The iotop command is an essential Linux utility that provides real-time monitoring of disk I/O usage by processes and threads. Similar to how top monitors CPU usage, iotop displays which processes are causing the most disk activity on your system. This powerful tool is invaluable for system administrators and developers who need to identify I/O bottlenecks and optimize system performance.
What is iotop Command?
iotop is a Python-based utility that monitors I/O usage information provided by the Linux kernel and displays a table of current I/O usage by processes or threads on the system. It requires kernel 2.6.20 or later with the CONFIG_TASKSTATS and CONFIG_TASK_DELAY_ACCT options enabled.
Key Features of iotop:
- Real-time I/O monitoring
- Process and thread-level visibility
- Read/write statistics
- Total I/O bandwidth usage
- Interactive process management
- Customizable display options
Installing iotop on Different Linux Distributions
Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install iotopCentOS/RHEL/Fedora:
# For CentOS/RHEL 7/8
sudo yum install iotop
# For Fedora/CentOS Stream
sudo dnf install iotopArch Linux:
sudo pacman -S iotopopenSUSE:
sudo zypper install iotopBasic iotop Usage and Syntax
The basic syntax for iotop is:
iotop [OPTIONS]Running iotop with Default Settings:
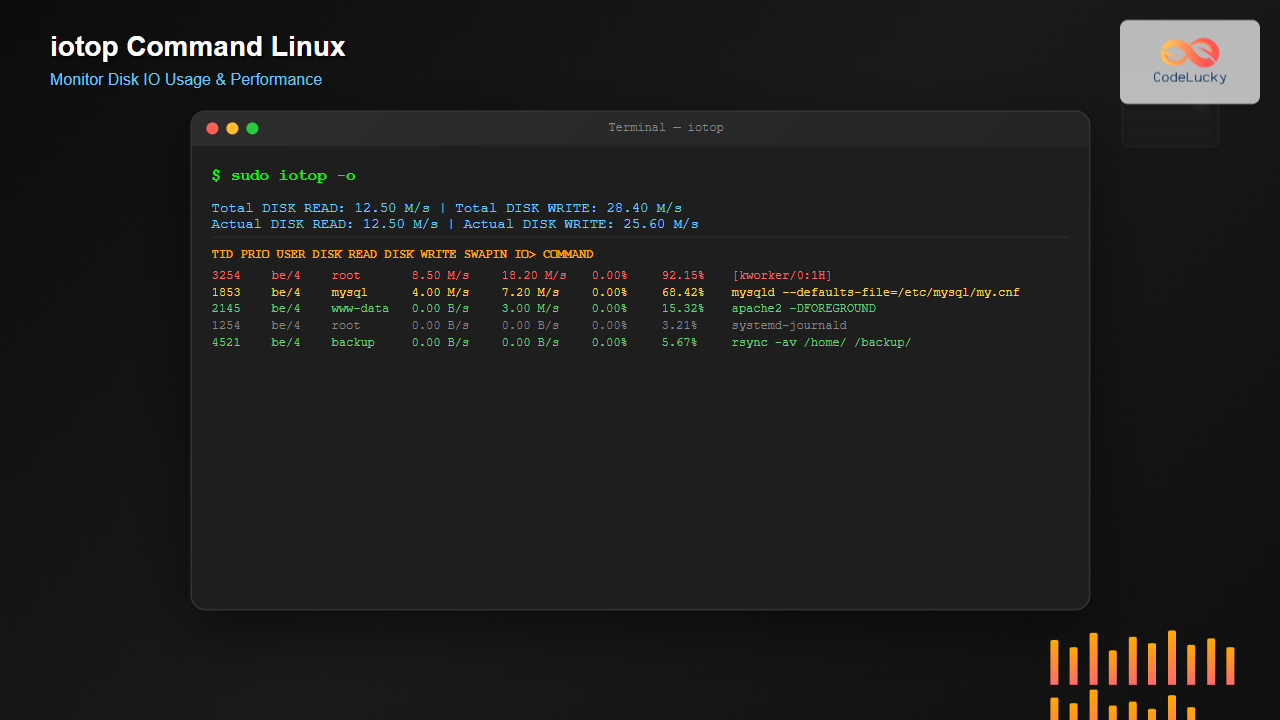
sudo iotopSample Output:
Total DISK READ : 2.50 M/s | Total DISK WRITE : 15.20 M/s
Actual DISK READ: 2.50 M/s | Actual DISK WRITE: 12.40 M/s
TID PRIO USER DISK READ DISK WRITE SWAPIN IO> COMMAND
3254 be/4 root 0.00 B/s 11.85 M/s 0.00 % 89.21 % [kworker/0:1H]
1853 be/4 mysql 2.50 M/s 3.35 M/s 0.00 % 45.32 % mysqld --defaults-file=/etc/mysql/my.cnf
2145 be/4 www-data 0.00 B/s 0.00 B/s 0.00 % 5.15 % apache2 -DFOREGROUND
1254 be/4 root 0.00 B/s 0.00 B/s 0.00 % 2.33 % systemd-journaldUnderstanding iotop Output
The iotop output consists of two main sections:
Header Section:
- Total DISK READ/WRITE: Total bandwidth for disk reads and writes
- Actual DISK READ/WRITE: Actual bandwidth to/from storage devices
Process Table Columns:
- TID: Thread ID
- PRIO: I/O priority (rt=real-time, be=best-effort, idle=idle)
- USER: User running the process
- DISK READ: Bandwidth of disk reads
- DISK WRITE: Bandwidth of disk writes
- SWAPIN: Percentage of time spent swapping in
- IO: Percentage of time spent in I/O
- COMMAND: Command name/line
Essential iotop Command Options
Display Only Active Processes (-o, –only):
sudo iotop -oThis option shows only processes or threads that are actively performing I/O operations.
