Understanding finance starts with learning the language behind it. Whether you’re budgeting, investing, or planning your future, financial literacy is your first step toward smarter money decisions. This guide by CodeLucky.com explains the key financial terms every beginner must know—with examples, easy definitions, and visual diagrams—to help you gain confidence in handling money, savings, and investments.
Why Understanding Financial Terms Matters
Think of financial terms as the ABCs of money management. Without them, reading a bank statement or investment plan feels like decoding a foreign language. Knowing these basics helps you:
- Make better investment and savings decisions.
- Understand how loans, interest, and budgeting work.
- Communicate confidently with bankers, investors, and financial planners.
1. Income
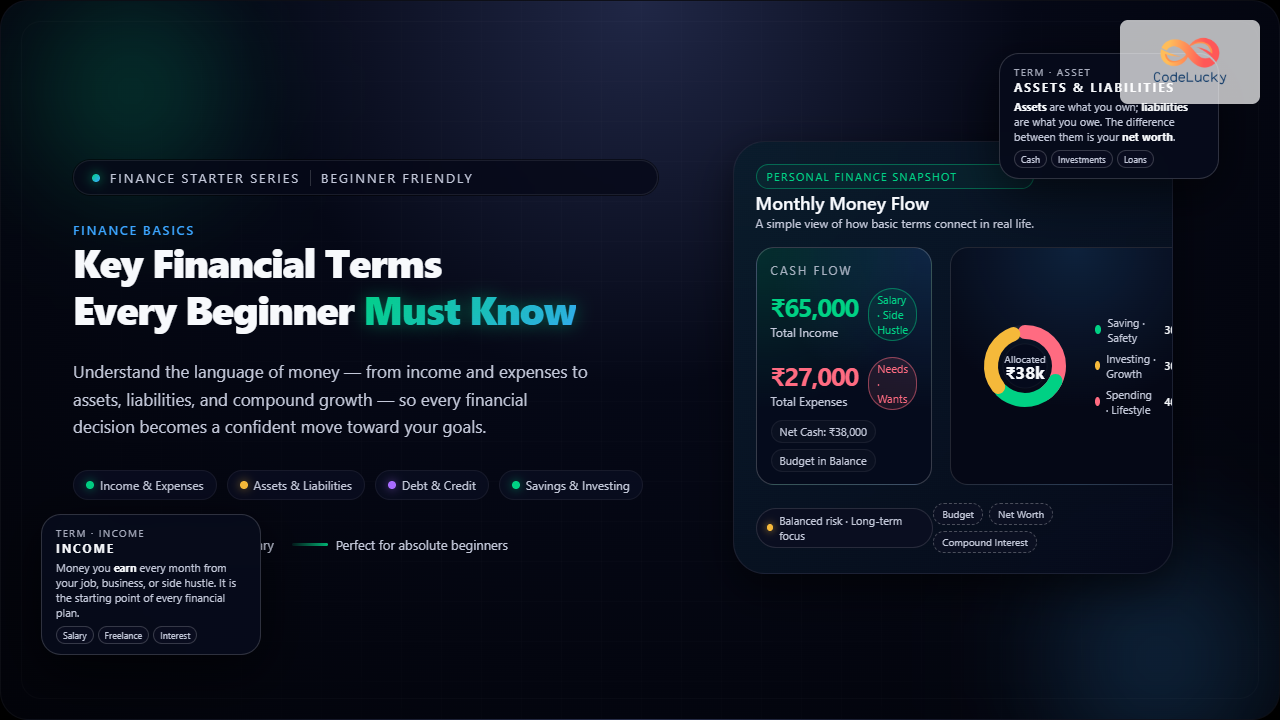
Income is the total money you earn through salary, business, investments, or any other sources. It’s your financial inflow.
Example: If you earn ₹60,000 from your job and ₹5,000 from freelance work, your monthly income is ₹65,000.
2. Expenses
Expenses are what you spend money on—like rent, groceries, and travel. They’re your financial outflows. Understanding them helps you track where your money goes.
Example: Monthly rent ₹15,000 + food ₹8,000 + travel ₹4,000 = Total expenses ₹27,000.
Tip: Always ensure your expenses are less than your income to maintain financial balance.
3. Budget
A budget is a plan that organizes your income and expenses for a specific period, usually a month. It helps control spending and promotes saving.
Example Interactive Budget Breakdown:
4. Assets and Liabilities
Assets are things you own that have value — like cash, property, or investments. Liabilities are things you owe, like loans or credit card balances.
Your net worth = Assets – Liabilities.
Example: If you own assets worth ₹8,00,000 and owe liabilities of ₹3,00,000, your net worth is ₹5,00,000.
5. Interest
Interest is the cost of borrowing money (if you’re taking a loan) or the reward for saving (if you’re investing).
- Simple Interest: Calculated only on the principal amount.
- Compound Interest: Calculated on both principal and previously earned interest.
Example: ₹10,000 invested at 10% annual simple interest gives ₹1,000 as interest per year. Under compound interest, earnings grow faster year after year.
6. Savings and Investments
Savings refer to money set aside for short-term goals, often kept in low-risk accounts. Investments involve putting money into assets with potential for higher returns, such as stocks or mutual funds, usually for long-term goals.
Example:
- Saving: ₹5,000 in a bank account for upcoming bills.
- Investment: ₹10,000 in mutual funds for future growth.
7. Inflation
Inflation means the general increase in prices of goods and services over time, which reduces the purchasing power of money.
Example: If coffee costs ₹100 today and ₹105 next year, inflation is 5%. You’ll need more money to buy the same item in the future.
Pro tip: Invest in instruments like equity or real estate that can beat inflation over time.
8. Credit Score
Your credit score is a three-digit number representing your creditworthiness based on your debt repayment history. It affects your ability to get loans and credit cards easily.
Example: A score above 750 is excellent, often resulting in lower interest rates on loans.
9. Diversification
Diversification is an investment strategy where you spread your money across different assets to reduce risk. “Don’t put all your eggs in one basket.”
Example: Instead of investing ₹50,000 entirely in one stock, divide it equally among stocks, bonds, and gold.
10. Return on Investment (ROI)
ROI measures the gain or loss generated on an investment relative to its cost. It helps evaluate how profitable your investments are.
Formula: ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) × 100
Example: If you invest ₹20,000 and earn ₹25,000, your ROI = (₹5,000 / ₹20,000) × 100 = 25%.
Putting It All Together
Finance might look complicated, but once you know these key terms, you’ll find it far easier to make sense of your income, expenses, and future planning. Whether you’re just beginning or managing your first investment, being financially literate empowers you to make informed, confident decisions.
Next Steps:
- Start tracking your monthly income and expenses.
- Build a simple emergency fund covering 3-6 months of expenses.
- Explore investment tools like mutual funds or SIPs to grow wealth over time.
Keep learning with CodeLucky.com — your reliable source for easy, engaging financial education built for beginners and future wealth builders.