What is Edge Computing OS?
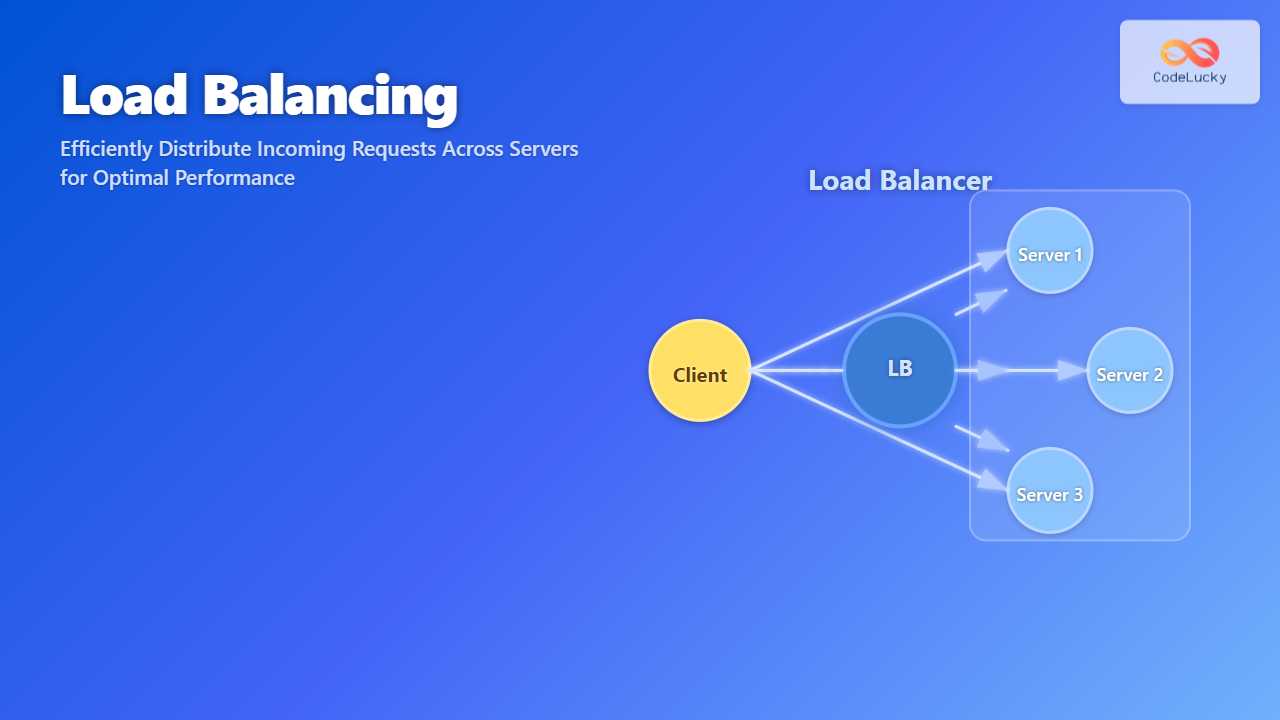
Edge Computing Operating Systems represent a paradigm shift in how we process and manage data in distributed environments. Unlike traditional cloud-centric approaches, edge computing OS brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it’s needed, reducing latency and bandwidth usage while improving response times for critical applications.
An Edge Computing OS is specifically designed to operate on resource-constrained devices at the network edge, managing local processing, real-time data analysis, and seamless integration with both IoT devices and cloud infrastructure. These operating systems must handle unique challenges including intermittent connectivity, limited computational resources, and the need for autonomous operation.
