Continuous Integration (CI) has revolutionized how development teams collaborate, integrate code changes, and deliver software. As a cornerstone of modern Agile development practices, CI automates the process of merging code changes from multiple developers into a shared repository, ensuring that integration issues are caught early and resolved quickly.
In today’s fast-paced development environment, manual code integration processes are not only time-consuming but also prone to errors that can derail entire projects. This comprehensive guide explores how continuous integration transforms development workflows, the tools that make it possible, and the best practices that ensure successful implementation.
What is Continuous Integration?
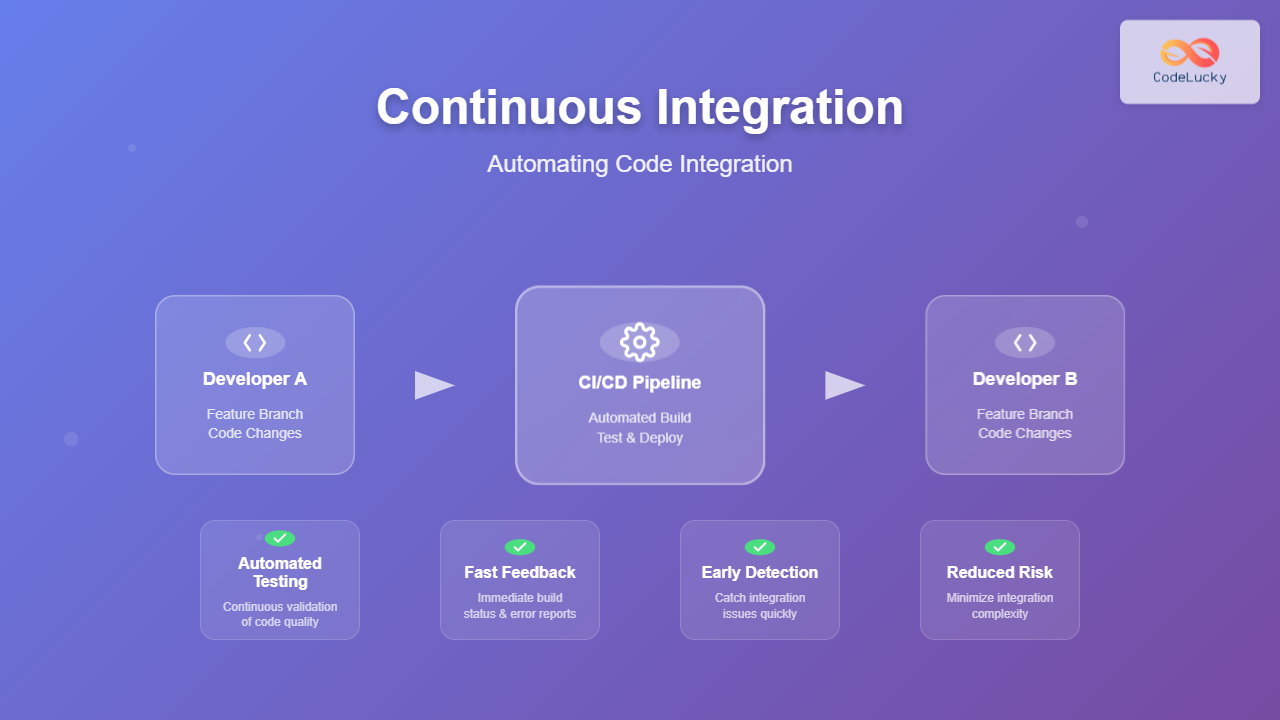
Continuous Integration is a software development practice where developers regularly merge their code changes into a central repository, followed by automated builds and tests. The primary goal is to detect integration issues as early as possible, making them easier and less expensive to fix.
Unlike traditional development approaches where integration happens at the end of a development cycle, CI promotes frequent integration—often multiple times per day. This approach ensures that the codebase remains in a deployable state and reduces the complexity of merging changes from different team members.
Core Principles of Continuous Integration
The foundation of effective CI rests on several key principles that guide implementation and daily practices:
Frequent Code Commits: Developers commit code changes to the shared repository at least once daily, preventing the accumulation of conflicting changes that become difficult to merge.
Automated Build Process: Every code commit triggers an automated build process that compiles the application and identifies compilation errors immediately.
Comprehensive Test Automation: Automated tests run with every build, ensuring that new changes don’t break existing functionality and meet quality standards.
Fast Feedback Loops: The CI system provides rapid feedback to developers about build status, test results, and integration issues, enabling quick resolution.
Shared Responsibility: All team members are responsible for maintaining the health of the shared codebase and addressing integration issues promptly.
Benefits of Continuous Integration
Organizations implementing CI experience significant improvements in development efficiency, code quality, and team collaboration. These benefits compound over time, creating substantial value for development teams and businesses.
Reduced Integration Risk
Traditional development approaches often result in “integration hell”—a period where merging code from different developers becomes extremely complex and time-consuming. CI eliminates this problem by integrating changes continuously, making each integration smaller and more manageable.
