Creating files directly from the Linux terminal is a fundamental skill for developers, system administrators, and Linux enthusiasts. This comprehensive guide will walk you through various methods to create files in Linux using command-line tools, along with clear examples and visual outputs to understand file creation better.
Introduction to File Creation in Linux Terminal
Unlike graphical interfaces, Linux terminal relies on commands to create and manage files. Understanding these commands saves time, increases productivity, and helps in scripting and automation. This guide covers the most common commands used to create files, their options, and practical usage.
Common Commands to Create Files in Linux
Here are some popular commands to create files using the Linux terminal:
touchechocatprintfnanoor text editors (briefly covered)
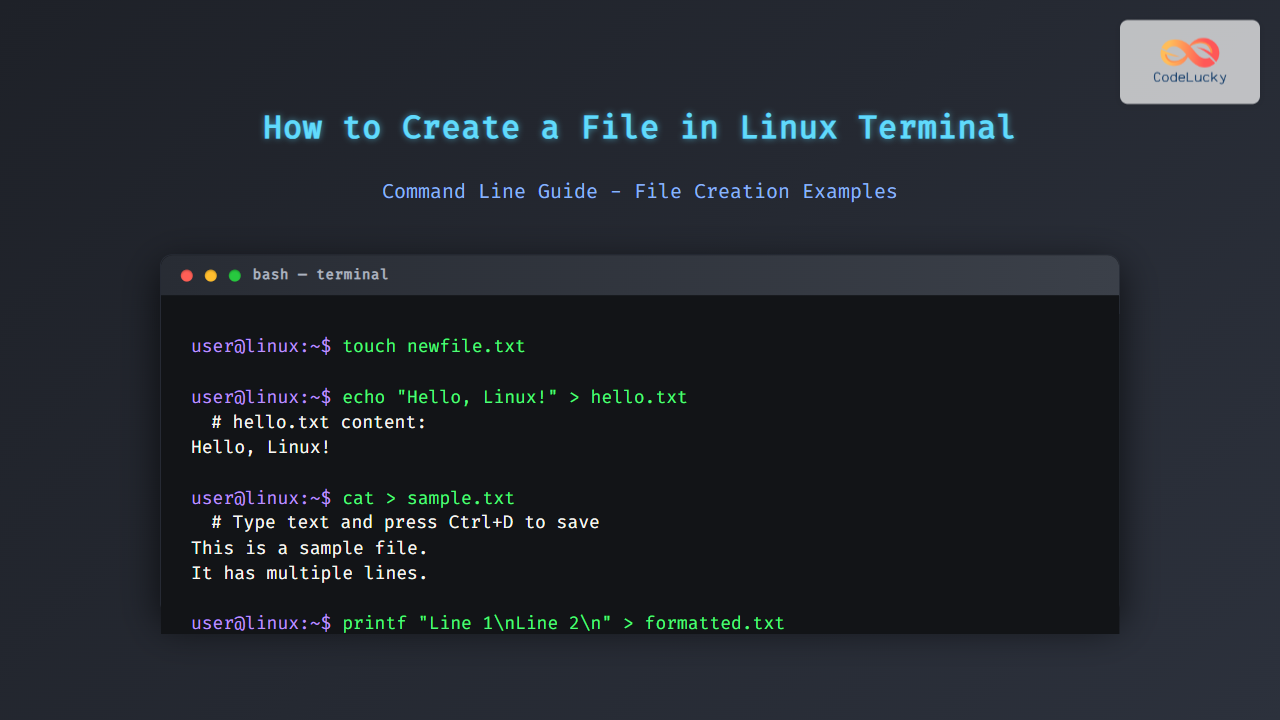
1. Creating an Empty File Using touch Command
The touch command is the simplest way to create an empty file or update the timestamp of an existing file.
$ touch newfile.txt
$ ls -l newfile.txt
-rw-rw-r-- 1 user user 0 Aug 30 19:43 newfile.txt
Explanation: This creates newfile.txt with zero bytes if it doesn’t exist already.
2. Creating a File with Text Using echo Command
The echo command prints text and can redirect that text into a new file:
$ echo "Hello, Linux!" > hello.txt
$ cat hello.txt
Hello, Linux!
Here, hello.txt is created with the text Hello, Linux!.
3. Using cat to Create a File and Add Content
cat can be used interactively to create files by typing content manually followed by Ctrl+D to save:
$ cat > sample.txt
This is a sample file.
It has multiple lines.
Press Ctrl+D to save.
After pressing Ctrl+D, the file is saved with the entered content.
4. Creating a File with Formatted Content Using printf
printf gives more control for formatted text creation:
$ printf "Line 1\nLine 2\n" > formatted.txt
$ cat formatted.txt
Line 1
Line 2
5. Creating and Editing Files Using Text Editors
You can create and edit a file by opening it in terminal-based editors such as nano, vi, or vim. For example, to create or edit notes.txt:
$ nano notes.txt
Inside the editor, type your content and save by pressing Ctrl+O then Enter, and exit with Ctrl+X.
Comparing File Creation Commands
| Command | Use Case | Creates Empty File? | Adds Content? | Interactive? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
touch |
Creates empty file or updates timestamps | Yes | No | No |
echo |
Creates file with single line | No (empty is overwritten) | Yes | No |
cat |
Interactive multi-line input | No | Yes | Yes |
printf |
Formatted content creation | No | Yes | No |
| Text Editors (nano, vim) | Editing and creating files | Depends on save | Yes | Yes |
Important Additional Tips
- Appending content: Use
>>instead of>to append text rather than overwrite.
$ echo "Appended text" >> hello.txtchmod to change them if needed.ls -l filename to check file existence and details.Summary Flowchart of Creating a File in Linux Terminal
Conclusion
Creating files in Linux from the terminal window can be accomplished with several simple commands, each suited for different scenarios—from empty files to files with content entered interactively or programmatically. Mastery of these commands equips users to handle Linux file operations efficiently, whether for scripting, development, or daily tasks.
Try out the commands yourself to explore which method fits your workflow best.