Core Architecture of Edge Computing OS
Kernel and Resource Management
Edge computing operating systems typically employ microkernel architectures to minimize resource overhead while maintaining system stability. The kernel focuses on essential services:
- Process Scheduling: Optimized for real-time and priority-based task execution
- Memory Management: Efficient allocation for limited RAM resources
- I/O Management: Direct hardware access for sensor integration
- Network Stack: Lightweight protocols for device communication
Container and Virtualization Support
Modern edge OS implementations leverage containerization technologies adapted for resource-constrained environments:
# Example EdgeX Foundry service configuration
version: '3.7'
services:
core-data:
image: edgexfoundry/core-data:2.0
container_name: edgex-core-data
environment:
- EDGEX_SECURITY_SECRET_STORE=false
ports:
- "48080:48080"
volumes:
- db-data:/data/db
networks:
- edgex-network
Key Components and Services
Device Abstraction Layer
The Device Abstraction Layer (DAL) provides unified interfaces for heterogeneous IoT devices, enabling seamless integration regardless of underlying hardware protocols:
// Example device driver interface
typedef struct {
char device_id[32];
int (*read_sensor)(int sensor_id, float *value);
int (*write_actuator)(int actuator_id, float value);
int (*configure)(const char *config);
} edge_device_t;
int register_device(edge_device_t *device) {
// Device registration logic
return add_to_device_registry(device);
}
Real-Time Processing Engine
Edge OS includes optimized processing engines for stream processing and real-time analytics:
Popular Edge Computing Operating Systems
Azure IoT Edge
Microsoft’s Azure IoT Edge extends cloud intelligence to edge devices through containerized modules:
{
"modulesContent": {
"$edgeAgent": {
"properties.desired": {
"modules": {
"tempSensor": {
"version": "1.0",
"type": "docker",
"status": "running",
"restartPolicy": "always",
"settings": {
"image": "mcr.microsoft.com/azureiotedge-simulated-temperature-sensor:1.0",
"createOptions": "{}"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
AWS IoT Greengrass
Amazon’s edge computing solution provides local compute, messaging, and ML inference capabilities:
# Greengrass Lambda function example
import greengrasssdk
import json
client = greengrasssdk.client('iot-data')
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# Process sensor data locally
temperature = event.get('temperature', 0)
if temperature > 30:
# Trigger local action
response = client.publish(
topic='alerts/temperature',
payload=json.dumps({'alert': 'High temperature detected'})
)
return {'status': 'processed'}
EdgeX Foundry
An open-source, vendor-neutral edge computing framework providing interoperability across IoT solutions:
// EdgeX device service example
package main
import (
"github.com/edgexfoundry/device-sdk-go/v2/pkg/startup"
"github.com/edgexfoundry/go-mod-core-contracts/v2/models"
)
func main() {
sd := &TemperatureDriver{}
startup.Bootstrap("device-temperature", "1.0.0", sd)
}
type TemperatureDriver struct{}
func (d *TemperatureDriver) HandleReadCommands(reqs []models.CommandRequest) ([]*models.CommandValue, error) {
// Read temperature sensor implementation
return results, nil
}
IoT Integration Patterns
Device-to-Edge Communication
Edge OS implementations support multiple communication protocols for IoT device integration:
- MQTT: Lightweight messaging for publish-subscribe patterns
- CoAP: Constrained Application Protocol for resource-limited devices
- HTTP/REST: Standard web protocols for modern devices
- WebSocket: Real-time bidirectional communication
// MQTT client implementation for edge devices
const mqtt = require('mqtt');
const client = mqtt.connect('mqtt://edge-gateway:1883');
client.on('connect', () => {
console.log('Connected to edge broker');
// Subscribe to sensor topics
client.subscribe('sensors/+/temperature');
client.subscribe('sensors/+/humidity');
});
client.on('message', (topic, message) => {
const data = JSON.parse(message.toString());
// Process sensor data locally
if (data.temperature > 25) {
// Trigger edge processing
processTemperatureAlert(data);
}
});
Edge-to-Cloud Synchronization
Efficient data synchronization between edge and cloud infrastructure is crucial for hybrid deployments:
Real-Time Processing and Analytics
Stream Processing Architecture
Edge computing OS implements stream processing frameworks optimized for low-latency, high-throughput data processing:
# Apache Kafka Streams for edge processing
from kafka import KafkaProducer, KafkaConsumer
import json
import threading
class EdgeStreamProcessor:
def __init__(self):
self.consumer = KafkaConsumer(
'sensor-data',
bootstrap_servers=['localhost:9092'],
value_deserializer=lambda m: json.loads(m.decode('utf-8'))
)
