The hexdump command is a powerful Linux utility that displays the contents of files in hexadecimal format, making it an essential tool for developers, system administrators, and security professionals. This comprehensive guide will teach you everything you need to know about using hexdump effectively.
What is the hexdump Command?
The hexdump command is a standard Unix/Linux utility that reads files and displays their contents in various formats, primarily hexadecimal. It’s particularly useful for examining binary files, debugging data corruption issues, and understanding file structures that aren’t human-readable in their raw form.
Basic Syntax and Usage
The basic syntax of the hexdump command is:
hexdump [options] [file...]If no file is specified, hexdump reads from standard input. Let’s start with a simple example:
$ echo "Hello World" | hexdump
0000000 6548 6c6c 206f 6f57 6c72 0a64
000000cThis output shows the hexadecimal representation of “Hello World” with addresses on the left and hex values on the right.
Essential hexdump Options
-C (Canonical Format)
The -C option displays output in canonical format, showing both hex and ASCII representations:
$ echo "Hello World" | hexdump -C
00000000 48 65 6c 6c 6f 20 57 6f 72 6c 64 0a |Hello World.|
0000000cThis format is most readable, showing:
- Offset address (00000000)
- Hex bytes (48 65 6c 6c…)
- ASCII representation (Hello World.)
-x (Two-byte Hexadecimal)
The -x option displays two-byte hex output:
$ echo "Hello World" | hexdump -x
0000000 6548 6c6c 206f 6f57 6c72 0a64
000000c-d (Decimal Format)
To display output in decimal format:
$ echo "Hello World" | hexdump -d
0000000 25928 27756 8303 28503 27762 2660
000000c-o (Octal Format)
For octal representation:
$ echo "Hello World" | hexdump -o
0000000 062510 066154 020157 067527 066562 005144
000000cAdvanced Options and Formatting
-n (Limit Bytes)
The -n option limits the number of bytes to display:
$ echo "Hello World" | hexdump -C -n 5
00000000 48 65 6c 6c 6f |Hello|
00000005-s (Skip Bytes)
Skip a specified number of bytes from the beginning:
$ echo "Hello World" | hexdump -C -s 6
00000006 57 6f 72 6c 64 0a |World.|
0000000c-v (Verbose)
The -v option displays all data without suppressing duplicate lines:
$ printf "AAAAAAAA" | hexdump
0000000 4141 4141 4141 4141
0000008
$ printf "AAAAAAAA" | hexdump -v
0000000 4141 4141 4141 4141
0000008Custom Format Strings
hexdump supports custom format strings using the -e option. The format string syntax is:
-e 'format_string'Format String Examples
Display each byte as a two-digit hex number:
$ echo "ABC" | hexdump -e '1/1 "%02x " "\n"'
41 42 43 0aDisplay with custom formatting:
$ echo "Hello" | hexdump -e '"%08_ax: " 8/1 "%02x " " |" 8/1 "%_p" "|\n"'
00000000: 48 65 6c 6c 6f 0a |Hello.|Practical Examples and Use Cases
Examining Binary Files
Create a binary file and examine it:
$ printf "\x00\x01\x02\x03\xff\xfe\xfd" > binary_file
$ hexdump -C binary_file
00000000 00 01 02 03 ff fe fd |.......|
00000007Analyzing ELF Headers
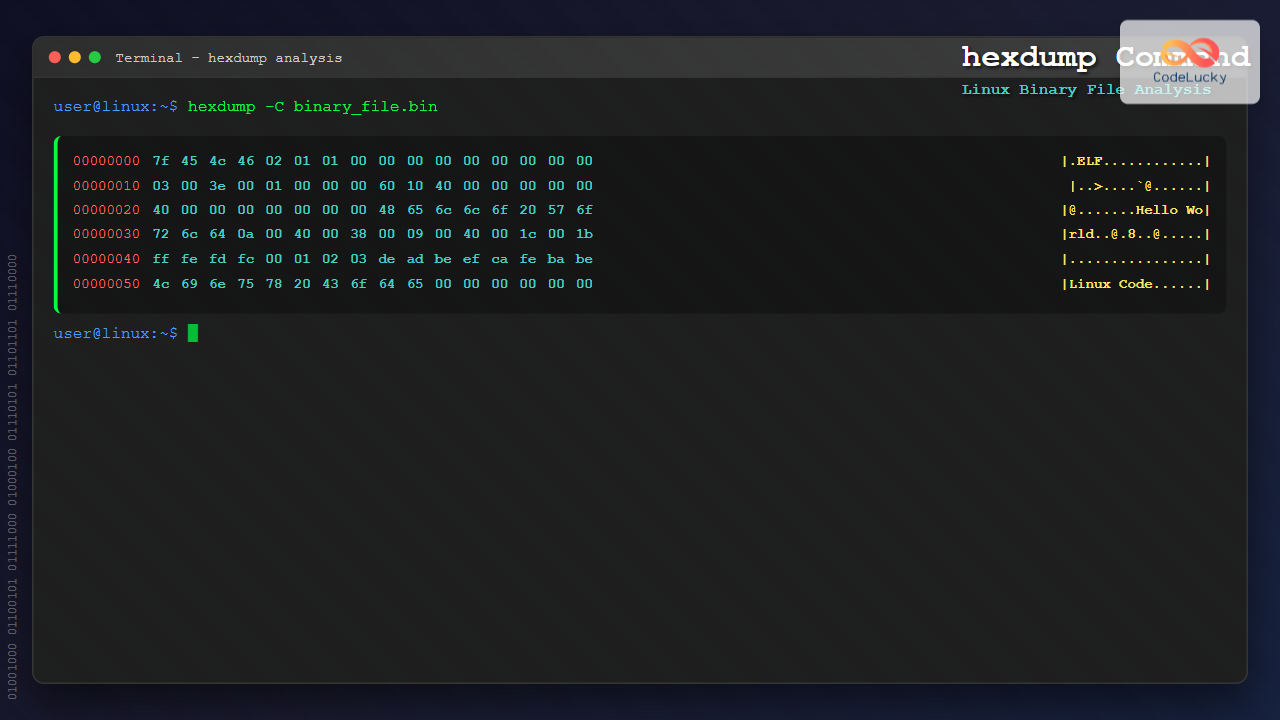
Examine the header of an executable:
$ hexdump -C -n 64 /bin/ls | head -5
00000000 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |.ELF............|
00000010 03 00 3e 00 01 00 00 00 30 6a 00 00 00 00 00 00 |..>.....0j......|
00000020 40 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 e8 f5 01 00 00 00 00 00 |@...............|
