The lsmod command is an essential Linux utility that displays information about currently loaded kernel modules in your system. Understanding how to use this command effectively is crucial for system administrators, developers, and anyone working with Linux kernel management.
What is the lsmod Command?
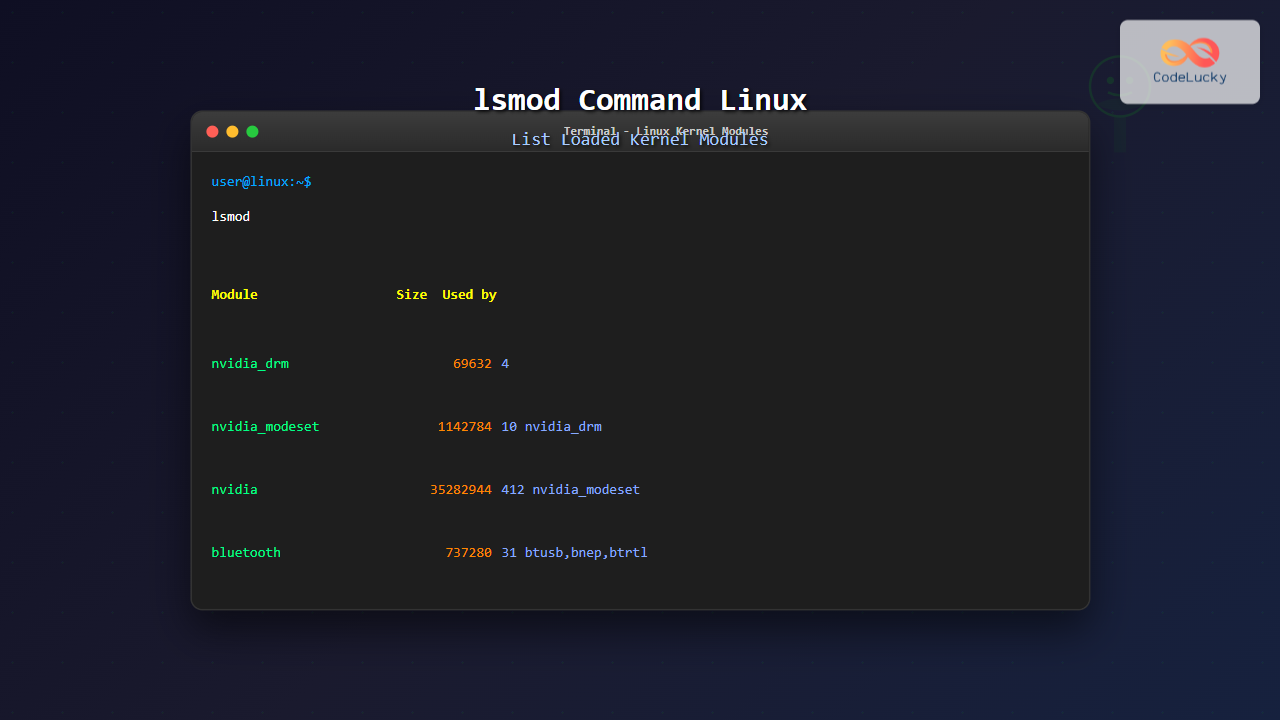
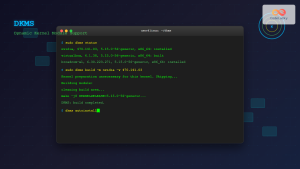
The lsmod command stands for “list modules” and provides a formatted view of the kernel modules currently loaded in memory. It reads information from the /proc/modules file and presents it in a user-friendly format showing module names, sizes, usage counts, and dependencies.
Basic Syntax and Usage
The basic syntax of the lsmod command is straightforward:
lsmod [options]In most cases, you’ll use lsmod without any options:
lsmodSample Output Explanation
When you run lsmod, you’ll see output similar to this:
Module Size Used by
nvidia_drm 69632 4
nvidia_modeset 1142784 10 nvidia_drm
nvidia 35282944 412 nvidia_modeset
bluetooth 737280 31 btusb,bnep,btrtl,btbcm,btintel
rfkill 32768 9 bluetooth,cfg80211
snd_hda_codec_hdmi 73728 1
snd_hda_intel 57344 5
snd_intel_dspcfg 32768 2 snd_hda_intel,snd_sof_intel_hda_commonThis output contains three columns:
- Module: The name of the loaded kernel module
- Size: Memory size occupied by the module in bytes
- Used by: Shows the usage count and which modules depend on this module
Understanding Module Dependencies
The “Used by” column reveals important dependency relationships between modules. For example, in the output above:
nvidiais used by 412 processes and thenvidia_modesetmodulebluetoothis used by multiple modules:btusb,bnep,btrtl,btbcm, andbtintel
Command Options and Variations
Basic lsmod Command
lsmodThis displays all currently loaded modules with their basic information.
