HTML TextArea disabled Property: Controlling Input in Textareas
The HTML <textarea> element is a fundamental component for collecting multi-line text input in web forms. The disabled property allows you to control whether a textarea is interactive or not. When a textarea is disabled, users cannot input or modify its content, and it is typically rendered in a way that visually indicates its disabled state. This article will explore the disabled property of the HTML <textarea> element, including its syntax, usage, and practical examples.
What is the disabled Property?
The disabled property is a boolean attribute that, when present on a <textarea> element, prevents the user from interacting with the textarea. This means the user cannot enter text, select text, or focus on the textarea. The disabled property is useful in scenarios where you want to prevent users from modifying a textarea based on certain conditions or form states.
Syntax
The disabled property can be set directly in the HTML or manipulated via JavaScript.
HTML
<textarea disabled>This textarea is disabled.</textarea>
JavaScript
const textarea = document.getElementById("myTextarea");
textarea.disabled = true; // To disable the textarea
textarea.disabled = false; // To enable the textarea
Attributes
The disabled property does not have any specific attributes beyond its presence or absence on the <textarea> tag.
| Attribute | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| `disabled` | `disabled` (or its absence) | When present, it disables the textarea, preventing user interaction. When absent, the textarea is enabled and interactive. |
Examples
Let’s explore several examples of how to use the disabled property in different scenarios.
Basic Usage: Disabling a Textarea
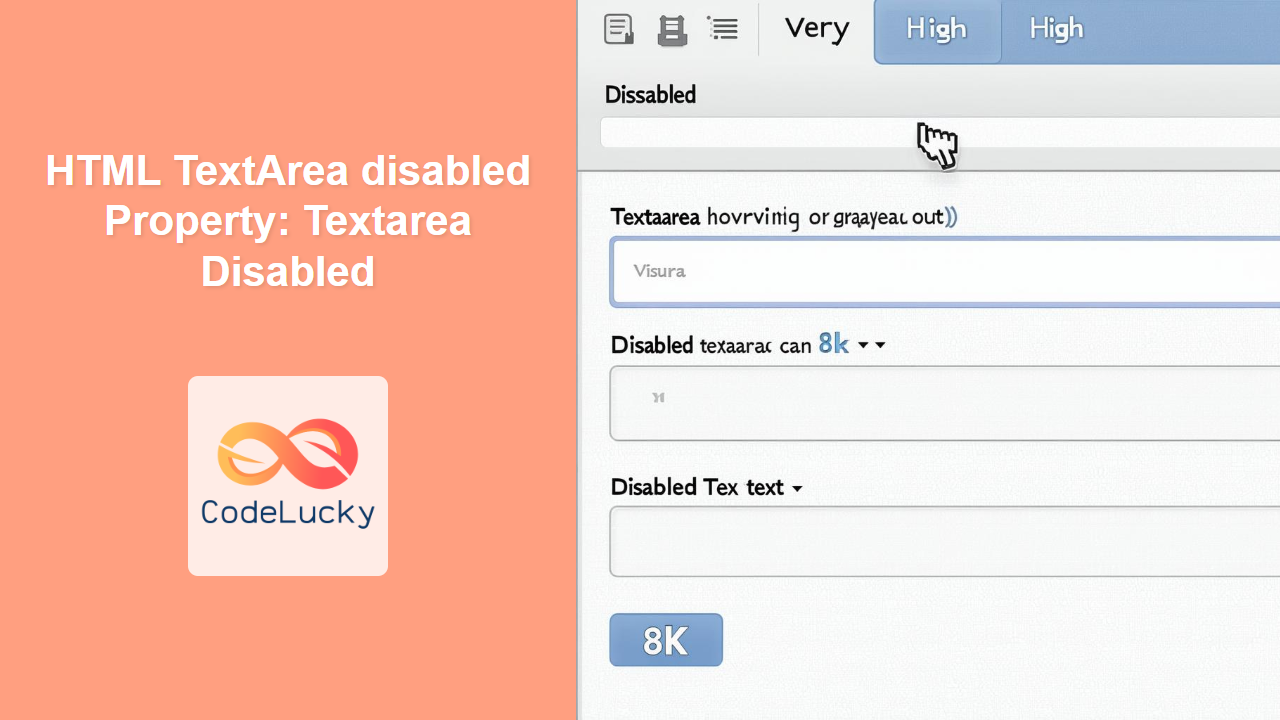
In this example, we’ll disable a textarea by default using the disabled attribute in HTML.