00000030 00 00 00 00 40 00 38 00 0d 00 40 00 1f 00 1e 00 |[email protected]...@.....|Debugging Network Packets
When working with network data or packet captures:
$ printf "\x45\x00\x00\x3c\x1c\x46\x40\x00\x40\x06" > packet.bin
$ hexdump -C packet.bin
00000000 45 00 00 3c 1c 46 40 00 40 06 |E..<.F@.@.|
0000000aComparing hexdump with Related Commands
hexdump vs od (Octal Dump)
Both commands serve similar purposes, but od is more traditional:
$ echo "Hello" | hexdump -C
00000000 48 65 6c 6c 6f 0a |Hello.|
00000006
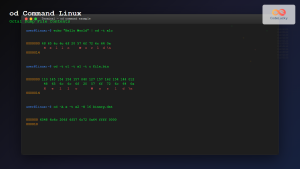
$ echo "Hello" | od -t x1z
0000000 48 65 6c 6c 6f 0a >Hello.<
0000006hexdump vs xxd
xxd is another popular hex viewer that comes with vim:
$ echo "Hello" | xxd
00000000: 4865 6c6c 6f0a Hello.Advanced Tips and Tricks
Creating Colorized Output
While hexdump doesn’t have built-in color support, you can pipe it through other tools:
$ echo "Hello World" | hexdump -C | grep --color=always -E '[0-9a-f]{2}'Reverse Engineering with hexdump
For reverse engineering, combine hexdump with other tools:
$ hexdump -C suspicious_file | grep -i "password\|key\|secret"Finding File Type Signatures
Check file magic numbers:
$ hexdump -C -n 16 image.jpg
00000000 ff d8 ff e0 00 10 4a 46 49 46 00 01 01 01 00 48 |......JFIF.....H|Troubleshooting Common Issues
Large File Handling
For large files, use the -n option to limit output:
$ hexdump -C -n 1024 large_file.bin | head -20Binary vs Text Files
Remember that hexdump treats all files as binary. For text files, you might see unexpected characters:
$ printf "Line1\nLine2\n" | hexdump -C
00000000 4c 69 6e 65 31 0a 4c 69 6e 65 32 0a |Line1.Line2.|
0000000cPerformance Considerations
For better performance with large files:
- Use
-nto limit bytes read - Use
-sto skip unnecessary data - Consider using
ddto extract specific portions first
$ dd if=large_file bs=1024 count=1 2>/dev/null | hexdump -CSecurity and Forensics Applications
hexdump is valuable for security analysis:
Detecting Hidden Data
$ hexdump -C document.pdf | tail -20 # Check end of file
$ hexdump -C image.jpg | grep -i "password\|user" # Search for stringsMalware Analysis
Examine suspicious executables:
$ hexdump -C -n 512 suspicious_binary | grep -E "(call|jmp|int)"Conclusion
The hexdump command is an indispensable tool for anyone working with binary data, debugging applications, or performing security analysis. Its flexibility in output formats and ability to handle any file type makes it perfect for low-level file examination. Whether you’re debugging network protocols, analyzing file formats, or investigating security incidents, mastering hexdump will significantly enhance your troubleshooting capabilities.
Practice with different file types and experiment with various options to become proficient with this powerful utility. Remember that hexdump works best when combined with other Linux tools like grep, awk, and sed for more advanced data analysis tasks.
- What is the hexdump Command?
- Basic Syntax and Usage
- Essential hexdump Options
- Advanced Options and Formatting
- Custom Format Strings
- Practical Examples and Use Cases
- Comparing hexdump with Related Commands
- Advanced Tips and Tricks
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Performance Considerations
- Security and Forensics Applications
- Conclusion