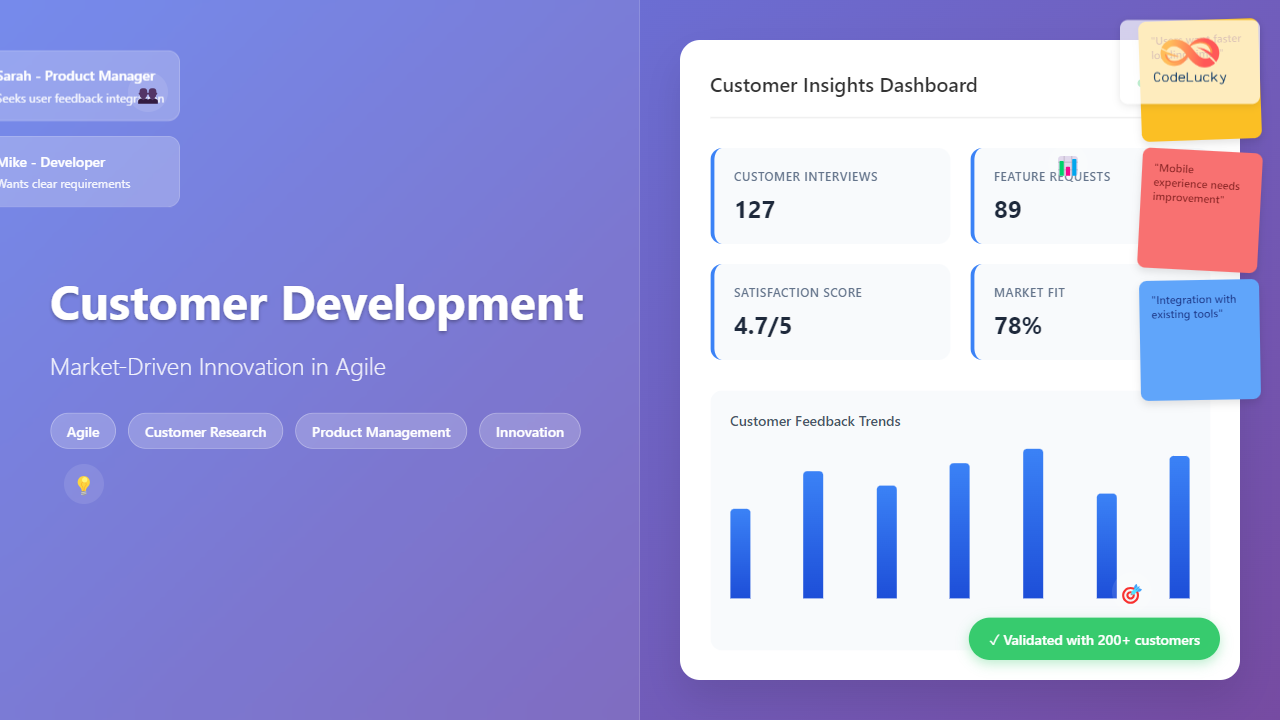
Customer development represents a fundamental shift from traditional product development, placing market validation and customer feedback at the core of innovation processes. In Agile environments, this approach transforms how teams build products by ensuring every feature addresses real customer needs rather than assumptions.
This comprehensive guide explores how to implement customer development within Agile frameworks, providing actionable strategies for creating products that truly resonate with your target market.
Understanding Customer Development in Agile Context
Customer development is a systematic approach to discovering and validating customer needs before building products. Unlike traditional development methods that rely on internal assumptions, customer development emphasizes continuous interaction with potential customers throughout the product lifecycle.
In Agile environments, customer development becomes even more powerful because it aligns perfectly with iterative development cycles. Each sprint can incorporate customer feedback, allowing teams to pivot quickly based on real market insights rather than theoretical requirements.
Core Principles of Market-Driven Innovation
Market-driven innovation operates on several key principles that distinguish it from technology-driven approaches:
Customer-Centric Focus: Every decision starts with understanding customer problems and pain points. This means conducting regular customer interviews, surveys, and observational studies to gather authentic insights about user behavior and preferences.
Hypothesis-Driven Development: Instead of building features based on assumptions, teams create testable hypotheses about customer needs and validate them through experiments and prototypes before full development.
Continuous Validation: Market validation isn’t a one-time activity but an ongoing process that continues throughout product development. Regular feedback loops ensure products remain aligned with evolving customer needs.
Rapid Experimentation: Quick, low-cost experiments help teams test ideas early and often, reducing the risk of building unwanted features or products that miss market demands.
The Customer Development Process Framework
Effective customer development follows a structured four-stage process that integrates seamlessly with Agile methodologies:
Stage 1: Customer Discovery
Customer discovery focuses on understanding the problem space before jumping into solutions. This stage involves deep customer research to identify pain points, motivations, and existing solutions customers currently use.
During this phase, Agile teams conduct extensive customer interviews, create detailed user personas, and map customer journeys to understand the full context of user experiences. The goal is to validate whether the problems you’re solving are significant enough for customers to pay for solutions.