When integration happens frequently, conflicts are smaller in scope and easier to resolve. Developers can address issues while the context is still fresh in their minds, leading to faster resolution times and higher code quality.
Early Bug Detection
Automated testing in CI pipelines catches bugs immediately after they’re introduced, rather than weeks or months later during integration phases. This early detection significantly reduces the cost of bug fixes, as issues are resolved when they’re simple and localized.
The immediate feedback helps developers maintain focus and productivity, as they don’t need to context-switch between different features when addressing bugs discovered much later in the development cycle.
Improved Code Quality
CI enforces consistent code quality standards through automated testing, code analysis, and formatting checks. Every code change must pass these quality gates before integration, ensuring the codebase maintains high standards throughout development.
Code review processes integrate seamlessly with CI systems, allowing teams to combine human insight with automated validation for comprehensive quality assurance.
Faster Time to Market
By maintaining a consistently deployable codebase, CI enables teams to release features and fixes more frequently. The reduced integration overhead and faster bug resolution contribute to shorter development cycles and quicker delivery of value to users.
Essential Components of a CI System
A robust CI system comprises several interconnected components that work together to automate the integration process and provide comprehensive feedback to development teams.
Version Control System
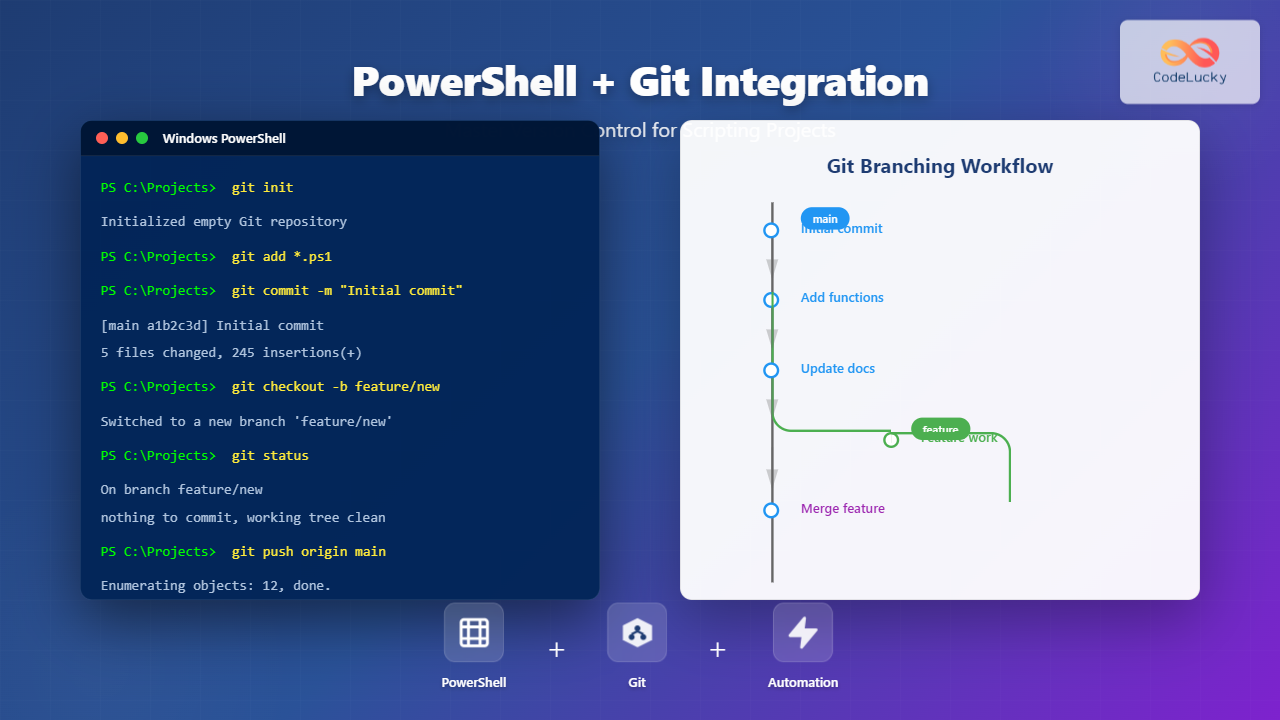
The version control system serves as the central hub for all code changes and the trigger point for CI processes. Modern distributed version control systems like Git provide the foundation for effective CI implementation.
Branching strategies play a crucial role in CI success. Popular approaches include feature branching, where developers work on isolated feature branches before merging to the main branch, and trunk-based development, where all developers commit directly to the main branch with feature flags controlling functionality exposure.
Build Automation
Automated build systems compile source code, manage dependencies, and package applications without manual intervention. Build scripts should be version-controlled alongside the application code, ensuring consistency across different environments and team members.
Modern build tools support incremental builds, dependency caching, and parallel execution to minimize build times and provide faster feedback to developers.
