CSS Flexbox revolutionized web layout by providing a powerful, flexible way to arrange elements within containers. The display: flex property transforms any element into a flex container, enabling sophisticated layout control with minimal code. This comprehensive guide explores every aspect of flex container properties with practical examples and interactive demonstrations.
What is CSS Flexbox?
Flexbox, short for Flexible Box Layout, is a CSS layout method designed for one-dimensional layouts. When you apply display: flex to an element, it becomes a flex container, and its direct children become flex items. This relationship forms the foundation of flexbox layouts.
Key Flexbox Concepts:
- Flex Container: The parent element with
display: flex - Flex Items: Direct children of the flex container
- Main Axis: Primary axis along which flex items are arranged
- Cross Axis: Perpendicular axis to the main axis
Basic Flexbox Syntax
Creating a flex container is straightforward. Simply apply the display: flex property to any element:
.container {
display: flex;
}
/* Alternative inline-flex for inline behavior */
.inline-container {
display: inline-flex;
}Visual Example: Basic Flex Container
Result: Items automatically arrange horizontally in a row, which is the default flex behavior.
Essential Flex Container Properties
1. flex-direction
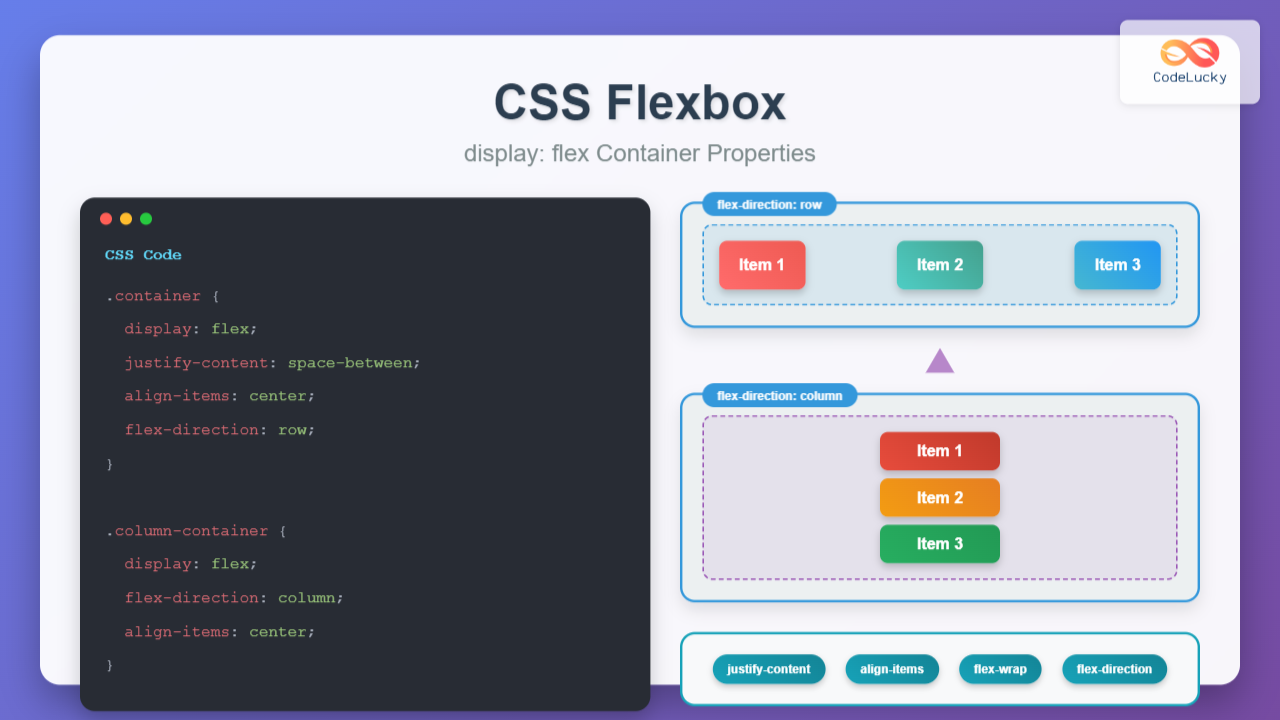
The flex-direction property controls the direction of the main axis, determining how flex items are arranged within the container.
.container {
display: flex;
flex-direction: row; /* Default: left to right */
flex-direction: row-reverse; /* Right to left */
flex-direction: column; /* Top to bottom */
flex-direction: column-reverse; /* Bottom to top */
}Visual Comparison of flex-direction Values:
flex-direction: row (default)
flex-direction: column
2. justify-content
The justify-content property aligns flex items along the main axis, controlling how extra space is distributed.
.container {
display: flex;
justify-content: flex-start; /* Default: start of container */
justify-content: flex-end; /* End of container */
justify-content: center; /* Center of container */
justify-content: space-between; /* Equal space between items */
justify-content: space-around; /* Equal space around items */
justify-content: space-evenly; /* Equal space everywhere */
}Interactive justify-content Examples:
justify-content: center
justify-content: space-between
3. align-items
The align-items property controls how flex items are aligned along the cross axis (perpendicular to the main axis).
.container {
display: flex;
align-items: stretch; /* Default: stretch to fill container */
align-items: flex-start; /* Align to start of cross axis */
align-items: flex-end; /* Align to end of cross axis */
align-items: center; /* Center on cross axis */
align-items: baseline; /* Align to text baseline */
}align-items Visual Examples:
align-items: center
4. flex-wrap
The flex-wrap property determines whether flex items should wrap to new lines when they don’t fit in the container.
.container {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: nowrap; /* Default: items stay on one line */
flex-wrap: wrap; /* Items wrap to new lines */
flex-wrap: wrap-reverse; /* Items wrap in reverse order */
}flex-wrap Demonstration:
flex-wrap: wrap
5. align-content
The align-content property aligns wrapped lines of flex items along the cross axis. This property only works when flex-wrap is set to wrap or wrap-reverse.
.container {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
align-content: stretch; /* Default: stretch lines */
align-content: flex-start; /* Pack lines to start */
align-content: flex-end; /* Pack lines to end */
align-content: center; /* Center lines */
align-content: space-between; /* Space between lines */
align-content: space-around; /* Space around lines */
}Shorthand Properties
flex-flow
The flex-flow property is a shorthand for flex-direction and flex-wrap:
/* Instead of writing both properties separately */
.container {
flex-direction: row;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
/* Use the shorthand */
.container {
flex-flow: row wrap;
}