Key activities include identifying target customer segments, conducting problem interviews, and analyzing competitive landscapes to understand how customers currently address their challenges.
Stage 2: Customer Validation
Customer validation tests whether your proposed solution effectively addresses the validated problems. This stage bridges the gap between understanding customer needs and building products that meet those needs.
Agile teams create minimum viable products (MVPs) or prototypes to test with real customers. The focus shifts from problem validation to solution validation, ensuring that your approach resonates with target users before investing significant development resources.
This stage involves solution interviews, prototype testing, and early adopter engagement to refine product concepts based on actual user interactions and feedback.
Stage 3: Customer Creation
Customer creation focuses on building scalable processes for acquiring and retaining customers. This stage validates that you can consistently attract customers and create sustainable growth patterns.
For Agile teams, this means developing and testing marketing strategies, onboarding processes, and customer success programs that support long-term business viability. The emphasis is on proving market demand and establishing repeatable customer acquisition channels.
Stage 4: Company Building
Company building transforms validated customer insights into scalable business operations. This final stage focuses on optimizing organizational structures, processes, and systems to support sustainable growth.
Agile teams transition from discovery mode to execution mode, implementing robust development processes, customer support systems, and operational frameworks that can scale with business growth.
Integrating Customer Development with Agile Sprints
Successfully combining customer development with Agile requires careful integration of customer research activities within sprint cycles. This integration ensures continuous customer feedback without disrupting development momentum.
Sprint Planning with Customer Insights
Effective sprint planning incorporates customer research findings directly into backlog prioritization and feature planning. Product owners should present customer feedback, usage analytics, and market research during sprint planning sessions to inform development priorities.
This approach ensures that development efforts align with validated customer needs rather than internal assumptions. Teams can prioritize features based on customer impact metrics, pain point severity, and market opportunity size.
Customer Feedback Integration Workflows
Establishing systematic workflows for collecting, analyzing, and acting on customer feedback is crucial for market-driven innovation. These workflows should operate continuously rather than as periodic activities.
Successful teams implement feedback collection mechanisms such as in-app feedback tools, regular customer interviews, support ticket analysis, and user behavior tracking. This data feeds directly into sprint retrospectives and planning sessions, creating a continuous feedback loop.
Customer feedback should be categorized, prioritized, and tracked through development cycles to ensure meaningful customer insights translate into product improvements.
Research Methods for Customer Development
Effective customer development relies on diverse research methods that provide comprehensive insights into customer needs, behaviors, and preferences. The choice of methods depends on your research objectives, timeline, and available resources.
Qualitative Research Techniques
Qualitative research provides deep insights into customer motivations, emotions, and thought processes that quantitative data alone cannot reveal.
Customer Interviews: One-on-one interviews remain the gold standard for understanding customer perspectives. Effective interviews focus on past behavior rather than future intentions, using open-ended questions to uncover underlying motivations and pain points.
Structure interviews around specific scenarios and ask customers to walk through their actual experiences rather than hypothetical situations. This approach reveals authentic insights about how customers actually behave versus how they think they behave.
Observational Studies: Watching customers use products or services in their natural environment provides insights that interviews alone cannot capture. Observational studies reveal gaps between what customers say and what they actually do.
Focus Groups: While less common in modern customer development, focus groups can be valuable for exploring group dynamics and social influences on customer decisions. However, they should supplement rather than replace individual interviews.
Quantitative Research Approaches
Quantitative research provides measurable data that helps validate qualitative insights and identify patterns across larger customer populations.
Surveys and Questionnaires: Well-designed surveys can gather feedback from large customer groups efficiently. Focus on specific, actionable questions rather than broad satisfaction metrics to generate useful insights.
Analytics and Usage Data: Product analytics reveal how customers actually use features, identify usage patterns, and highlight areas where customers struggle or disengage.
A/B Testing: Controlled experiments allow teams to test different approaches with real customers and measure the impact of changes on key metrics.
Mixed-Method Research Strategies
The most effective customer development combines qualitative and quantitative methods to create comprehensive customer understanding. Qualitative research helps identify what questions to ask, while quantitative research measures the prevalence and impact of identified patterns.
Start with qualitative research to understand customer perspectives, then use quantitative methods to validate findings across larger populations. This approach ensures that insights are both deep and broadly applicable.
Building Customer-Centric Product Roadmaps
Customer-centric roadmaps prioritize features and improvements based on validated customer needs rather than internal preferences or technical convenience. These roadmaps evolve continuously as new customer insights emerge.
Prioritization Frameworks
Effective prioritization frameworks balance customer impact with business objectives and technical feasibility. Popular frameworks include the RICE model (Reach, Impact, Confidence, Effort) and the Kano model for understanding customer satisfaction drivers.
The RICE framework helps teams evaluate features based on how many customers they’ll reach, the impact on those customers, confidence in estimates, and development effort required. This quantitative approach reduces bias in feature prioritization.
The Kano model categorizes features into basic expectations, performance features, and delighters, helping teams understand which features will truly differentiate their products in the market.
