The machinectl command is a powerful utility in Linux systems that provides comprehensive management capabilities for systemd containers and virtual machines. As part of the systemd ecosystem, it offers administrators a unified interface to control, monitor, and interact with various types of isolated environments including containers, VMs, and chroots.
What is machinectl?
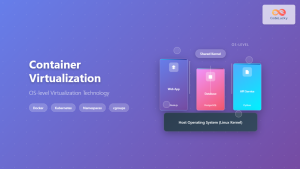
machinectl is the command-line interface to systemd-machined, a system service that manages local containers and virtual machines. It’s designed to work seamlessly with various container technologies like systemd-nspawn, Docker, and virtualization platforms such as libvirt and QEMU/KVM.
Key Features
- Unified Management: Single interface for different container and VM technologies
- Image Management: Download, import, and manage container images
- Resource Monitoring: Track resource usage and performance metrics
- Network Integration: Advanced networking capabilities for containers
- Security: Built-in security features and isolation mechanisms
Installation and Prerequisites
machinectl comes pre-installed with most modern Linux distributions that use systemd. To verify installation:
which machinectlExpected Output:
/usr/bin/machinectlIf not installed, you can install it on different distributions:
Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install systemd-containerCentOS/RHEL/Fedora:
sudo dnf install systemd-containerBasic machinectl Syntax
The general syntax for machinectl follows this pattern:
machinectl [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS...]Essential machinectl Commands
1. Listing Machines
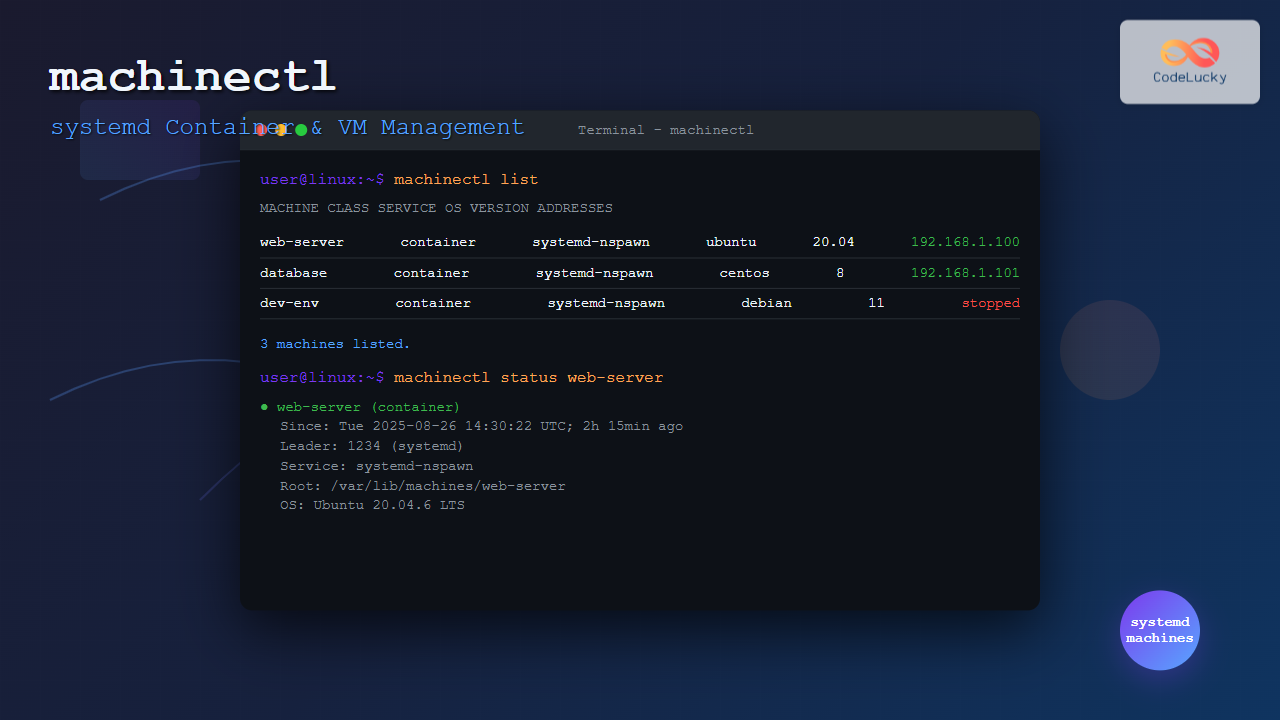
View all running containers and VMs:
machinectl listSample Output:
MACHINE CLASS SERVICE OS VERSION ADDRESSES
web-server container systemd-nspawn ubuntu 20.04 192.168.1.100
database container systemd-nspawn centos 8 192.168.1.101
2 machines listed.2. Machine Status Information
Get detailed status of a specific machine:
machinectl status web-serverSample Output:
web-server(a1b2c3d4e5f6)
Since: Tue 2025-08-26 14:30:22 UTC; 2h 15min ago
Leader: 1234 (systemd)
Service: systemd-nspawn
Root: /var/lib/machines/web-server
OS: Ubuntu 20.04.6 LTS
Unit: [email protected]
├─1234 /lib/systemd/systemd --system
└─system.slice
├─apache2.service
│ └─1456 /usr/sbin/apache2 -DFOREGROUND3. Starting and Stopping Machines
Start a container or VM:
machinectl start web-serverStop a running machine:
machinectl stop web-serverRestart a machine:
machinectl restart web-server4. Enabling Auto-start
Enable automatic startup on boot:
machinectl enable web-serverDisable auto-start:
machinectl disable web-serverImage Management
1. Listing Available Images
View downloaded images:
machinectl list-imagesSample Output:
NAME TYPE RO USAGE CREATED MODIFIED
ubuntu-20.04 raw no 2.1G Tue 2025-08-26 12:00:00 UTC n/a
centos-8 raw no 1.8G Mon 2025-08-25 15:30:00 UTC n/a
2 images listed.2. Downloading Images
Pull container images from registries:
machinectl pull-tar --verify=no https://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/focal/current/focal-server-cloudimg-amd64-root.tar.xz ubuntu-focal3. Importing Local Images
Import from a local tar file:
machinectl import-tar /path/to/image.tar.xz my-container4. Removing Images
Delete an unused image:
machinectl remove ubuntu-20.04Interactive Shell Access
1. Login to Machine
Get an interactive shell in a running container:
machinectl login web-server2. Execute Commands
Run single commands without interactive login:
machinectl shell web-server /bin/bash -c "ps aux | grep apache"3. Copy Files
Copy files to/from containers:
# Copy to container
machinectl copy-to web-server /local/file.txt /container/path/
# Copy from container
machinectl copy-from web-server /container/path/file.txt /local/path/Advanced machinectl Operations
1. Binding Directories
Mount host directories in containers:
machinectl bind web-server /host/data /container/data2. Resource Management
Set memory limits:
systemctl set-property [email protected] MemoryMax=1GSet CPU limits:
systemctl set-property [email protected] CPUQuota=50%3. Network Configuration
Show network interfaces:
