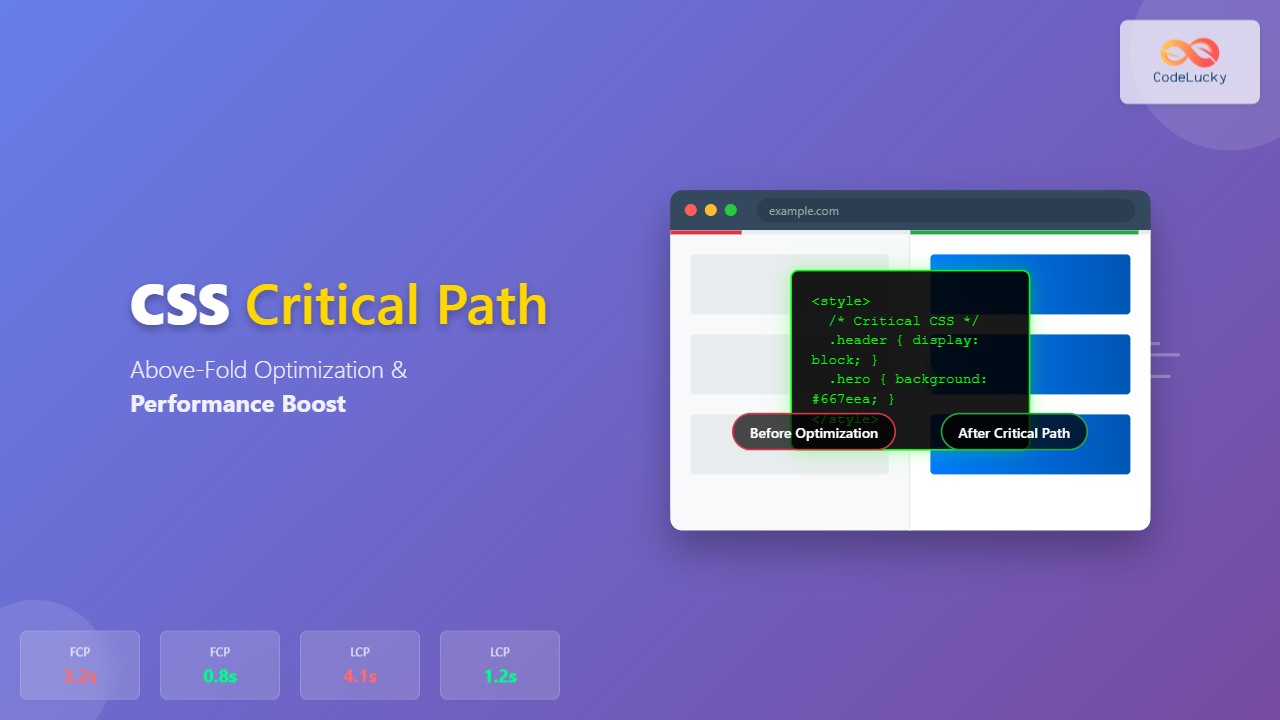
The critical rendering path represents the sequence of steps browsers take to convert HTML, CSS, and JavaScript into pixels on the screen. CSS critical path optimization focuses on prioritizing the CSS needed to render above-the-fold content, dramatically reducing page load times and improving user experience.
Understanding the Critical Rendering Path
When a browser loads a webpage, it follows a specific sequence: parsing HTML, building the DOM tree, parsing CSS to create the CSSOM (CSS Object Model), combining both to form the render tree, calculating layout, and finally painting pixels. CSS is render-blocking by default, meaning the browser won’t display content until all CSS is downloaded and parsed.
Critical Path Timeline
Traditional rendering blocks on all CSS
Identifying Above-Fold Content
Above-the-fold content refers to the portion of a webpage visible without scrolling. This typically includes the header, navigation, hero section, and initial content blocks. The goal is to identify and prioritize CSS that styles these elements.
Tools for Critical CSS Identification
Several tools can help identify critical CSS:
- Chrome DevTools Coverage Tab: Shows which CSS rules are used during initial page load
- Critical CSS generators: Tools like Penthouse, Critical, or online generators
- Lighthouse audits: Provides suggestions for render-blocking resources
- Manual analysis: Examining viewport dimensions and content structure
Manual Critical CSS Extraction Example
Let’s examine a typical webpage structure and identify critical CSS:
<!-- HTML Structure -->
<header class="main-header">
<nav class="navbar">...</nav>
</header>
<main>
<section class="hero-section">...</section>
<section class="content-section">...</section>
</main>For this structure, critical CSS would include styles for .main-header, .navbar, and .hero-section, while .content-section styles could be deferred if they’re below the fold.