Roadmap Communication Strategies
Transparent roadmap communication builds trust with customers and stakeholders while managing expectations about future development priorities. Effective communication explains not just what features are planned, but why they’re important to customers.
Share customer research findings that support roadmap decisions, helping stakeholders understand the reasoning behind prioritization choices. This approach builds confidence in customer-driven decision making.
Measuring Customer Development Success
Successful customer development requires clear metrics that track progress toward market-driven innovation goals. These metrics should measure both the effectiveness of customer research activities and their impact on product success.
Customer Research Metrics
Track the quantity and quality of customer interactions to ensure adequate market feedback. Metrics might include number of customer interviews conducted, survey response rates, and time from feedback collection to implementation.
Quality metrics focus on the depth and actionability of insights gathered. Track how many research findings translate into product changes and measure the impact of those changes on customer satisfaction and business metrics.
Product-Market Fit Indicators
Product-market fit represents the ultimate goal of customer development efforts. Key indicators include customer retention rates, organic growth metrics, and customer satisfaction scores.
Sean Ellis’s product-market fit survey asks customers how disappointed they would be if they could no longer use your product. When 40% or more of customers say they would be “very disappointed,” you’ve likely achieved product-market fit.
Other indicators include low customer acquisition costs, high lifetime value, and strong word-of-mouth referrals from satisfied customers.
Common Customer Development Pitfalls
Understanding common mistakes helps teams avoid pitfalls that can derail customer development efforts and lead to market-disconnected products.
Confirmation Bias in Research
Teams often unconsciously seek feedback that confirms existing beliefs rather than challenging assumptions. This bias leads to building products that satisfy internal preferences rather than customer needs.
Combat confirmation bias by actively seeking disconfirming evidence, asking open-ended questions, and involving diverse team members in customer research activities.
Analysis Paralysis
While customer research is crucial, excessive analysis can delay product development and miss market opportunities. Balance research thoroughness with development speed by setting research time limits and making decisions with imperfect information.
Use the 80/20 rule: gather enough information to make confident decisions, but don’t wait for perfect data that may never come.
Feature Creep from Customer Requests
Not all customer feedback should become features. Some requests may represent edge cases that don’t align with broader market needs or strategic objectives.
Evaluate customer requests against strategic goals and broader market research to ensure feature development serves the majority of target customers effectively.
Advanced Customer Development Strategies
As teams mature in customer development practices, advanced strategies can provide deeper insights and more sophisticated market validation approaches.
Cohort Analysis for Customer Insights
Cohort analysis tracks customer behavior over time, revealing patterns that single-point measurements miss. This approach helps identify which customer segments provide the most value and which features drive long-term engagement.
Analyze customer cohorts based on acquisition channels, feature usage patterns, or demographic characteristics to understand which customers are most likely to succeed with your product.
Predictive Customer Analytics
Advanced analytics can predict customer behavior, identify at-risk customers, and suggest personalized experiences based on usage patterns and historical data.
Use machine learning models to identify patterns in customer data that predict churn, expansion opportunities, or feature adoption. These insights inform proactive customer development strategies.
Tools and Technologies for Customer Development
Modern customer development benefits from various tools that streamline research, analysis, and implementation of customer insights.
Research and Feedback Tools
Customer interview platforms like Calendly and Zoom facilitate scheduling and conducting customer research sessions. Survey tools such as Typeform and SurveyMonkey enable efficient feedback collection from large customer groups.
In-app feedback tools like Hotjar and FullStory provide real-time insights into customer behavior and pain points during product usage.
Analytics and Data Platforms
Customer analytics platforms like Mixpanel and Amplitude track user behavior and identify patterns in product usage. Customer relationship management (CRM) systems help organize and analyze customer interactions across all touchpoints.
Data visualization tools such as Tableau or Google Data Studio transform customer data into actionable insights that inform product development decisions.
Future of Customer Development in Agile
Customer development continues evolving with new technologies and methodologies that enhance market-driven innovation capabilities.
AI-Enhanced Customer Insights
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are transforming how teams gather and analyze customer feedback. Natural language processing can analyze customer support tickets, reviews, and survey responses to identify common themes and sentiment patterns.
Predictive analytics help teams anticipate customer needs and market trends, enabling proactive product development rather than reactive responses to customer feedback.
Real-Time Customer Development
Modern tools enable real-time customer feedback collection and analysis, allowing Agile teams to make data-driven decisions within sprint cycles rather than waiting for periodic research initiatives.
Continuous customer development becomes possible through automated feedback collection, real-time analytics, and integrated communication channels that connect development teams directly with customers.
Customer development represents a fundamental shift toward market-driven innovation that ensures products meet real customer needs rather than internal assumptions. By integrating customer development practices with Agile methodologies, teams can build products that truly resonate with their target markets while maintaining development velocity and flexibility.
Success in customer development requires commitment to continuous learning, systematic research practices, and willingness to challenge assumptions based on customer feedback. Teams that master these practices build products that customers love and achieve sustainable market success.