The Excel WORKDAY function is an essential tool for business professionals who need to calculate future or past business dates while automatically excluding weekends and holidays. Whether you’re managing project deadlines, calculating delivery dates, or planning employee schedules, understanding how to use the WORKDAY function can significantly streamline your workflow.
What is the Excel WORKDAY Function?
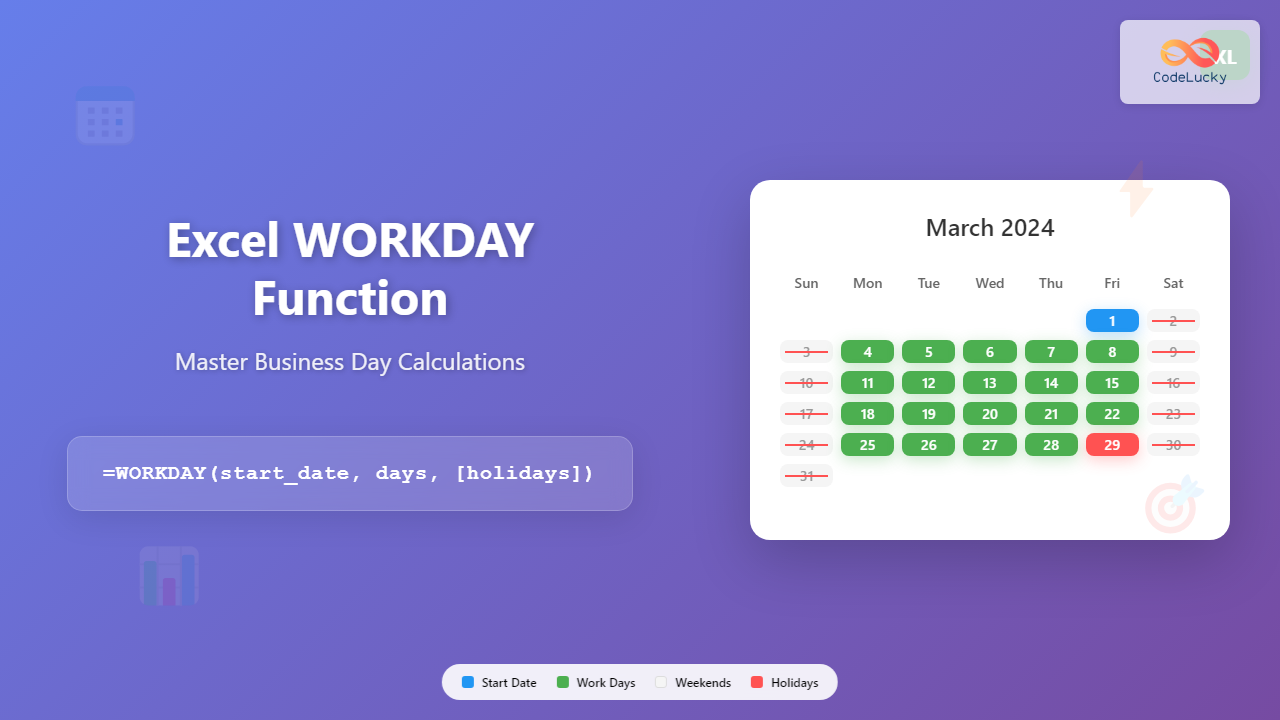
The WORKDAY function in Excel calculates a date that is a specified number of working days before or after a given start date. By default, it excludes Saturdays and Sundays as non-working days, but you can also specify custom holidays to exclude from the calculation.
This function is particularly valuable for:
- Project management and deadline calculations
- Invoice due date calculations
- Employee vacation and leave planning
- Service level agreement (SLA) tracking
- Financial reporting and business planning
WORKDAY Function Syntax
The basic syntax of the WORKDAY function is:
=WORKDAY(start_date, days, [holidays])Parameters Explained
start_date (Required): The initial date from which you want to calculate the working days. This can be a cell reference, a date value, or a date function.
days (Required): The number of working days to add to or subtract from the start_date. Use positive numbers to calculate future dates and negative numbers for past dates.
holidays (Optional): A range of cells containing dates that should be excluded from the calculation as non-working days. This parameter allows you to account for company-specific holidays, national holidays, or other non-working days.
Basic WORKDAY Function Examples
Example 1: Simple Forward Calculation
To find the date that is 10 working days after January 1, 2024:
=WORKDAY("1/1/2024", 10)This formula will return January 15, 2024, automatically skipping the weekends that fall within this period.
Example 2: Backward Calculation
To find the date that is 5 working days before March 15, 2024:
=WORKDAY("3/15/2024", -5)This will return March 8, 2024, working backward and excluding weekends.