CSS Critical Path Implementation Strategies
1. Inline Critical CSS
The most effective approach is inlining critical CSS directly in the HTML head. This eliminates the render-blocking request for above-fold styles:
<head>
<style>
/* Critical CSS - Inlined */
.main-header {
background: #fff;
box-shadow: 0 2px 4px rgba(0,0,0,0.1);
position: fixed;
top: 0;
width: 100%;
z-index: 1000;
}
.navbar {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
padding: 1rem 2rem;
max-width: 1200px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.hero-section {
background: linear-gradient(135deg, #667eea 0%, #764ba2 100%);
color: white;
text-align: center;
padding: 8rem 2rem 4rem;
margin-top: 80px; /* Account for fixed header */
}
</style>
</head>2. Asynchronous CSS Loading
Load non-critical CSS asynchronously to prevent render blocking:
<!-- Preload non-critical CSS -->
<link rel="preload" href="styles.css" as="style" onload="this.onload=null;this.rel='stylesheet'">
<noscript><link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css"></noscript>
<!-- Alternative: Load with JavaScript -->
<script>
function loadCSS(href) {
const link = document.createElement('link');
link.rel = 'stylesheet';
link.href = href;
document.head.appendChild(link);
}
// Load after critical path
window.addEventListener('load', () => {
loadCSS('non-critical.css');
});
</script>3. Media Query Optimization
Use media queries to conditionally load CSS based on device characteristics:
<!-- Critical CSS for all devices -->
<style>
/* Base critical styles */
.header { display: block; }
</style>
<!-- Device-specific non-critical CSS -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="mobile.css" media="(max-width: 768px)">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="desktop.css" media="(min-width: 769px)">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="print.css" media="print">Interactive Critical Path Analyzer
Here’s an interactive tool to demonstrate critical path optimization:
Critical Path Simulator
Timeline Visualization
Performance Metrics
Advanced Optimization Techniques
Resource Hints
Leverage browser resource hints to optimize CSS loading:
<!-- DNS prefetch for external CSS -->
<link rel="dns-prefetch" href="//fonts.googleapis.com">
<!-- Preconnect to establish early connection -->
<link rel="preconnect" href="https://fonts.gstatic.com" crossorigin>
<!-- Prefetch non-critical resources -->
<link rel="prefetch" href="secondary-styles.css">
<!-- Preload critical resources -->
<link rel="preload" href="critical-fonts.woff2" as="font" type="font/woff2" crossorigin>CSS Containment
Use CSS containment to optimize rendering performance:
/* Contain layout and style changes */
.article-section {
contain: layout style;
}
/* Contain paint operations */
.carousel-item {
contain: paint;
}
/* Strict containment for isolated components */
.widget {
contain: strict;
}Performance Measurement and Monitoring
Core Web Vitals Impact
Critical path optimization directly affects Core Web Vitals:
- First Contentful Paint (FCP): Reduced by inlining critical CSS
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Improved through faster above-fold rendering
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Minimized by including layout-affecting styles in critical CSS
Measurement Tools
Essential Performance Tools
Built-in performance profiling and coverage analysis
Automated performance testing in CI/CD pipelines
Detailed waterfall analysis and filmstrip view
Track actual user experience metrics
Build Process Integration
Automated Critical CSS Extraction
Integrate critical CSS extraction into your build process:
// webpack.config.js with critical CSS plugin
const HtmlCriticalWebpackPlugin = require('html-critical-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new HtmlCriticalWebpackPlugin({
base: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
src: 'index.html',
dest: 'index.html',
inline: true,
minify: true,
extract: true,
width: 1300,
height: 900,
penthouse: {
blockJSRequests: false,
}
})
]
};Gulp Task Example
const gulp = require('gulp');
const critical = require('critical');
gulp.task('critical', () => {
return critical.generate({
inline: true,
base: 'dist/',
src: 'index.html',
dest: 'index-critical.html',
dimensions: [
{ width: 320, height: 480 },
{ width: 768, height: 1024 },
{ width: 1280, height: 960 }
],
penthouse: {
timeout: 30000,
pageLoadSkipTimeout: 5000
}
});
});Common Pitfalls and Solutions
Over-Inlining CSS
Avoid inlining too much CSS, which can increase HTML size and hurt caching. Keep critical CSS under 14KB for optimal performance.
Dynamic Content Considerations
For dynamic content, consider using CSS custom properties for critical values:
:root {
--hero-bg: url('default-hero.jpg');
--brand-color: #007bff;
}
.hero-section {
background-image: var(--hero-bg);
background-color: var(--brand-color);
}
/* Update via JavaScript when content loads */
document.documentElement.style.setProperty('--hero-bg', 'url("dynamic-hero.jpg")');Font Loading Optimization
Include font-face declarations in critical CSS with proper fallbacks:
@font-face {
font-family: 'CustomFont';
src: url('font.woff2') format('woff2');
font-display: swap;
}
body {
font-family: 'CustomFont', 'Helvetica Neue', Arial, sans-serif;
}
/* Optional: Preload critical font */
<link rel="preload" href="font.woff2" as="font" type="font/woff2" crossorigin>Best Practices Summary
Critical Path Optimization Checklist
Identification
- ✓ Analyze above-fold content
- ✓ Use coverage tools
- ✓ Measure viewport dimensions
- ✓ Test on multiple devices
Implementation
- ✓ Inline critical CSS
- ✓ Defer non-critical CSS
- ✓ Use resource hints
- ✓ Optimize font loading
Monitoring
- ✓ Track Core Web Vitals
- ✓ Monitor FCP and LCP
- ✓ Set performance budgets
- ✓ Automate testing
Conclusion
CSS critical path optimization is essential for modern web performance. By identifying and prioritizing above-the-fold CSS, implementing proper loading strategies, and continuously monitoring performance metrics, you can significantly improve user experience and search engine rankings. The techniques covered in this guide provide a comprehensive approach to mastering critical path optimization, from basic inlining to advanced build process integration.
Remember that optimization is an iterative process. Regularly audit your critical path, measure performance impacts, and adjust your strategy based on real-world usage patterns. The investment in critical path optimization pays dividends in user satisfaction, conversion rates, and overall site performance.