Show Processes Instead of Threads (-P, –processes):
sudo iotop -PGroups threads by process, showing process-level I/O statistics instead of individual threads.
Show Accumulated I/O (-a, –accumulated):
sudo iotop -aDisplays accumulated I/O instead of bandwidth, showing total bytes read/written since iotop started.
Non-Interactive Mode (-b, –batch):
sudo iotop -b -n 3Runs in batch mode with 3 iterations, useful for scripts and logging.
Set Update Delay (-d, –delay):
sudo iotop -d 5Sets the delay between updates to 5 seconds (default is 1 second).
Advanced iotop Usage Examples
Monitor Specific User Activity:
sudo iotop -u mysqlShows I/O activity only for processes owned by the mysql user.
Monitor with Custom Delay and Process View:
sudo iotop -P -d 2 -oUpdates every 2 seconds, shows processes instead of threads, and displays only active processes.
Export I/O Data for Analysis:
sudo iotop -b -n 10 -d 5 -o > io_analysis.txtCaptures 10 snapshots every 5 seconds of active processes and saves to a file.
Monitor High I/O Processes:
sudo iotop -a -o -d 3Shows accumulated I/O for active processes with 3-second intervals.
Interactive iotop Commands
While iotop is running interactively, you can use these keyboard shortcuts:
| Key | Action |
|---|---|
r |
Reverse sort order |
o |
Toggle showing only active processes |
p |
Toggle between processes and threads |
a |
Toggle between bandwidth and accumulated I/O |
q |
Quit iotop |
i |
Change I/O priority of a process |
Practical Use Cases and Examples
1. Identifying Database Performance Issues:
sudo iotop -u mysql -P -aMonitor MySQL processes to identify high I/O operations that might indicate inefficient queries or missing indexes.
2. Web Server I/O Analysis:
sudo iotop -u www-data -o -d 1Monitor Apache/Nginx processes for high I/O activity that could indicate log writing issues or file serving bottlenecks.
3. System Backup Monitoring:
sudo iotop -P -d 5Monitor backup processes to ensure they’re not overwhelming the system’s I/O capacity.
4. Development Environment Optimization:
sudo iotop -u developer -a -oTrack I/O patterns during development to optimize application performance.
Troubleshooting Common iotop Issues
Permission Denied Error:
If you see “Permission denied” errors, ensure you’re running iotop as root or with sudo:
sudo iotopCONFIG_TASKSTATS Not Enabled:
If iotop fails to start, check if the required kernel options are enabled:
zcat /proc/config.gz | grep -E "(CONFIG_TASKSTATS|CONFIG_TASK_DELAY_ACCT)"High CPU Usage by iotop:
Reduce the update frequency to lower CPU usage:
sudo iotop -d 5 # Update every 5 seconds instead of 1Alternative I/O Monitoring Tools
iostat (from sysstat package):
iostat -x 1Provides device-level I/O statistics.
atop:
atop -d 1System and process monitor with I/O information.
pidstat:
pidstat -d 1Shows I/O statistics for individual processes.
Best Practices for Using iotop
- Start with basic monitoring: Use
sudo iotop -oto see only active processes - Combine with other tools: Use alongside
top,htop, andiostatfor comprehensive monitoring - Monitor during peak hours: Run iotop during high-traffic periods to identify bottlenecks
- Use batch mode for logging: Capture data for later analysis using the
-boption - Focus on accumulated I/O: Use
-aoption to understand total I/O impact over time - Regular monitoring: Make iotop part of your regular system monitoring routine
Security Considerations
Since iotop requires root privileges to access kernel I/O statistics, consider these security aspects:
- Only grant iotop access to trusted users
- Use sudo with specific iotop permissions instead of full root access
- Monitor iotop usage in multi-user environments
- Consider using restricted environments for iotop access
Conclusion
The iotop command is an indispensable tool for Linux system administrators and developers who need to monitor and optimize disk I/O performance. By understanding its features, options, and best practices, you can effectively identify I/O bottlenecks, optimize system performance, and maintain healthy server environments.
Whether you’re troubleshooting slow database queries, monitoring backup processes, or optimizing application performance, iotop provides the real-time visibility needed to make informed decisions about your system’s I/O usage. Regular use of iotop as part of your monitoring toolkit will help ensure optimal system performance and quick identification of potential issues.
Remember to combine iotop with other system monitoring tools for a comprehensive view of your system’s performance, and always run it with appropriate permissions to access the kernel’s I/O statistics effectively.
- What is iotop Command?
- Installing iotop on Different Linux Distributions
- Basic iotop Usage and Syntax
- Understanding iotop Output
- Essential iotop Command Options
- Advanced iotop Usage Examples
- Interactive iotop Commands
- Practical Use Cases and Examples
- Troubleshooting Common iotop Issues
- Alternative I/O Monitoring Tools
- Best Practices for Using iotop
- Security Considerations
- Conclusion