What is the Excel PERMUT Function?
The PERMUT function in Microsoft Excel calculates the number of permutations for a given number of objects that can be selected from a total set of objects. In mathematical terms, it determines how many different ways you can arrange a subset of items where the order matters.
This function is particularly valuable for statistical analysis, probability calculations, and scenarios where you need to determine the number of possible arrangements or sequences from a dataset.
PERMUT Function Syntax
The syntax for the PERMUT function is straightforward:
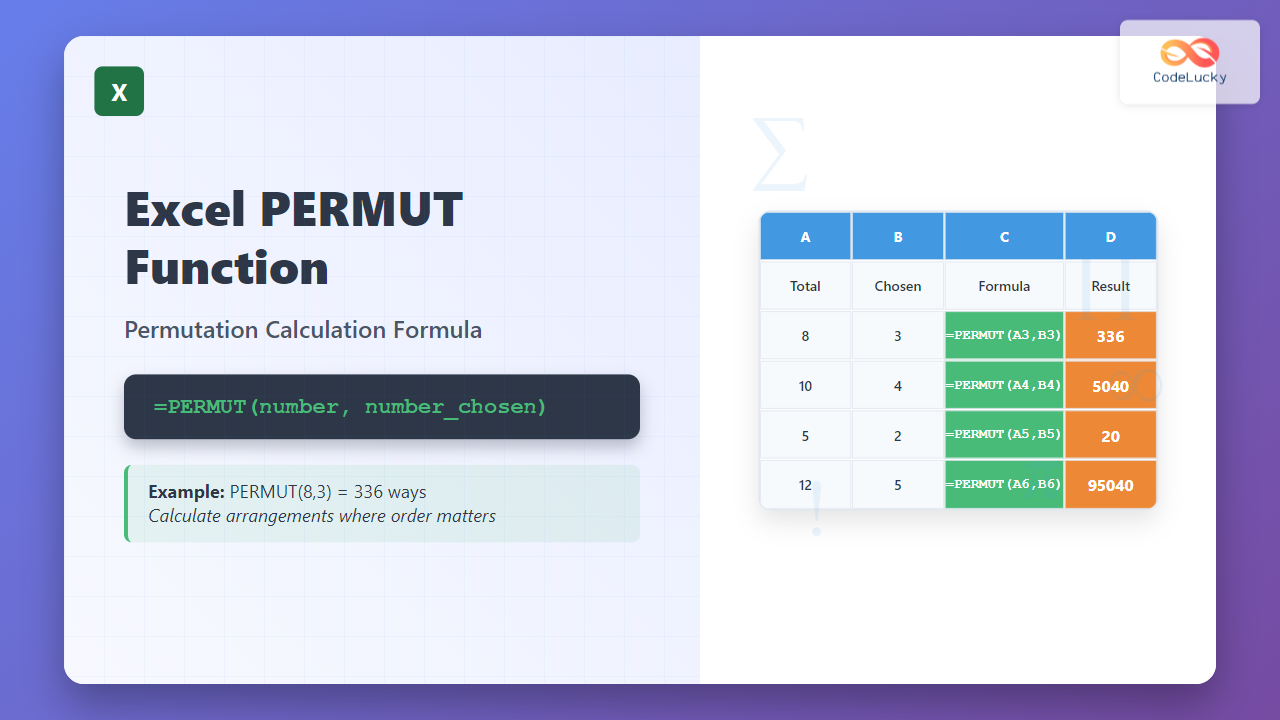
=PERMUT(number, number_chosen)
Parameters Explained
- number (required): The total number of objects in the set. This must be a positive integer greater than or equal to 0.
- number_chosen (required): The number of objects to choose from the total set. This must be a positive integer greater than or equal to 0, and cannot exceed the total number.
How PERMUT Function Works
The PERMUT function calculates permutations using the mathematical formula:
P(n,r) = n! / (n-r)!
Where:
- n = total number of objects (number parameter)
- r = number of objects chosen (number_chosen parameter)
- ! = factorial notation
For example, if you have 5 objects and want to choose 3, the calculation would be: 5! / (5-3)! = 120 / 2 = 60 permutations.
Basic PERMUT Function Examples
Example 1: Simple Permutation Calculation
Calculate how many ways you can arrange 3 people from a group of 8:
=PERMUT(8,3)
Result: 336
This means there are 336 different ways to arrange 3 people from a group of 8 where order matters.
Example 2: Complete Set Permutation
Calculate all possible arrangements of 4 objects:
=PERMUT(4,4)
Result: 24
When choosing all objects from the set, you get the factorial of the total number (4! = 24).
Example 3: Single Object Selection
Calculate permutations when choosing only 1 object from 10:
=PERMUT(10,1)
Result: 10
When choosing only one object, the number of permutations equals the total number of objects.
