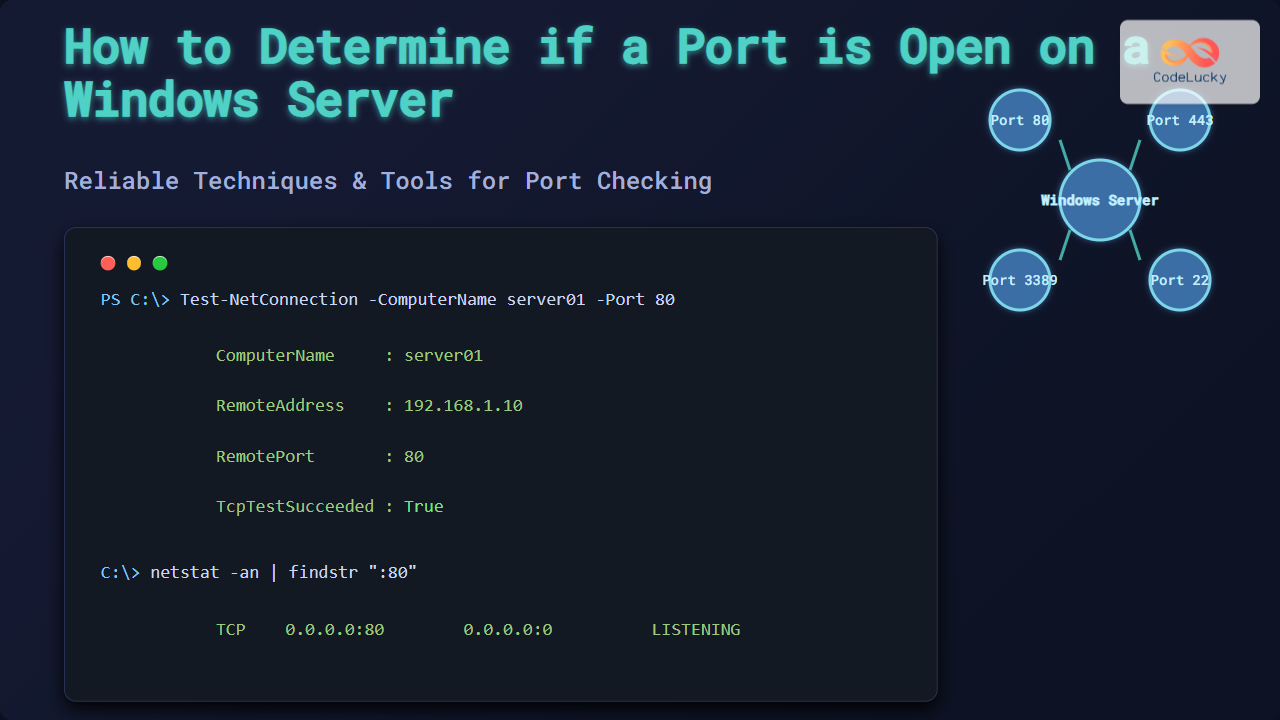
Determining if a port is open on a Windows Server is a crucial skill for system administrators and developers to troubleshoot connectivity issues, ensure firewall configurations are correct, and maintain network security. This guide provides a comprehensive set of methods and tools to check open ports on a Windows Server with detailed examples, command outputs, and visual diagrams to simplify understanding.
Understanding Ports and Their Importance on Windows Server
A port is a logical communication endpoint used by software applications and services to exchange data over a network. Each TCP or UDP port is identified by a number between 0 and 65535. Knowing whether a port is open (listening and accessible) is essential for ensuring network services function properly.
Common Scenarios Requiring Port Status Checks
- Verifying if a web server (e.g., IIS or Apache) is listening on port 80 or 443
- Checking if SQL Server operates on port 1433 and is accessible
- Diagnosing firewall issues blocking network traffic
- Monitoring security by ensuring unnecessary ports are closed
Methods to Determine if a Port is Open on Windows Server
1. Using PowerShell
PowerShell provides powerful cmdlets to check open ports and network connections.
