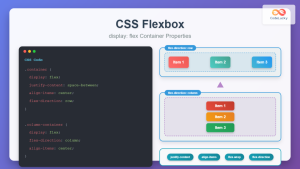
The flex-flow property is a powerful CSS shorthand that combines two fundamental flexbox properties: flex-direction and flex-wrap. This single property gives you complete control over how flex items flow within their container, making your CSS more concise and maintainable.
What is CSS Flex-Flow?
CSS flex-flow is a shorthand property that sets both the direction of flex items and whether they should wrap to new lines. Instead of writing two separate properties, you can define both behaviors in one declaration.
Syntax
flex-flow: <flex-direction> <flex-wrap>;Understanding the Component Properties
Flex-Direction Values
The flex-direction component controls the main axis direction:
- row (default): Items flow horizontally from left to right
- row-reverse: Items flow horizontally from right to left
- column: Items flow vertically from top to bottom
- column-reverse: Items flow vertically from bottom to top
Flex-Wrap Values
The flex-wrap component determines wrapping behavior:
- nowrap (default): Items stay on one line
- wrap: Items wrap to new lines as needed
- wrap-reverse: Items wrap to new lines in reverse order
Complete Flex-Flow Property Values
Here are all possible combinations of flex-flow values:
/* Direction only */
flex-flow: row;
flex-flow: column;
flex-flow: row-reverse;
flex-flow: column-reverse;
/* Wrap only */
flex-flow: wrap;
flex-flow: nowrap;
flex-flow: wrap-reverse;
/* Direction and wrap combined */
flex-flow: row wrap;
flex-flow: column nowrap;
flex-flow: row-reverse wrap;
flex-flow: column-reverse wrap-reverse;Interactive Examples
Example 1: Basic Flex-Flow Demonstration
Example 2: Responsive Card Layout
Card 1
This card demonstrates how flex-flow: row wrap creates a responsive layout that adapts to container width.
Card 2
Cards automatically wrap to new lines when there isn’t enough horizontal space.
Card 3
Each card maintains its minimum width while growing to fill available space.
Card 4
This creates a flexible, responsive grid without media queries.
.card-container {
display: flex;
flex-flow: row wrap;
gap: 20px;
}
.card {
flex: 1 1 250px;
min-width: 250px;
}Practical Use Cases
1. Navigation Menu
.nav-menu {
display: flex;
flex-flow: row wrap;
}2. Image Gallery
.gallery {
display: flex;
flex-flow: row wrap;
gap: 10px;
}
.gallery-item {
flex: 1 1 200px;
}Comparison: Flex-Flow vs Individual Properties
Traditional Approach
/* Using separate properties */
.container {
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}Shorthand Approach
/* Using flex-flow shorthand */
.container {
display: flex;
flex-flow: row wrap;
}Benefits of using flex-flow:
- Reduces CSS code length
- Improves code readability
- Ensures consistency between direction and wrap properties
- Easier to maintain and update
Common Patterns and Best Practices
1. Responsive Design Pattern
/* Mobile-first approach */
.container {
display: flex;
flex-flow: column nowrap;
}
/* Tablet and desktop */
@media (min-width: 768px) {
.container {
flex-flow: row wrap;
}
}2. Form Layout Pattern
.form-container {
display: flex;
flex-flow: column wrap;
}
.form-row {
display: flex;
flex-flow: row wrap;
}Browser Support and Compatibility
The flex-flow property enjoys excellent browser support:
- Chrome: 29+ (full support)
- Firefox: 28+ (full support)
- Safari: 9+ (full support)
- Edge: 12+ (full support)
- Internet Explorer: 11+ (full support)
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Issue 1: Items Not Wrapping
Problem: Flex items overflow container instead of wrapping.
Solution: Ensure you’re using wrap in your flex-flow value:
/* Wrong */
flex-flow: row nowrap;
/* Correct */
flex-flow: row wrap;Issue 2: Unexpected Direction
Problem: Items flow in wrong direction.
Solution: Check the order of values in flex-flow:
/* Direction comes first, then wrap */
flex-flow: column wrap; /* Correct */
flex-flow: wrap column; /* This won't work as expected */Performance Considerations
Using flex-flow shorthand offers several performance benefits:
- Reduced CSS Size: Shorthand properties result in smaller CSS files
- Faster Parsing: Browsers can parse shorthand properties more efficiently
- Better Caching: Smaller CSS files improve caching performance
- Maintenance: Single property changes are easier to track and debug
Advanced Techniques
Dynamic Flex-Flow with CSS Variables
:root {
--flex-direction: row;
--flex-wrap: wrap;
}
.dynamic-container {
display: flex;
flex-flow: var(--flex-direction) var(--flex-wrap);
}
/* Change layout with media queries */
@media (max-width: 768px) {
:root {
--flex-direction: column;
--flex-wrap: nowrap;
}
}Flex-Flow with Container Queries
@container (min-width: 400px) {
.responsive-container {
flex-flow: row wrap;
}
}
@container (max-width: 399px) {
.responsive-container {
flex-flow: column nowrap;
}
}Conclusion
The CSS flex-flow property is an essential tool for modern web developers, offering a clean and efficient way to control flexbox layouts. By combining flex-direction and flex-wrap into a single property, it simplifies your CSS while providing powerful layout control.
Key takeaways:
- Use
flex-flowto set both direction and wrap behavior in one declaration - Most common patterns are
row wrapfor responsive layouts andcolumn nowrapfor vertical stacking - Combine with other flex properties for complete layout control
- Test across different screen sizes to ensure responsive behavior
- Consider using CSS variables for dynamic layouts
Master the flex-flow property, and you’ll have a powerful tool for creating flexible, responsive layouts that adapt beautifully to any screen size or container width.
- What is CSS Flex-Flow?
- Understanding the Component Properties
- Complete Flex-Flow Property Values
- Interactive Examples
- Practical Use Cases
- Comparison: Flex-Flow vs Individual Properties
- Common Patterns and Best Practices
- Browser Support and Compatibility
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Performance Considerations
- Advanced Techniques
- Conclusion