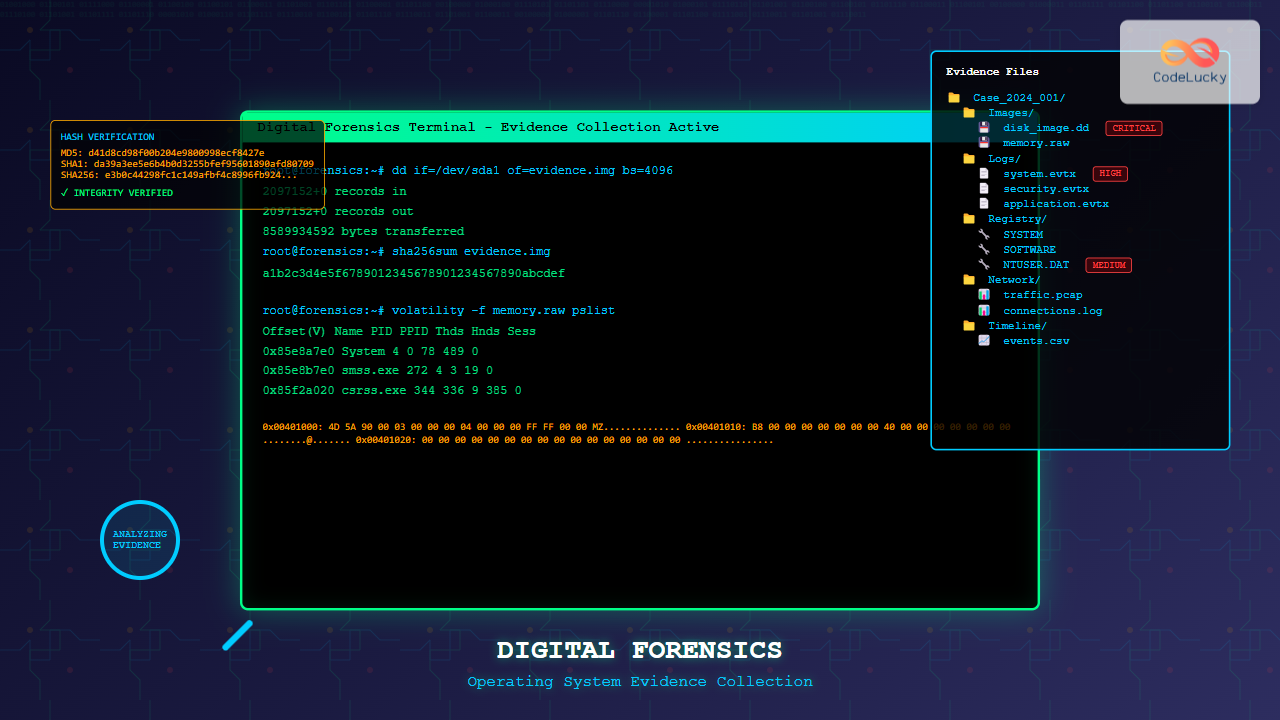
Introduction to Desktop Virtualization
Desktop virtualization represents a paradigm shift in how organizations deliver computing resources to end users. By separating the desktop operating system and applications from the physical hardware, Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) enables centralized management, enhanced security, and improved flexibility in modern IT environments.
This technology allows multiple virtual desktops to run on centralized servers while users access them remotely through thin clients, laptops, or mobile devices. The result is a more manageable, secure, and cost-effective desktop computing solution that scales with organizational needs.
Understanding VDI Architecture
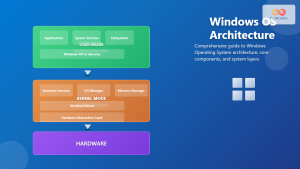
The foundation of successful desktop virtualization lies in understanding its core architectural components. A typical VDI implementation consists of several interconnected layers that work together to deliver seamless desktop experiences.
Core Components Breakdown
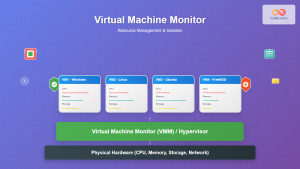
Connection Broker serves as the central orchestrator, managing user authentication, desktop assignment, and connection routing. This component determines which virtual desktop a user receives and handles load balancing across the infrastructure.
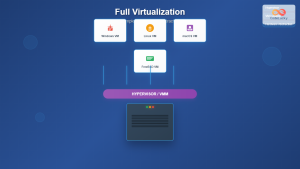
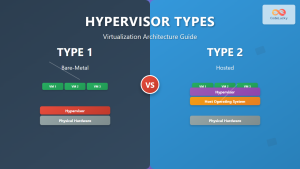
Hypervisor Layer provides the virtualization platform where multiple virtual machines run simultaneously on physical servers. Popular choices include VMware vSphere, Microsoft Hyper-V, and Citrix XenServer.