machinectl show web-serverCreating Containers with systemd-nspawn
1. Basic Container Creation
Create a new container from an existing image:
# Create container directory
sudo mkdir -p /var/lib/machines/new-container
# Bootstrap Ubuntu container
sudo debootstrap focal /var/lib/machines/new-container http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/
# Start the container
machinectl start new-container2. Container with Custom Configuration
Create a container with specific network settings:
sudo systemd-nspawn -M web-app -D /var/lib/machines/web-app --network-veth --bootMonitoring and Troubleshooting
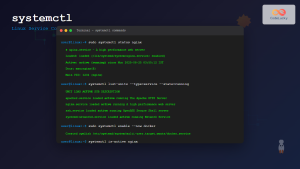
1. Show Properties
Display detailed machine properties:
machinectl show web-serverSample Output:
Name=web-server
Id=a1b2c3d4e5f6789
Class=container
Service=systemd-nspawn
[email protected]
Leader=1234
RootDirectory=/var/lib/machines/web-server
Timestamp=1724677822000000
TimestampMonotonic=123456782. Viewing Logs
Check container logs:
journalctl -M web-serverFollow real-time logs:
journalctl -M web-server -f3. Resource Usage
Monitor resource consumption:
systemd-cgtopSecurity Best Practices
1. User Namespaces
Enable user namespace isolation:
sudo systemd-nspawn -M secure-container -D /var/lib/machines/secure-container --private-users=pick --boot2. Read-only Root
Create containers with read-only root filesystem:
sudo systemd-nspawn -M readonly-container -D /var/lib/machines/readonly-container --read-only --boot3. Capability Dropping
Remove dangerous capabilities:
sudo systemd-nspawn -M limited-container -D /var/lib/machines/limited-container --drop-capability=CAP_SYS_ADMIN --bootCommon machinectl Options
| Option | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
-H, --host |
Connect to remote host | machinectl -H user@remote list |
-l, --full |
Show full output | machinectl list -l |
--no-pager |
Disable pager | machinectl status --no-pager web-server |
--no-legend |
Hide column headers | machinectl list --no-legend |
Troubleshooting Common Issues
1. Container Won’t Start
Check systemd service status:
systemctl status [email protected]2. Network Issues
Verify network bridge configuration:
ip link showCheck iptables rules:
sudo iptables -L -n3. Permission Problems
Ensure proper ownership:
sudo chown -R root:root /var/lib/machines/container-namePerformance Optimization
1. Memory Management
Configure swap accounting:
echo 'GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="cgroup_enable=memory swapaccount=1"' | sudo tee -a /etc/default/grub
sudo update-grub2. Storage Optimization
Use btrfs subvolumes for better snapshot management:
sudo btrfs subvolume create /var/lib/machines/container-nameIntegration with Other Tools
1. Docker Integration
machinectl can manage Docker containers through systemd:
docker run -d --name nginx-container nginx
machinectl list2. Podman Integration
Similarly works with Podman containers:
podman run -d --name web-service httpd
machinectl listConclusion
The machinectl command is an essential tool for modern Linux system administrators working with containers and virtual machines. Its integration with systemd provides a unified management experience that simplifies container orchestration, monitoring, and maintenance tasks.
Key takeaways for effective machinectl usage:
- Use
machinectl listfor quick overview of all machines - Leverage
machinectl statusfor detailed troubleshooting - Implement proper security measures with user namespaces and capability dropping
- Regular monitoring with
journalctlandsystemd-cgtop - Automate container management with systemd service integration
As containerization continues to grow in importance, mastering machinectl will significantly enhance your ability to manage complex containerized environments efficiently and securely.
- What is machinectl?
- Installation and Prerequisites
- Basic machinectl Syntax
- Essential machinectl Commands
- Image Management
- Interactive Shell Access
- Advanced machinectl Operations
- Creating Containers with systemd-nspawn
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Security Best Practices
- Common machinectl Options
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Performance Optimization
- Integration with Other Tools
- Conclusion