self.producer = KafkaProducer(
bootstrap_servers=['localhost:9092'],
value_serializer=lambda v: json.dumps(v).encode('utf-8')
)
def process_stream(self):
for message in self.consumer:
data = message.value
# Real-time processing
if self.is_anomaly(data):
alert = {
'timestamp': data['timestamp'],
'device_id': data['device_id'],
'anomaly_type': 'temperature_spike',
'severity': 'high'
}
# Send to local alert topic
self.producer.send('local-alerts', alert)
def is_anomaly(self, data):
return data.get('temperature', 0) > 35
Machine Learning at the Edge
Edge OS supports lightweight ML inference engines for real-time decision making:
# TensorFlow Lite inference on edge devices
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
class EdgeMLProcessor:
def __init__(self, model_path):
# Load TensorFlow Lite model
self.interpreter = tf.lite.Interpreter(model_path=model_path)
self.interpreter.allocate_tensors()
self.input_details = self.interpreter.get_input_details()
self.output_details = self.interpreter.get_output_details()
def predict(self, sensor_data):
# Prepare input data
input_data = np.array(sensor_data, dtype=np.float32)
input_data = input_data.reshape(self.input_details[0]['shape'])
# Set input tensor
self.interpreter.set_tensor(
self.input_details[0]['index'],
input_data
)
# Run inference
self.interpreter.invoke()
# Get prediction
output_data = self.interpreter.get_tensor(
self.output_details[0]['index']
)
return output_data[0]
Distributed System Coordination
Edge Cluster Management
Modern edge deployments often involve multiple edge nodes working in coordination:
Consensus and Coordination Protocols
Edge OS implements distributed consensus mechanisms for maintaining consistency across edge nodes:
// Raft consensus implementation for edge coordination
package main
import (
"github.com/hashicorp/raft"
"time"
)
type EdgeCoordinator struct {
raft *raft.Raft
fsm *EdgeFSM
}
func (ec *EdgeCoordinator) ProposeConfiguration(config EdgeConfig) error {
data := encodeConfig(config)
// Propose configuration change
future := ec.raft.Apply(data, 5*time.Second)
if err := future.Error(); err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}
type EdgeFSM struct {
config EdgeConfig
}
func (fsm *EdgeFSM) Apply(log *raft.Log) interface{} {
var config EdgeConfig
decodeConfig(log.Data, &config)
// Apply configuration to local edge node
fsm.config = config
return nil
}
Security and Privacy Considerations
Zero Trust Architecture
Edge computing OS implements zero trust security models where every device and communication is verified:
# Edge security policy configuration
security_policies:
authentication:
method: "mutual_tls"
certificate_authority: "/etc/edge/ca.pem"
client_certificates: "/etc/edge/certs/"
authorization:
rbac_enabled: true
policies:
- role: "sensor_reader"
permissions: ["read:sensors/*"]
- role: "actuator_controller"
permissions: ["write:actuators/*", "read:sensors/*"]
network:
encryption: "AES256"
firewall_rules:
- allow: "IoT_VLAN"
ports: [1883, 8883]
- deny: "*"
ports: "*"
Data Privacy and Compliance
Edge OS ensures data privacy through local processing and selective cloud synchronization:
# Privacy-preserving data processing
class PrivacyFilter:
def __init__(self, privacy_rules):
self.rules = privacy_rules
def filter_sensitive_data(self, data):
filtered_data = data.copy()
for field, rule in self.rules.items():
if field in filtered_data:
if rule['action'] == 'anonymize':
filtered_data[field] = self.anonymize(
filtered_data[field],
rule['method']
)
elif rule['action'] == 'remove':
del filtered_data[field]
return filtered_data
def anonymize(self, value, method):
if method == 'hash':
return hashlib.sha256(str(value).encode()).hexdigest()[:8]
elif method == 'mask':
return '*' * len(str(value))
return value
Performance Optimization Strategies
Resource Management
Edge OS employs sophisticated resource management techniques to maximize performance on constrained hardware:
- Dynamic CPU Scaling: Adjusting processor frequency based on workload
- Memory Compression: Utilizing zRAM and swap optimization
- Storage Tiering: Intelligent data placement across storage media
- Network Optimization: Traffic prioritization and bandwidth management
// Resource monitor implementation
typedef struct {
float cpu_usage;
float memory_usage;
float network_utilization;
int active_connections;
} resource_metrics_t;
int optimize_resources(resource_metrics_t *metrics) {
if (metrics->cpu_usage > 80.0) {
// Scale down non-critical processes
scale_background_tasks(0.5);
// Enable CPU frequency scaling
set_cpu_governor("conservative");
}
if (metrics->memory_usage > 85.0) {
// Trigger memory cleanup
compact_memory();
// Reduce cache sizes
adjust_cache_limits(0.7);
}
return 0;
}
Development and Deployment
Edge Application Development Framework
