The Exponential Search Algorithm is an advanced searching technique that combines the efficiency of range expansion with the power of Binary Search. It is especially effective for searching in sorted arrays, making it a useful algorithm for large datasets where Binary Search alone would require knowing the bounds beforehand. In this article, we will cover Exponential Search in detail with step-by-step explanations, diagrams, and Python examples.
What is Exponential Search?
Exponential Search is a search algorithm designed for sorted arrays. It works in two phases:
- Exponential Range Finding — Quickly find the range where the element could exist by doubling the search index at each step.
- Binary Search within the Range — Once the possible range is identified, perform a Binary Search inside it.
This combination makes the algorithm particularly efficient when the element is closer to the beginning of the array, as it reduces search space dramatically.
Time Complexity of Exponential Search
- Best Case: O(1), when the element is at the first position.
- Worst Case: O(log i) + O(log i) = O(log i), where
iis the index of the element being searched. - Space Complexity: O(1), iterative approach requires no extra space.
Working of Exponential Search (Step by Step)
Let’s break down how the algorithm works:
- Start from index
1(since index 0 is checked separately). - Keep doubling the index (
bound *= 2) until the array value at that index is greater than or equal to the target OR the end of the array is reached. - Perform Binary Search between the previous bound and current bound.
Python Implementation of Exponential Search
def binary_search(arr, left, right, target):
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if arr[mid] == target:
return mid
elif arr[mid] < target:
left = mid + 1
else:
right = mid - 1
return -1
def exponential_search(arr, target):
if arr[0] == target:
return 0
bound = 1
while bound < len(arr) and arr[bound] <= target:
bound *= 2
left = bound // 2
right = min(bound, len(arr)-1)
return binary_search(arr, left, right, target)
# Example usage
arr = [2, 3, 4, 10, 15, 20, 35, 50, 65, 80, 100]
target = 35
index = exponential_search(arr, target)
print("Array:", arr)
print("Searching for:", target)
print("Found at index:", index)
Example Walkthrough
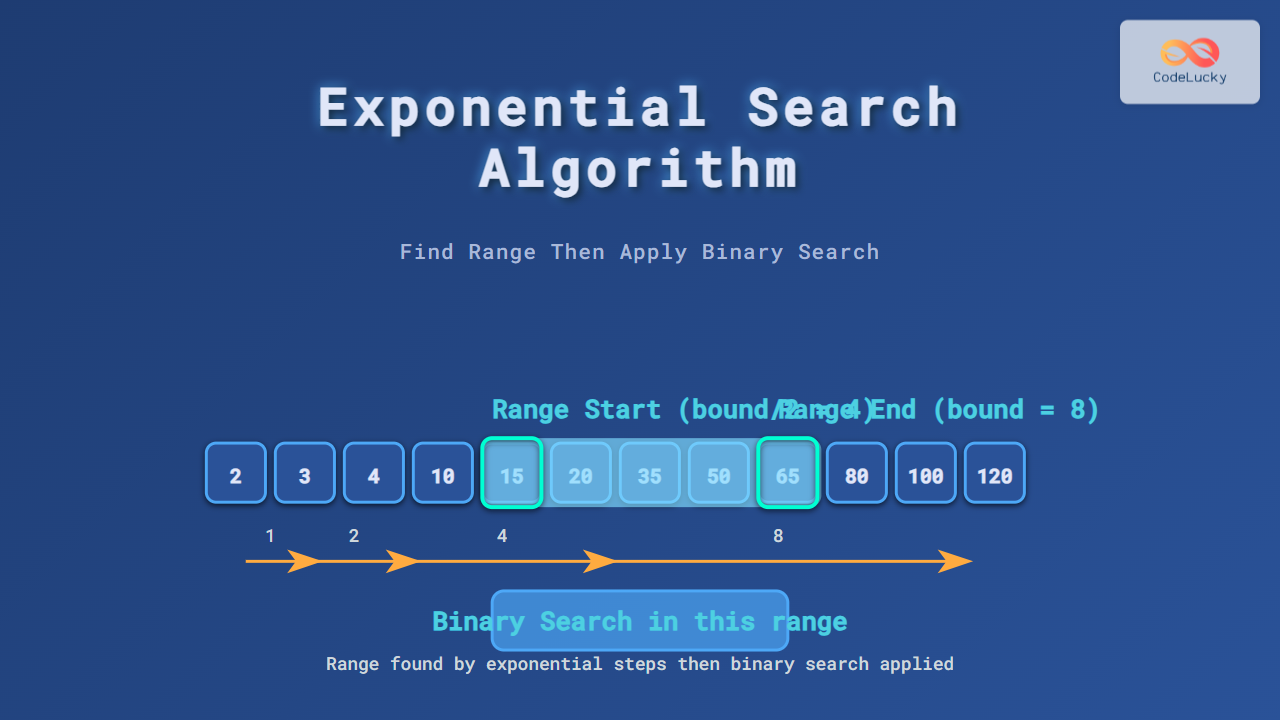
Suppose we want to search for 35 in the array:
Array: [2, 3, 4, 10, 15, 20, 35, 50, 65, 80, 100]
Target: 35
Steps:
- Check index 0 → 2 ≠ 35
- bound = 1 → arr[1] = 3
- bound = 2 → arr[2] = 4
- bound = 4 → arr[4] = 15
- bound = 8 → arr[8] = 65 (greater than 35)
- Now search between index 4 and 8 using Binary Search.
Output of Python Example
Array: [2, 3, 4, 10, 15, 20, 35, 50, 65, 80, 100]
Searching for: 35
Found at index: 6
When to Use Exponential Search?
Exponential Search is particularly useful in the following scenarios:
- When the dataset is large and sorted.
- When the upper bound of the search space is not known in advance.
- When the target is located closer to the beginning of the array.
Comparison with Other Search Algorithms
| Algorithm | Time Complexity | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Search | O(n) | Small or unsorted datasets |
| Binary Search | O(log n) | Known boundaries in sorted array |
| Exponential Search | O(log i), where i is position | Unknown boundaries, very large sorted arrays |
Interactive Example (Try It Yourself)
You can run this script to test exponential search with different targets:
arr = list(range(1, 101)) # Sorted array 1 to 100
targets = [1, 25, 50, 75, 100]
for t in targets:
print(f"Target {t} found at index {exponential_search(arr, t)}")
Conclusion
The Exponential Search Algorithm provides a powerful hybrid approach: it first rapidly identifies a potential range using exponential growth, then efficiently searches within that range using Binary Search. It is especially valuable in problems involving large, sorted datasets where boundaries are not clearly defined. By understanding its working principle and implementation, you can apply Exponential Search effectively in algorithm-based interviews, competitive programming, and real-world applications.