iptables is the most powerful and flexible firewall solution available for Linux systems, offering granular control over network traffic through advanced rule creation and management. This comprehensive guide explores sophisticated iptables configurations that go beyond basic filtering to provide enterprise-level security.
Understanding iptables Architecture
iptables operates through a sophisticated chain-based system where packets traverse different tables and chains based on their origin, destination, and purpose. The three primary tables are:
- Filter Table: Default table for packet filtering (INPUT, OUTPUT, FORWARD chains)
- NAT Table: Network Address Translation (PREROUTING, POSTROUTING, OUTPUT chains)
- Mangle Table: Packet alteration and quality of service
Advanced Chain Management
Creating custom chains allows for modular rule organization and improved performance:
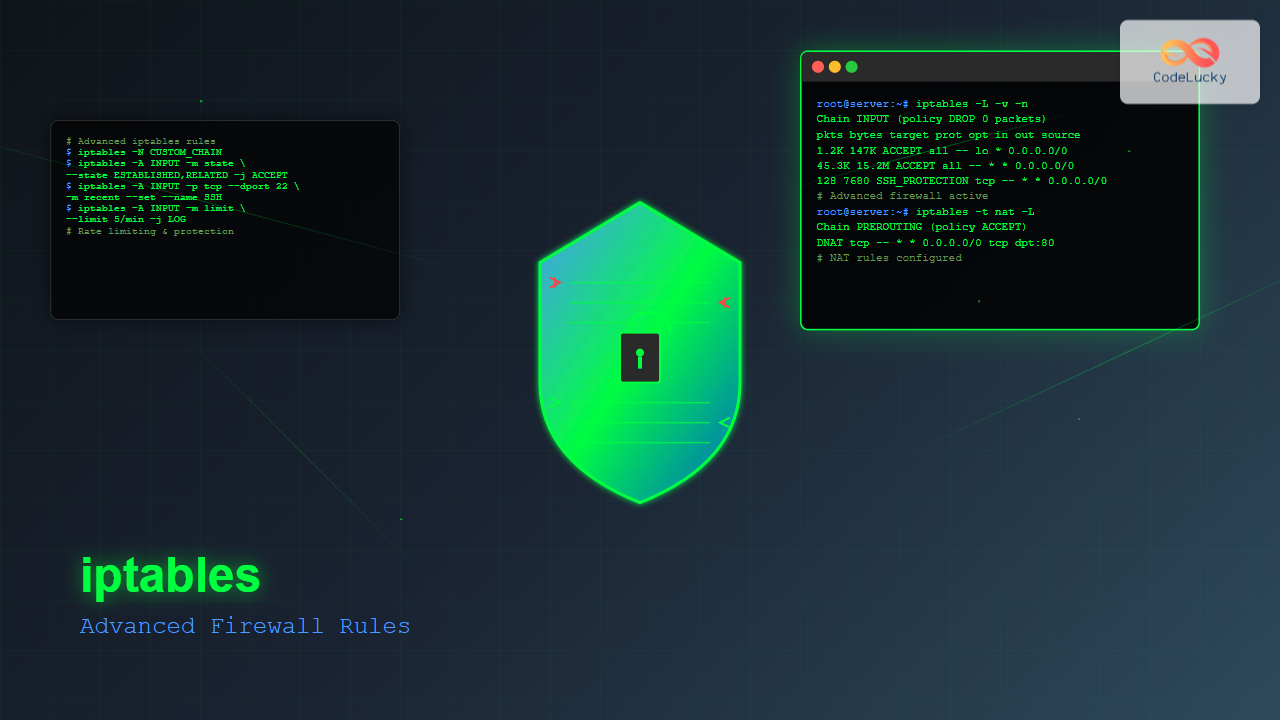
# Create custom chain for SSH protection
iptables -N SSH_PROTECTION
# Add rules to custom chain
iptables -A SSH_PROTECTION -m recent --set --name SSH
iptables -A SSH_PROTECTION -m recent --update --seconds 60 --hitcount 4 --name SSH -j DROP
iptables -A SSH_PROTECTION -j ACCEPT
# Jump to custom chain from INPUT
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j SSH_PROTECTIONComplex Matching Criteria
Connection State Tracking
Advanced connection tracking enables sophisticated traffic analysis:
# Allow established connections
iptables -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
# Block invalid packets
iptables -A INPUT -m state --state INVALID -j DROP
# Connection tracking with connlimit
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -m connlimit --connlimit-above 10 -j REJECTTime-Based Rules
Implement time-sensitive access controls:
# Allow SSH only during business hours
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -m time --timestart 09:00 --timestop 17:00 --weekdays Mon,Tue,Wed,Thu,Fri -j ACCEPT
# Block social media during work hours
iptables -A OUTPUT -d facebook.com,twitter.com -m time --timestart 09:00 --timestop 17:00 --weekdays Mon,Tue,Wed,Thu,Fri -j DROPRate Limiting and DoS Protection
Implement sophisticated rate limiting to prevent abuse:
# Limit incoming connections per IP
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -m limit --limit 5/min --limit-burst 10 -j ACCEPT
# Advanced rate limiting with hashlimit
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -m hashlimit --hashlimit-mode srcip --hashlimit 1/min --hashlimit-burst 3 --hashlimit-name ssh_limit -j ACCEPT
# SYN flood protection
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --syn -m limit --limit 1/s --limit-burst 3 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --syn -j DROPAdvanced NAT Configuration
Port Forwarding with Conditions
# Conditional port forwarding based on source
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -s 192.168.1.0/24 -p tcp --dport 8080 -j DNAT --to-destination 10.0.1.100:80
# Load balancing across multiple servers
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -m statistic --mode nth --every 3 --packet 0 -j DNAT --to-destination 10.0.1.100:80
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -m statistic --mode nth --every 2 --packet 0 -j DNAT --to-destination 10.0.1.101:80
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination 10.0.1.102:80Advanced SNAT Rules
# Source NAT with multiple external IPs
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.1.0/24 -m statistic --mode nth --every 2 --packet 0 -j SNAT --to-source 203.0.113.10
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.1.0/24 -j SNAT --to-source 203.0.113.11Packet Marking and Quality of Service
Use the mangle table for advanced traffic shaping:
# Mark packets for QoS
iptables -t mangle -A OUTPUT -p tcp --sport 22 -j MARK --set-mark 1