Example 1: Check Listening Ports Using Get-NetTCPConnection
Get-NetTCPConnection -State Listen | Where-Object { $_.LocalPort -eq 80 }This command filters and shows if port 80 is currently listening on the server.
Sample Output:
LocalAddress LocalPort RemoteAddress RemotePort State AppliedSetting
------------ --------- ------------- ---------- ----- --------------
0.0.0.0 80 0.0.0.0 0 Listen
Example 2: Test if TCP Port is Open on a Remote Host
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName www.example.com -Port 80PowerShell attempts a TCP connection to the specified remote server and port and reports the connectivity status.
Sample Output:
ComputerName : www.example.com
RemoteAddress : 93.184.216.34
RemotePort : 80
InterfaceAlias : Ethernet
SourceAddress : 192.168.1.50
TcpTestSucceeded : True
2. Using Command Prompt (netstat & telnet)
Traditional tools like netstat and telnet are still valuable for port checking on Windows environments.
Check Listening Ports with netstat
netstat -an | findstr :80This command lists any TCP or UDP connections or listeners on port 80.
Sample Output:
TCP 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
Testing Remote Port with telnet
telnet allows you to see if a remote port is accepting connections.
telnet www.example.com 80If the screen goes blank or you see a cursor, the port is open. If you get a connection error, it is closed or blocked.
Note: Telnet client feature may need to be installed via Windows Features.
3. Using Portqry Command-Line Tool
Portqry is a Microsoft tool specialized in port querying with detailed output covering TCP/UDP, useful for firewall and service diagnostics.
Basic Usage:
portqry -n www.example.com -p tcp -e 80Checks TCP port 80 on the remote host and reports one of the following: Listening, Not Listening, or Filtered.
4. Using Windows Firewall with Advanced Security
The built-in Windows Firewall provides logs and rule settings that can hint at port accessibility.
Steps:
- Open Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security
- Check Inbound Rules for enabled rules allowing traffic on the port
- Enable logging for dropped packets to diagnose blocked ports
5. Using Third-Party Tools (Optional)
GUI tools like TCPView, CurrPorts, or network scanners (Nmap) offer visualization and advanced filtering.
Summary Table of Port Checking Commands
| Tool/Command | Purpose | Example | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| PowerShell – Get-NetTCPConnection | List listening ports on local machine | Get-NetTCPConnection -State Listen |
Built-in, detailed info |
| PowerShell – Test-NetConnection | Test remote port connectivity | Test-NetConnection -ComputerName example.com -Port 80 |
Simple remote port test |
| netstat | Show network connections and listening ports | netstat -an | findstr :80 |
Available in CMD |
| telnet | Test remote port open status | telnet example.com 80 |
Needs Client feature enabled |
| Portqry | Detailed TCP/UDP port query tool | portqry -n example.com -p tcp -e 80 |
Free, powerful |
Interactive PowerShell Example
Below is a PowerShell script snippet to check if multiple ports are open on a remote server and print the results. Copy and paste in PowerShell to run:
$server = "www.example.com"
$ports = @(80, 443, 3389)
foreach ($port in $ports) {
$result = Test-NetConnection -ComputerName $server -Port $port
if ($result.TcpTestSucceeded) {
Write-Host "Port $port on $server is OPEN" -ForegroundColor Green
} else {
Write-Host "Port $port on $server is CLOSED or BLOCKED" -ForegroundColor Red
}
}
Best Practices for Port Management on Windows Server
- Regularly audit open ports and remove unnecessary ones to enhance security.
- Keep firewall rules tightly scoped to allow only essential traffic.
- Use logging tools to monitor rejected connections for troubleshooting.
- Document port usage for installed applications for quick reference.
Conclusion
Knowing how to determine whether a port is open on a Windows Server is fundamental for effective network and system administration. Using tools like PowerShell, netstat, telnet, and Portqry empowers administrators to confidently verify port status, troubleshoot connectivity, and secure their servers. The illustrated commands, outputs, and diagrams in this guide offer practical insights to master port checking in any Windows Server environment.