Desktop Pools represent collections of virtual desktops with similar configurations. These can be persistent (assigned to specific users) or non-persistent (dynamically allocated from a pool).
VDI Implementation Models
Organizations can choose from several VDI deployment models, each offering distinct advantages depending on specific requirements and constraints.
Persistent vs Non-Persistent VDI
Persistent VDI provides users with dedicated virtual desktops that retain changes across sessions. This model offers a traditional desktop experience but requires more storage and management overhead.
Non-persistent VDI delivers fresh desktop instances for each session, with changes discarded after logout. This approach reduces storage requirements and simplifies management but may limit user customization.
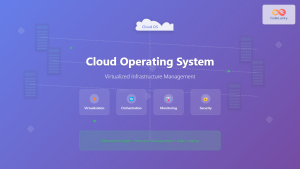
Cloud vs On-Premises Deployment
Cloud VDI leverages public cloud platforms like AWS WorkSpaces, Microsoft Windows Virtual Desktop, or Google Cloud. This model offers rapid deployment and scalability but may have ongoing operational costs and data sovereignty considerations.
On-premises VDI provides complete control over infrastructure and data but requires significant upfront investment and internal expertise for management and maintenance.
Planning Your VDI Implementation
Successful VDI deployment requires comprehensive planning that addresses technical, operational, and business requirements. The planning phase determines the long-term success and adoption of your virtual desktop infrastructure.
User Assessment and Profiling
Begin by categorizing users based on their computing requirements, application usage patterns, and performance expectations. Create user profiles that define resource allocations, security requirements, and desktop configurations.
| User Type | CPU Requirements | RAM | Storage | Graphics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Task Worker | 1-2 vCPU | 2-4 GB | 20-40 GB | Basic |
| Knowledge Worker | 2-4 vCPU | 4-8 GB | 40-80 GB | Standard |
| Power User | 4-8 vCPU | 8-16 GB | 80-200 GB | Enhanced |
| Designer/Engineer | 8+ vCPU | 16-32 GB | 200+ GB | GPU-accelerated |
Infrastructure Sizing and Capacity Planning
Calculate total resource requirements by multiplying user counts by individual resource needs, then add overhead for the hypervisor, management components, and growth projections. Consider peak usage patterns and concurrent user loads when determining server specifications.
Storage considerations include base image storage, user profile storage, application data, and snapshot requirements. Plan for IOPS requirements based on user activity patterns and concurrent access needs.
Step-by-Step VDI Deployment
The deployment process follows a structured approach that ensures proper configuration and testing at each stage. This methodical implementation reduces risks and improves the chances of successful adoption.
Phase 1: Infrastructure Preparation
Network Infrastructure Setup
- Configure VLANs for management, virtual machine, and user traffic separation
- Implement Quality of Service (QoS) policies for VDI traffic prioritization
- Establish redundant network paths for high availability
- Configure DNS and DHCP services for virtual desktop addressing
Storage System Configuration
- Deploy shared storage systems with appropriate RAID configurations
- Configure storage networks (SAN/NAS) with redundant paths
- Implement storage tiering for optimal performance and cost
- Set up backup and disaster recovery solutions
Phase 2: Hypervisor and Management Platform Installation
Install and configure your chosen hypervisor platform across all physical servers. Ensure consistent configuration and version compatibility across the environment. Configure cluster settings for high availability and resource sharing.
Phase 3: Desktop Template Creation
Create optimized base images that serve as templates for virtual desktops. This process involves installing the operating system, applications, and configurations that users require.
Template Optimization Steps:
- Install minimal OS components required for functionality
- Remove unnecessary services and startup programs
- Configure anti-virus exclusions for VDI-specific folders
- Apply latest security patches and updates
- Install and configure VDI agent software
- Optimize registry settings for virtual environments
- Create system snapshot before sealing the template
VDI Management and Administration
Effective VDI management requires understanding the unique operational requirements of virtual desktop environments. Unlike traditional desktop management, VDI administration focuses on centralized control and automated processes.
Desktop Pool Management
Automated Pool Provisioning enables dynamic creation and deletion of virtual desktops based on demand. Configure policies that automatically provision new desktops during peak hours and de-provision unused desktops during off-peak periods.
User Assignment Strategies determine how users connect to specific desktops. Implement load balancing algorithms that distribute users across available resources while maintaining consistent performance levels.
Performance Monitoring and Optimization
Establish comprehensive monitoring that tracks resource utilization, user experience metrics, and infrastructure health. Key performance indicators include:
- Desktop login times and session establishment duration
- Application launch performance and responsiveness
- Network latency and bandwidth utilization
- Storage IOPS and response times
- CPU and memory utilization across hosts
Security Implementation in VDI Environments
VDI environments present unique security advantages and challenges that require specialized approaches to protect both centralized infrastructure and distributed access points.