Modern edge OS provides SDKs and frameworks for rapid application development:
// Edge application using Node.js framework
const EdgeApp = require('@edge/app-framework');
class TemperatureMonitor extends EdgeApp {
constructor() {
super();
this.setupSensors();
this.setupMLModel();
}
async setupSensors() {
// Configure temperature sensors
this.tempSensor = await this.connectDevice('temp-sensor-01');
// Set up data stream
this.tempSensor.on('data', (reading) => {
this.processTemperature(reading);
});
}
async processTemperature(reading) {
// Local ML inference
const prediction = await this.mlModel.predict(reading);
if (prediction.anomaly_score > 0.8) {
// Trigger local alert
this.emit('alert', {
type: 'temperature_anomaly',
severity: prediction.severity,
timestamp: reading.timestamp
});
}
// Store locally
await this.localDB.store('temperature_readings', reading);
}
}
// Deploy and start the application
const app = new TemperatureMonitor();
app.start();
Container Orchestration
Edge OS supports lightweight container orchestration for managing distributed applications:
# K3s deployment manifest for edge services
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: edge-data-processor
namespace: edge-services
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: data-processor
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: data-processor
spec:
containers:
- name: processor
image: edge/data-processor:v1.2
resources:
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 512Mi
requests:
cpu: 200m
memory: 256Mi
env:
- name: EDGE_NODE_ID
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.nodeName
Future Trends and Innovations
5G Integration
Next-generation edge OS will leverage 5G network capabilities for ultra-low latency applications, enabling new use cases like autonomous vehicles, remote surgery, and real-time industrial control systems.
AI-Driven Optimization
Future edge operating systems will incorporate AI-driven resource management, predictive maintenance, and autonomous optimization capabilities, reducing the need for manual configuration and tuning.
Quantum-Safe Security
As quantum computing advances, edge OS will integrate quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms to ensure long-term security of distributed IoT networks.
Best Practices for Implementation
Design Principles
When implementing edge computing solutions, follow these key principles:
- Locality First: Process data as close to the source as possible
- Graceful Degradation: Ensure systems continue operating during network failures
- Resource Efficiency: Optimize for limited CPU, memory, and storage
- Security by Design: Implement security measures from the ground up
- Scalability: Design for horizontal scaling across edge nodes
Monitoring and Observability
Implement comprehensive monitoring solutions to maintain edge infrastructure health:
# Edge monitoring agent
class EdgeMonitor:
def __init__(self):
self.metrics_collector = MetricsCollector()
self.health_checker = HealthChecker()
self.alert_manager = AlertManager()
def collect_system_metrics(self):
metrics = {
'timestamp': time.time(),
'cpu_percent': psutil.cpu_percent(),
'memory_percent': psutil.virtual_memory().percent,
'disk_usage': psutil.disk_usage('/').percent,
'network_io': psutil.net_io_counters(),
'temperature': self.read_system_temperature(),
'active_containers': self.count_active_containers()
}
# Check thresholds and trigger alerts
self.check_health_thresholds(metrics)
# Send to local time-series database
self.metrics_collector.store(metrics)
return metrics
def check_health_thresholds(self, metrics):
if metrics['cpu_percent'] > 90:
self.alert_manager.send_alert(
'high_cpu_usage',
f"CPU usage: {metrics['cpu_percent']}%"
)
if metrics['memory_percent'] > 95:
self.alert_manager.send_alert(
'high_memory_usage',
f"Memory usage: {metrics['memory_percent']}%"
)
Edge Computing OS represents a fundamental shift in distributed computing, bringing intelligence and processing power closer to data sources. As IoT deployments continue to grow and real-time applications become more demanding, edge computing operating systems will play an increasingly critical role in enabling responsive, efficient, and secure distributed systems. The combination of local processing capabilities, seamless cloud integration, and optimized resource management makes edge OS an essential component of modern IoT and distributed system architectures.
- What is Edge Computing OS?
- Core Architecture of Edge Computing OS
- Key Components and Services
- Popular Edge Computing Operating Systems
- IoT Integration Patterns
- Real-Time Processing and Analytics
- Distributed System Coordination
- Security and Privacy Considerations
- Performance Optimization Strategies
- Development and Deployment
- Future Trends and Innovations
- Best Practices for Implementation