iptables -t mangle -A OUTPUT -p tcp --sport 80 -j MARK --set-mark 2
iptables -t mangle -A OUTPUT -p tcp --sport 443 -j MARK --set-mark 2
# DSCP marking for VoIP traffic
iptables -t mangle -A OUTPUT -p udp --dport 5060 -j DSCP --set-dscp 46Geographic IP Blocking
Block traffic from specific countries using GeoIP modules:
# Block traffic from specific countries (requires xtables-addons)
iptables -A INPUT -m geoip --src-cc CN,RU -j DROP
# Allow only specific countries for admin access
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -m geoip ! --src-cc US,CA,GB -j DROPAdvanced Logging and Monitoring
Implement comprehensive logging strategies:
# Custom log prefixes for different rule types
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -m state --state NEW -j LOG --log-prefix "SSH_ATTEMPT: " --log-level 4
# Rate-limited logging to prevent log flooding
iptables -A INPUT -j LOG --log-prefix "DROPPED: " --log-level 4 -m limit --limit 5/min --limit-burst 10
# NFLOG for advanced packet analysis
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j NFLOG --nflog-group 1 --nflog-prefix "HTTP_TRAFFIC"Security Hardening Rules
Anti-Spoofing Protection
# Block spoofed packets from local network ranges
iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -s 10.0.0.0/8 -j DROP
iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -s 172.16.0.0/12 -j DROP
iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -s 192.168.0.0/16 -j DROP
iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -s 127.0.0.0/8 -j DROPTCP Flag Validation
# Block invalid TCP flag combinations
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL NONE -j DROP
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL ALL -j DROP
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL FIN,URG,PSH -j DROP
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL SYN,RST,ACK,FIN,URG -j DROPApplication-Specific Rules
Web Server Protection
# Create web server protection chain
iptables -N WEB_PROTECTION
# Allow legitimate HTTP/HTTPS traffic
iptables -A WEB_PROTECTION -p tcp -m multiport --dports 80,443 -m state --state NEW -m limit --limit 10/min --limit-burst 20 -j ACCEPT
# Block common attack patterns
iptables -A WEB_PROTECTION -p tcp --dport 80 -m string --string "SELECT * FROM" --algo bm -j DROP
iptables -A WEB_PROTECTION -p tcp --dport 80 -m string --string "UNION SELECT" --algo bm -j DROP
# Apply web protection
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m multiport --dports 80,443 -j WEB_PROTECTIONDatabase Server Protection
# Restrict database access to application servers only
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 3306 -s 192.168.1.100 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 3306 -s 192.168.1.101 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 3306 -j DROP
# Connection limiting for database
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 3306 -m connlimit --connlimit-above 10 --connlimit-mask 32 -j REJECTPerformance Optimization
Optimize iptables performance for high-traffic environments:
# Use NOTRACK for high-volume traffic
iptables -t raw -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j NOTRACK
iptables -t raw -A OUTPUT -p tcp --sport 80 -j NOTRACK
# Early DROP rules for known bad traffic
iptables -I INPUT 1 -m recent --name BLACKLIST --rcheck --seconds 3600 -j DROP
# Efficient rule ordering (most specific first)
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -s 192.168.1.100 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j DROPRule Persistence and Management
Saving and Restoring Rules
# Save current rules
iptables-save > /etc/iptables/rules.v4
# Restore rules on boot (Ubuntu/Debian)
apt-get install iptables-persistent
# Manual restore
iptables-restore < /etc/iptables/rules.v4Rule Testing and Validation