Centralized Security Controls
Image-level Security involves hardening base templates with security configurations that apply to all virtual desktops. This centralized approach ensures consistent security posture across the entire desktop fleet.
Network Micro-segmentation isolates virtual desktops into secure network zones based on user roles, data sensitivity, and compliance requirements. Implement firewall rules that restrict lateral movement between desktop sessions.
Access Control and Authentication
Deploy multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all VDI access, integrating with existing identity management systems. Configure role-based access controls that automatically assign appropriate desktop pools and application access based on user group membership.
Endpoint Security Considerations:
- Implement device certificates for trusted endpoint identification
- Configure endpoint compliance policies before desktop access
- Deploy remote attestation for device integrity verification
- Enable conditional access based on location and device risk
Troubleshooting Common VDI Issues
VDI environments can experience unique challenges that require specific troubleshooting approaches. Understanding common issues and their resolutions ensures smooth operations and user satisfaction.
Performance-Related Problems
Slow Login Times often result from storage bottlenecks, insufficient network bandwidth, or inefficient user profile handling. Investigate storage IOPS capacity, network utilization during peak hours, and profile redirection configurations.
Application Performance Issues may indicate resource contention, improper application virtualization, or compatibility problems. Monitor CPU and memory utilization per desktop and investigate application-specific optimizations.
Connectivity and Access Issues
Desktop Assignment Failures typically occur due to insufficient desktop pool capacity, failed template provisioning, or connection broker misconfiguration. Verify pool availability, template health, and broker service status.
Network-related Problems manifest as connection drops, poor graphics performance, or audio/video synchronization issues. Analyze network packet loss, latency measurements, and QoS policy effectiveness.
Best Practices for VDI Success
Implementing these proven best practices significantly improves VDI deployment success rates and long-term operational efficiency.
Infrastructure Design Principles
Build for Scale by designing infrastructure that can accommodate 20-30% growth beyond initial requirements. Implement modular architecture that allows incremental capacity additions without major redesign.
Prioritize Storage Performance as storage bottlenecks represent the most common cause of VDI performance issues. Invest in high-performance storage systems with sufficient IOPS capacity for concurrent user loads.
Operational Excellence
Automate Routine Tasks including desktop provisioning, patch management, and capacity scaling. Automation reduces administrative overhead and improves consistency across the environment.
Implement Comprehensive Monitoring with proactive alerting for performance degradation, capacity thresholds, and service failures. Monitor user experience metrics alongside infrastructure performance indicators.
User Experience Optimization
Profile Management Strategy significantly impacts user experience and storage requirements. Implement roaming profiles with folder redirection and consider profile streaming technologies for improved login performance.
Application Delivery Optimization through application virtualization, published applications, or containerization reduces desktop resource requirements and improves application management efficiency.
Future Trends in Desktop Virtualization
The desktop virtualization landscape continues evolving with emerging technologies and changing workplace requirements. Organizations planning VDI implementations should consider these trends for future-proofing their investments.
Cloud-Native VDI Solutions
Desktop as a Service (DaaS) offerings from major cloud providers eliminate infrastructure management complexity while providing global scalability. These solutions integrate seamlessly with cloud-based productivity suites and identity services.
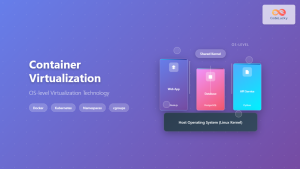
Containerized Desktop Applications enable more efficient resource utilization and faster application delivery compared to traditional virtual machines. Container-based approaches reduce storage requirements and improve deployment flexibility.
Enhanced User Experience Technologies
GPU Virtualization makes graphics-intensive applications accessible through VDI, expanding the use cases to include CAD, video editing, and gaming applications. Modern GPU virtualization solutions provide near-native performance for demanding workloads.
AI-Powered Optimization automatically adjusts resource allocation based on user behavior patterns and application requirements. These systems predict capacity needs and optimize performance without manual intervention.
Conclusion
Desktop virtualization through VDI implementation represents a strategic technology investment that transforms how organizations deliver computing resources. Success requires careful planning, proper infrastructure design, and ongoing optimization based on user needs and performance metrics.
The key to successful VDI deployment lies in understanding your organization’s specific requirements, selecting appropriate technologies, and following proven implementation methodologies. With proper planning and execution, VDI delivers significant benefits including enhanced security, simplified management, and improved user flexibility.
As workplace requirements continue evolving toward remote and hybrid models, VDI provides the foundation for secure, scalable, and efficient desktop computing that adapts to changing organizational needs. Organizations that invest in well-designed VDI infrastructures position themselves for long-term success in the digital workplace era.