in MB)
-m 64
# Default port
-p 11211
# User to run memcached
-u memcache
# Listen on all interfaces
-l 0.0.0.0
# Enable verbose logging
-v
# Run as daemon
-d
# PID file location
-P /var/run/memcached/memcached.pid
# Log file location
-L /var/log/memcached.logSystemd Service Configuration
Create or modify the systemd service file at /etc/systemd/system/memcached.service:
[Unit]
Description=Memcached
Before=httpd.service
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=notify
ExecStart=/usr/bin/memcached -m 512 -p 11211 -u memcached -l 127.0.0.1
ExecReload=/bin/kill -SIGUSR1 $MAINPID
Restart=always
User=memcached
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetStarting and Managing Memcached Service
Basic Service Management
# Start memcached service
sudo systemctl start memcached
# Enable auto-start on boot
sudo systemctl enable memcached
# Check service status
sudo systemctl status memcached
# Restart service
sudo systemctl restart memcached
# Stop service
sudo systemctl stop memcachedExpected Output:
● memcached.service - Memcached
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/memcached.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2025-08-26 09:19:15 IST; 2min ago
Main PID: 1234 (memcached)
CGroup: /system.slice/memcached.service
└─1234 /usr/bin/memcached -m 512 -p 11211 -u memcached -l 127.0.0.1Essential Memcached Commands
Connecting to Memcached
Connect using telnet or netcat:
# Connect via telnet
telnet localhost 11211
# Connect via netcat
nc localhost 11211Basic Data Operations
Storing Data (SET Command)
set key flags exptime bytes
valueExample:
set user:1001 0 3600 12
John Doe UserOutput: STORED
Retrieving Data (GET Command)
get user:1001Output:
VALUE user:1001 0 12
John Doe User
ENDAdding Data (ADD Command)
add new_key 0 3600 5
HelloOutput: STORED (if key doesn’t exist) or NOT_STORED (if key exists)
Replacing Data (REPLACE Command)
replace user:1001 0 3600 8
Jane DoeOutput: STORED (if key exists) or NOT_STORED (if key doesn’t exist)
Advanced Commands
Increment and Decrement
# Set initial counter
set counter 0 0 1
5
# Increment by 1
incr counter 1
# Increment by 10
incr counter 10
# Decrement by 5
decr counter 5Delete Operations
# Delete specific key
delete user:1001
# Flush all data (use with caution!)
flush_allInformation and Statistics Commands
Basic Statistics
statsSample Output:
STAT pid 1234
STAT uptime 86400
STAT time 1724654355
STAT version 1.6.21
STAT curr_items 1500
STAT total_items 15000
STAT bytes 1048576
STAT curr_connections 10
STAT total_connections 1000
STAT connection_structures 15
STAT get_hits 8500
STAT get_misses 1500
STAT hit_ratio 85.00%
ENDMemory Statistics
stats slabsItem Statistics
stats itemsConnection Statistics
stats connsCommand-Line Tools and Utilities
memcached-tool
Display statistics and manage memcached instances:
# Display basic stats
memcached-tool localhost:11211 stats
# Display detailed item information
memcached-tool localhost:11211 display
# Move items between slab classes
memcached-tool localhost:11211 move 7 9memcstat (from libmemcached-tools)
# Show server statistics
memcstat --servers=localhost:11211
# Show detailed memory usage
memcstat --servers=localhost:11211 --analyzePerformance Tuning and Optimization
Memory Allocation Strategies
Setting Appropriate Memory Size
# For 4GB system, allocate 1GB to memcached
memcached -m 1024 -p 11211 -u memcached -d
# Monitor memory usage
echo "stats" | nc localhost 11211 | grep bytesConnection and Threading Configuration
# Increase maximum connections
memcached -m 512 -c 2048 -p 11211 -u memcached -d
# Set thread count (typically CPU cores × 2)
memcached -m 512 -t 8 -p 11211 -u memcached -dNetwork Optimization
TCP Settings
# Disable Nagle's algorithm for better performance
memcached -m 512 -p 11211 -T -u memcached -d
# Set TCP no delay
echo 'net.ipv4.tcp_nodelay = 1' >> /etc/sysctl.confMonitoring and Troubleshooting
Real-time Monitoring Script
Create a monitoring script memcached_monitor.sh:
#!/bin/bash
while true; do
echo "=== Memcached Statistics $(date) ==="
echo "stats" | nc localhost 11211 | grep -E "(curr_items|bytes|get_hits|get_misses|curr_connections)"
echo
sleep 5
doneLog Analysis
# View memcached logs
sudo tail -f /var/log/memcached.log
# Check for connection issues
sudo grep -i "connection" /var/log/memcached.log
# Monitor error patterns
sudo grep -i "error\|fail" /var/log/memcached.logCommon Troubleshooting Commands
Check Port Availability
# Verify memcached is listening
sudo netstat -tlnp | grep :11211
# Test connection
telnet localhost 11211Process Management
# Find memcached processes
ps aux | grep memcached
# Check memory usage
sudo pmap -d $(pgrep memcached)
# Monitor system resources
htop -p $(pgrep memcached)Security Considerations
Network Security
# Bind to localhost only (default)
memcached -l 127.0.0.1 -p 11211
# Use firewall rules
sudo ufw allow from 192.168.1.0/24 to any port 11211
sudo ufw deny 11211User Permissions
# Create dedicated user
sudo useradd -r -s /bin/false memcached
# Set proper permissions
sudo chown memcached:memcached /var/log/memcached.log
sudo chmod 640 /etc/memcached.confIntegration Examples
PHP Integration
$memcache = new Memcache;
$memcache->connect('localhost', 11211);
// Store data
$memcache->set('user_1001', $user_data, 0, 3600);
// Retrieve data
$cached_data = $memcache->get('user_1001');Python Integration
import memcache
# Connect to memcached
mc = memcache.Client(['127.0.0.1:11211'])
# Store data
mc.set('session_data', session_info, time=3600)
# Retrieve data
data = mc.get('session_data')Best Practices and Tips
Key Naming Conventions
- Use descriptive, hierarchical key names:
user:profile:1001 - Keep keys under 250 characters
- Avoid spaces and special characters
- Use consistent naming patterns across your application
Expiration Strategies
# Short-term cache (5 minutes)
set temp_data 0 300 10
short_term
# Long-term cache (24 hours)
set static_content 0 86400 15
persistent_data
# No expiration (until server restart or memory pressure)
set permanent_config 0 0 8
config_dataError Handling
# Always check for connection before operations
echo "version" | nc -w 1 localhost 11211 > /dev/null 2>&1
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
echo "Memcached is accessible"
else
echo "Memcached connection failed"
fiConclusion
Memcached is a powerful caching solution that can significantly improve your application’s performance when properly configured and managed. By following the commands, configurations, and best practices outlined in this guide, you’ll be able to implement and maintain a robust caching system on your Linux servers.
Remember to regularly monitor your memcached instances, adjust memory allocation based on usage patterns, and implement proper security measures to ensure optimal performance and security. With these tools and techniques, you’ll be well-equipped to leverage memcached’s full potential in your high-performance applications.
- What is Memcached?
- Installing Memcached on Linux
- Configuring Memcached
- Starting and Managing Memcached Service
- Essential Memcached Commands
- Command-Line Tools and Utilities
- Performance Tuning and Optimization
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Security Considerations
- Integration Examples
- Best Practices and Tips
- Conclusion