Filtering Output with grep
To find specific modules, combine lsmod with grep:
# Find audio-related modules
lsmod | grep snd
# Find network-related modules
lsmod | grep net
# Find USB-related modules
lsmod | grep usbSorting Output by Size
To see modules sorted by memory usage:
# Sort by size (largest first)
lsmod | sort -k2 -nr
# Sort by size (smallest first)
lsmod | sort -k2 -nPractical Examples and Use Cases
Example 1: Checking Graphics Driver Modules
$ lsmod | grep -i nvidia
nvidia_drm 69632 4
nvidia_modeset 1142784 10 nvidia_drm
nvidia 35282944 412 nvidia_modesetThis shows all NVIDIA-related modules and their dependencies, useful for troubleshooting graphics issues.
Example 2: Monitoring USB Modules
$ lsmod | grep usb
usbhid 57344 0
hid 147456 2 usbhid,hid_generic
usb_storage 81920 1
usbcore 299008 6 usbhid,usb_storage,btusb,xhci_hcd,xhci_pciThis helps identify USB-related kernel modules when diagnosing USB device issues.
Example 3: Finding the Largest Modules
$ lsmod | head -1; lsmod | sort -k2 -nr | head -10
Module Size Used by
nvidia 35282944 412 nvidia_modeset
i915 2093056 12
xfs 1540096 1
libcrc32c 16384 4 nf_conntrack,nf_nat,xfs,raid456This shows the largest modules by memory consumption, helpful for memory optimization.
Alternative Ways to View Module Information
Using /proc/modules Directly
cat /proc/modules | head -5This shows the raw module information that lsmod formats.
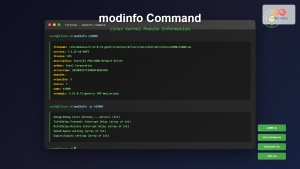
Using modinfo for Detailed Module Information
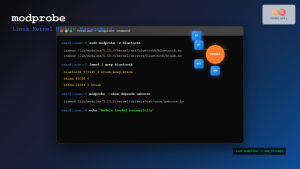
# Get detailed information about a specific module
modinfo nvidia
# Get just the description
modinfo -d nvidiaTroubleshooting with lsmod
Identifying Missing Modules
When hardware isn’t working, check if required modules are loaded:
# Check for Wi-Fi modules
lsmod | grep -i wifi
lsmod | grep -i wlan
# Check for sound modules
lsmod | grep -i snd
lsmod | grep -i audioFinding Module Conflicts
Sometimes modules conflict with each other. Use lsmod to identify loaded modules before troubleshooting:
# Save current module list
lsmod > /tmp/modules_before.txt
# After making changes, compare
lsmod > /tmp/modules_after.txt
diff /tmp/modules_before.txt /tmp/modules_after.txtSecurity Considerations
The lsmod command is generally safe to use and doesn’t require root privileges. However, the information it provides can be valuable for system reconnaissance, so consider this in security-sensitive environments.
Related Commands
Several other commands work alongside lsmod for module management:
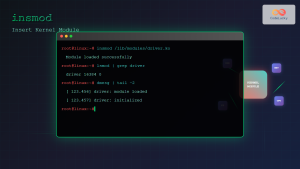
modprobe: Load and unload kernel modulesinsmod: Insert a module into the kernelrmmod: Remove a module from the kernelmodinfo: Show information about a kernel moduledepmod: Generate module dependency information
Performance Impact and Best Practices
The lsmod command has minimal performance impact as it simply reads from the /proc filesystem. Here are some best practices:
- Use lsmod regularly to monitor system state
- Combine with other commands for comprehensive module management
- Save module lists before system changes for comparison
- Use filtering to focus on specific module categories
Common Error Scenarios
While lsmod rarely fails, you might encounter these situations:
- Permission denied: Usually not an issue with lsmod, but related module management commands may require root access
- Empty output: Indicates no modules are loaded (rare in modern systems)
- Module not found: When filtering, no modules match your criteria
Conclusion
The lsmod command is a fundamental tool for Linux system administration and troubleshooting. By understanding how to use it effectively, you can better manage your system’s kernel modules, diagnose hardware issues, and optimize system performance. Whether you’re a system administrator, developer, or Linux enthusiast, mastering lsmod will enhance your ability to work with the Linux kernel effectively.
Remember that lsmod provides a snapshot of your system’s current state, and module loading can change based on hardware detection, system boot, and manual intervention. Regular monitoring with lsmod helps maintain awareness of your system’s kernel module status and can be invaluable for troubleshooting and optimization tasks.