# Test rules with specific timeout
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j DROP
# Set automatic removal after 5 minutes for testing
echo "iptables -D INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j DROP" | at now + 5 minutes
# Backup before making changes
iptables-save > /tmp/iptables-backup-$(date +%Y%m%d-%H%M%S)Troubleshooting Advanced Rules
Debug complex iptables configurations:
# Monitor packet flow through chains
iptables -L -v -n --line-numbers
# Real-time rule hit monitoring
watch -n 1 'iptables -L -v -n | grep -E "(Chain|pkts)"'
# Detailed connection tracking
cat /proc/net/nf_conntrack
# Test specific rule matching
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j LOG --log-prefix "TEST: "
tail -f /var/log/messages | grep "TEST:"Security Best Practices
- Default Deny Policy: Set default DROP policy for all chains
- Minimal Rules: Only allow necessary traffic
- Regular Auditing: Review rules periodically for relevance
- Logging Strategy: Log significant events without overwhelming systems
- Testing Environment: Test complex rules before production deployment
Complete Advanced Configuration Example
#!/bin/bash
# Advanced iptables configuration script
# Flush existing rules
iptables -F
iptables -X
iptables -t nat -F
iptables -t nat -X
iptables -t mangle -F
iptables -t mangle -X
# Set default policies
iptables -P INPUT DROP
iptables -P FORWARD DROP
iptables -P OUTPUT ACCEPT
# Allow loopback
iptables -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT
# Allow established connections
iptables -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
# Create custom chains
iptables -N SSH_BRUTE_FORCE
iptables -N WEB_ATTACKS
iptables -N SCAN_DETECT
# SSH brute force protection
iptables -A SSH_BRUTE_FORCE -m recent --set --name SSH
iptables -A SSH_BRUTE_FORCE -m recent --update --seconds 300 --hitcount 5 --name SSH -j LOG --log-prefix "SSH_BRUTE_FORCE: "
iptables -A SSH_BRUTE_FORCE -m recent --update --seconds 300 --hitcount 5 --name SSH -j DROP
iptables -A SSH_BRUTE_FORCE -j ACCEPT
# Web attack detection
iptables -A WEB_ATTACKS -p tcp --dport 80 -m string --string "admin" --algo bm -j LOG --log-prefix "WEB_ADMIN_ACCESS: "
iptables -A WEB_ATTACKS -p tcp --dport 80 -m string --string "../" --algo bm -j DROP
iptables -A WEB_ATTACKS -j ACCEPT
# Port scan detection
iptables -A SCAN_DETECT -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL SYN -m recent --set --name PORTSCAN
iptables -A SCAN_DETECT -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL SYN -m recent --update --seconds 60 --hitcount 10 --name PORTSCAN -j DROP
iptables -A SCAN_DETECT -j ACCEPT
# Apply protection chains
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j SSH_BRUTE_FORCE
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j WEB_ATTACKS
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -j SCAN_DETECT
# Service-specific rules
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -m limit --limit 100/min -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 443 -m limit --limit 100/min -j ACCEPT
# Save rules
iptables-save > /etc/iptables/rules.v4Advanced iptables configuration requires careful planning and testing. Start with basic rules and gradually add complexity while monitoring system performance and security effectiveness. Regular maintenance and updates ensure your firewall remains effective against evolving threats.
- Understanding iptables Architecture
- Advanced Chain Management
- Complex Matching Criteria
- Rate Limiting and DoS Protection
- Advanced NAT Configuration
- Packet Marking and Quality of Service
- Geographic IP Blocking
- Advanced Logging and Monitoring
- Security Hardening Rules
- Application-Specific Rules
- Performance Optimization
- Rule Persistence and Management
- Troubleshooting Advanced Rules
- Security Best Practices
- Complete Advanced Configuration Example