Advanced PERMUT Function Applications
Business Scenario: Product Display Arrangements
A retail store wants to display 4 featured products from their inventory of 12 items in a specific order on their main shelf. Calculate the possible arrangements:
=PERMUT(12,4)
Result: 11,880 different display arrangements
Educational Scenario: Exam Question Ordering
A teacher needs to create different versions of an exam by selecting and ordering 6 questions from a question bank of 15:
=PERMUT(15,6)
Result: 3,603,600 possible exam variations
Sports Tournament Bracket
Calculate the number of ways to arrange the top 5 finishers from a competition of 20 participants:
=PERMUT(20,5)
Result: 1,860,480 possible ranking arrangements
PERMUT vs COMBIN: Understanding the Difference
It’s crucial to understand when to use PERMUT versus COMBIN:
- PERMUT: Use when order matters (arrangements, sequences, rankings)
- COMBIN: Use when order doesn’t matter (selections, groups, combinations)
Comparison Example
Selecting 3 people from a group of 5:
- PERMUT(5,3) = 60 (different arrangements like ABC, BAC, CAB are counted separately)
- COMBIN(5,3) = 10 (ABC, BAC, CAB are considered the same group)
Common PERMUT Function Errors and Solutions
Error #NUM!
This error occurs when:
- Either argument is negative
- Arguments are not integers (Excel truncates decimal values)
- The number_chosen exceeds the total number
Solution: Ensure both arguments are non-negative integers and number_chosen ≤ number.
Error #VALUE!
This error appears when arguments are not numeric values.
Solution: Verify that both parameters contain numeric values or cell references to numeric data.
Practical Tips for Using PERMUT Function
1. Cell Reference Usage
Instead of hardcoding values, use cell references for flexibility:
=PERMUT(A1,B1)
This allows easy modification of values without changing the formula.
2. Combining with Other Functions
Use PERMUT with other Excel functions for complex calculations:
=PERMUT(COUNTA(A:A),3)
This calculates permutations based on the count of non-empty cells in column A.
3. Data Validation
Create data validation rules to prevent invalid inputs that would cause errors in PERMUT calculations.
Real-World PERMUT Function Use Cases
Quality Control Testing
Manufacturing companies use PERMUT to determine testing sequences for products, ensuring comprehensive quality assessment through different arrangement patterns.
Marketing Campaign Analysis
Digital marketers calculate the number of ways to sequence advertisements or promotional content to optimize customer engagement strategies.
Project Management
Project managers use PERMUT to analyze different task ordering possibilities, helping optimize workflow sequences and resource allocation.
Financial Portfolio Analysis
Investment advisors calculate permutations to determine different investment ordering strategies and risk assessment scenarios.
Performance Considerations
When working with large numbers, be aware that permutation calculations can result in very large values:
- PERMUT(50,10) results in over 37 billion permutations
- Excel can handle calculations up to approximately 15 significant digits
- For extremely large results, consider using logarithmic approaches or specialized statistical software
Alternative Approaches and Related Functions
Manual Calculation Verification
You can verify PERMUT results using FACT function:
=FACT(8)/FACT(8-3)
This should equal PERMUT(8,3).
Related Excel Functions
- COMBIN: Calculates combinations (order doesn’t matter)
- FACT: Calculates factorial values
- MULTINOMIAL: Calculates multinomial coefficients
- PERMUTA: Calculates permutations with repetition (Excel 2013+)
Best Practices for PERMUT Function
1. Documentation
Always document your PERMUT calculations with clear comments explaining what the permutation represents in your specific context.
2. Input Validation
Implement checks to ensure input values are appropriate for your calculation needs and won’t result in errors.
3. Result Interpretation
Remember that PERMUT results can be very large numbers. Consider whether the calculated permutations are practically meaningful in your application.
4. Testing
Test your PERMUT formulas with known values to verify accuracy before applying them to critical business calculations.
Troubleshooting PERMUT Function Issues
Unexpected Results
If PERMUT returns unexpected results:
- Verify you need permutations (order matters) rather than combinations
- Check that your input parameters are correct
- Ensure you’re not confusing permutations with other mathematical concepts
Performance Issues
For worksheets with many PERMUT calculations:
- Consider using manual calculation mode
- Optimize by reducing unnecessary recalculations
- Use efficient cell referencing methods
Conclusion
The Excel PERMUT function is a powerful tool for calculating permutations in various professional and academic scenarios. By understanding its syntax, applications, and limitations, you can effectively utilize this function for statistical analysis, business planning, and mathematical problem-solving.
Whether you’re analyzing product arrangements, creating test variations, or solving complex mathematical problems, the PERMUT function provides accurate and efficient permutation calculations. Remember to consider whether order matters in your specific use case, as this determines whether PERMUT or COMBIN is the appropriate function for your needs.
Master the PERMUT function by practicing with different scenarios and combining it with other Excel functions to create comprehensive analytical solutions for your data analysis requirements.
- What is the Excel PERMUT Function?
- PERMUT Function Syntax
- How PERMUT Function Works
- Basic PERMUT Function Examples
- Advanced PERMUT Function Applications
- PERMUT vs COMBIN: Understanding the Difference
- Common PERMUT Function Errors and Solutions
- Practical Tips for Using PERMUT Function
- Real-World PERMUT Function Use Cases
- Performance Considerations
- Alternative Approaches and Related Functions
- Best Practices for PERMUT Function
- Troubleshooting PERMUT Function Issues
- Conclusion