<textarea id="disabledTextarea" disabled>
This textarea is disabled and cannot be edited.
</textarea>
The textarea is rendered in a disabled state, typically grayed out, and users cannot interact with it.
Dynamically Disabling a Textarea with JavaScript
Here, we’ll use JavaScript to toggle the disabled state of a textarea based on a checkbox.
<label>
<input type="checkbox" id="enableTextarea" /> Enable Textarea
</label>
<textarea id="dynamicTextarea" disabled>
This textarea is initially disabled. Check the box to enable it.
</textarea>
<script>
const enableCheckbox = document.getElementById("enableTextarea");
const dynamicTextarea = document.getElementById("dynamicTextarea");
enableCheckbox.addEventListener("change", function () {
dynamicTextarea.disabled = !this.checked;
});
</script>
In this example, the textarea is initially disabled. When the checkbox is checked, the JavaScript code enables the textarea, allowing users to interact with it.
Disabling a Textarea Based on Form Validation
In a real-world scenario, you might want to disable a textarea until certain form fields are validated.
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" />
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" />
<textarea id="conditionalTextarea" disabled>
This textarea will be enabled when name and email are filled correctly.
</textarea>
<script>
const nameInput = document.getElementById("name");
const emailInput = document.getElementById("email");
const conditionalTextarea = document.getElementById("conditionalTextarea");
function validateForm() {
const nameValue = nameInput.value.trim();
const emailValue = emailInput.value.trim();
if (nameValue !== "" && emailValue.includes("@")) {
conditionalTextarea.disabled = false;
} else {
conditionalTextarea.disabled = true;
}
}
nameInput.addEventListener("input", validateForm);
emailInput.addEventListener("input", validateForm);
</script>
In this example, the textarea is initially disabled. It becomes enabled only when the “Name” field is not empty and the “Email” field contains an “@” symbol, indicating a valid email format.
Disabling a Textarea During Asynchronous Operations
When performing asynchronous operations, such as submitting a form, you might want to disable the textarea to prevent multiple submissions or modifications during the process.
<textarea id="asyncTextarea">
This textarea will be disabled during submission.
</textarea>
<button id="submitButton">Submit</button>
<script>
const asyncTextarea = document.getElementById("asyncTextarea");
const submitButton = document.getElementById("submitButton");
submitButton.addEventListener("click", function () {
asyncTextarea.disabled = true;
submitButton.disabled = true;
// Simulate asynchronous submission
setTimeout(() => {
asyncTextarea.disabled = false;
submitButton.disabled = false;
alert("Submission complete!");
}, 2000);
});
</script>
In this example, the textarea and submit button are disabled when the “Submit” button is clicked. After a simulated 2-second submission, the textarea and button are re-enabled.
Accessibility Considerations
- Visual Indication: Ensure that the disabled state is visually clear to users. Use CSS to style the textarea appropriately (e.g., grayed out with reduced opacity).
- Screen Readers: Screen readers announce disabled textareas as non-interactive elements. Provide alternative instructions or explanations if necessary.
- Keyboard Navigation: Disabled textareas should not be focusable via keyboard navigation (Tab key).
Tips and Best Practices
- Use CSS for Styling: Style disabled textareas using CSS to provide a consistent visual indication of their state.
- Conditional Logic: Implement robust conditional logic to determine when a textarea should be disabled or enabled based on form state or user interactions.
- Form Validation: Integrate the
disabledproperty with form validation to prevent submission of incomplete or invalid data. - Accessibility: Always consider accessibility when using the
disabledproperty to ensure that disabled textareas are clearly identified and do not hinder user experience.
Conclusion
The disabled property of the HTML <textarea> element is a versatile tool for controlling user input and enhancing the interactivity of web forms. By dynamically enabling and disabling textareas based on various conditions, you can create more user-friendly and robust form experiences. Always remember to consider accessibility and provide clear visual cues to users regarding the state of textareas.