Example 3: Using Cell References
If your start date is in cell A1 and the number of days is in cell B1:
=WORKDAY(A1, B1)Advanced WORKDAY Usage with Holidays
Including Holiday Exclusions
To make your calculations more accurate, you can specify holidays that should be excluded from the working day calculation. First, create a list of holiday dates in a range of cells, then reference that range in your WORKDAY formula.
For example, if your holidays are listed in cells D1:D5:
=WORKDAY(A1, B1, D1:D5)Creating a Holiday Reference Table
Consider creating a dedicated holiday reference table with the following structure:
| Holiday Name | Date |
|---|---|
| New Year’s Day | 1/1/2024 |
| Independence Day | 7/4/2024 |
| Thanksgiving | 11/28/2024 |
| Christmas | 12/25/2024 |
Then reference the date column in your WORKDAY formula to ensure these holidays are properly excluded from your business day calculations.
Practical Business Applications
Project Management Deadlines
Use WORKDAY to calculate project milestones and delivery dates. If a project starts on Monday and requires 15 working days to complete:
=WORKDAY(TODAY(), 15, HolidayRange)Invoice Due Date Calculations
For “Net 30” payment terms that exclude weekends and holidays:
=WORKDAY(InvoiceDate, 30, HolidayRange)Employee Leave Tracking
Calculate return dates from vacation or leave periods:
=WORKDAY(LeaveStartDate, LeaveDuration, HolidayRange)Common Errors and Troubleshooting
#VALUE! Error
This error typically occurs when:
- The start_date parameter is not a valid date
- The days parameter is not a number
- Date formats are inconsistent
Solution: Ensure all date inputs are properly formatted and recognized by Excel as dates.
#NUM! Error
This error appears when the calculated result would be an invalid date (before January 1, 1900, or after December 31, 9999).
Solution: Check your input values to ensure the calculated date falls within Excel’s valid date range.
WORKDAY vs NETWORKDAYS Functions
While WORKDAY calculates a future or past date based on working days, the NETWORKDAYS function calculates the number of working days between two dates. Use WORKDAY when you need to find a specific date, and NETWORKDAYS when you need to count working days.
When to Use WORKDAY:
- Calculating deadline dates
- Finding project completion dates
- Determining due dates for payments or deliverables
When to Use NETWORKDAYS:
- Calculating project duration in working days
- Measuring time between events
- Analyzing productivity metrics
Tips for Optimizing WORKDAY Function Usage
1. Create Named Ranges for Holidays
Instead of using cell references like D1:D10, create a named range called “Holidays” for better formula readability:
=WORKDAY(A1, B1, Holidays)2. Use Dynamic Holiday Lists
Create dynamic holiday lists that automatically update based on the year. This ensures your WORKDAY calculations remain accurate across different years without manual updates.
3. Combine with Other Date Functions
Enhance your WORKDAY formulas by combining them with other Excel date functions like TODAY(), EOMONTH(), or DATE() for more sophisticated calculations.
4. Format Results Properly
Ensure your WORKDAY results are formatted as dates to display properly. Use Excel’s date formatting options to present results in your preferred date format.
Regional Considerations and International Usage
The WORKDAY function uses Saturday and Sunday as default weekend days, which works for most Western business environments. However, if you’re working in regions with different weekend patterns (such as Friday-Saturday weekends in some Middle Eastern countries), consider using the WORKDAY.INTL function instead, which allows you to specify custom weekend days.
Best Practices for WORKDAY Implementation
To maximize the effectiveness of the WORKDAY function in your spreadsheets:
- Maintain accurate holiday lists: Keep your holiday reference tables updated annually
- Use consistent date formats: Ensure all dates in your spreadsheet follow the same format
- Document your formulas: Add comments explaining complex WORKDAY calculations for future reference
- Test with known dates: Verify your formulas work correctly by testing with dates you can manually calculate
- Consider time zones: Be aware of time zone differences when working with international teams
Conclusion
The Excel WORKDAY function is a powerful tool for business date calculations that can save time and reduce errors in your spreadsheet workflows. By understanding its syntax, parameters, and practical applications, you can streamline project management, financial planning, and scheduling tasks. Remember to account for holidays specific to your business or region, and always validate your results to ensure accuracy in your business calculations.
Whether you’re a project manager tracking deadlines, an accountant calculating payment due dates, or a human resources professional managing employee schedules, mastering the WORKDAY function will enhance your Excel proficiency and improve your productivity in date-related calculations.
- What is the Excel WORKDAY Function?
- WORKDAY Function Syntax
- Basic WORKDAY Function Examples
- Advanced WORKDAY Usage with Holidays
- Practical Business Applications
- Common Errors and Troubleshooting
- WORKDAY vs NETWORKDAYS Functions
- Tips for Optimizing WORKDAY Function Usage
- Regional Considerations and International Usage
- Best Practices for WORKDAY Implementation
- Conclusion