Automated Testing Framework
Comprehensive test automation forms the backbone of CI validation. The testing pyramid provides a strategic approach to test coverage:
Unit Tests: Fast, isolated tests that validate individual components and functions. These tests run quickly and provide immediate feedback about code correctness.
Integration Tests: Tests that validate interactions between different components, ensuring that integrated parts work correctly together.
End-to-End Tests: Comprehensive tests that validate complete user workflows, ensuring the application functions correctly from a user perspective.
CI Server and Orchestration
The CI server orchestrates the entire integration process, monitoring version control for changes, triggering builds, running tests, and reporting results. Modern CI platforms provide scalable infrastructure, extensive integrations, and sophisticated pipeline management capabilities.
Popular CI Tools and Platforms
The CI ecosystem offers numerous tools and platforms, each with unique strengths and ideal use cases. Understanding these options helps teams select the most appropriate solution for their specific requirements.
Jenkins
Jenkins remains one of the most popular open-source CI platforms, offering extensive customization through plugins and support for virtually any development stack. Its flexibility makes it ideal for complex enterprise environments with specific integration requirements.
Jenkins provides distributed build capabilities, allowing teams to scale their CI infrastructure across multiple machines and environments. The extensive plugin ecosystem enables integration with virtually any tool or service in the development workflow.
GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions offers seamless integration with GitHub repositories, providing built-in CI/CD capabilities without external tool configuration. The platform supports workflows defined in YAML files stored alongside application code.
The marketplace of pre-built actions accelerates pipeline development, while the tight integration with GitHub’s ecosystem simplifies authentication, notifications, and deployment processes.
GitLab CI/CD
GitLab provides a complete DevOps platform with integrated CI/CD capabilities. The platform offers built-in container registry, security scanning, and deployment features, creating a unified development experience.
GitLab’s auto-scaling capabilities and Kubernetes integration make it particularly attractive for cloud-native applications and containerized workloads.
Azure DevOps
Microsoft’s Azure DevOps platform provides comprehensive CI/CD capabilities alongside project management, version control, and testing tools. The platform integrates seamlessly with Microsoft’s development ecosystem while supporting multi-platform development.
Azure Pipelines support both cloud-hosted and self-hosted agents, providing flexibility in infrastructure management and compliance requirements.
Implementing Continuous Integration
Successful CI implementation requires careful planning, gradual adoption, and continuous refinement. Teams should approach implementation systematically, focusing on foundational elements before adding advanced features.
Setting Up Version Control
Establish a clear branching strategy that supports your team’s workflow and CI goals. Feature branching allows developers to work in isolation while trunk-based development promotes more frequent integration.
Configure branch protection rules to enforce CI requirements, preventing direct pushes to main branches and requiring successful builds before merging pull requests.
Creating Build Scripts
Develop automated build scripts that can run consistently across different environments. These scripts should handle dependency management, compilation, testing, and packaging without manual intervention.
Use build tools appropriate for your technology stack, such as Maven or Gradle for Java, npm or Yarn for JavaScript, or Make for C/C++ projects. Ensure build scripts are version-controlled and documented for team consistency.
Configuring Automated Testing
Start with a solid foundation of unit tests that provide fast feedback about code correctness. Gradually add integration and end-to-end tests as the CI process matures.
Implement test parallelization and selective test execution to minimize CI pipeline duration while maintaining comprehensive coverage. Use test reporting tools to provide clear visibility into test results and coverage metrics.
Pipeline Configuration
Design CI pipelines that balance thoroughness with speed. Consider implementing pipeline stages that allow fast feedback for common issues while running more comprehensive validations in parallel or subsequent stages.
Configure appropriate triggers for different types of changes, such as running full test suites for main branch changes while using lighter validation for feature branch commits.
Best Practices for Continuous Integration
Successful CI implementation extends beyond tool configuration to encompass team practices, workflow optimization, and continuous improvement initiatives.
Commit Frequently and Early
Encourage developers to commit code changes at least once daily, even for incomplete features. Use feature flags or branching strategies to prevent incomplete functionality from affecting production systems while maintaining integration frequency.
Small, frequent commits are easier to review, test, and debug than large, infrequent changes that accumulate multiple modifications across different system components.
Maintain Fast Build Times
Keep CI pipeline execution times under 10 minutes to maintain developer productivity and encourage frequent commits. Use techniques like incremental builds, dependency caching, and parallel execution to optimize performance.
Monitor build performance metrics and continuously optimize bottlenecks. Consider splitting lengthy pipelines into fast feedback loops for critical validations and slower comprehensive checks that run in parallel.
Fix Broken Builds Immediately
Treat broken builds as critical issues that require immediate attention. Establish team protocols for build failures, including notification systems and escalation procedures for persistent issues.
Consider implementing build monitoring dashboards that provide real-time visibility into build status and historical trends, helping teams identify patterns and improvement opportunities.
Comprehensive Test Coverage
Maintain sufficient test coverage to catch regressions while avoiding excessive test maintenance overhead. Focus on testing critical business logic and integration points rather than achieving arbitrary coverage percentages.
Regularly review and refactor tests to ensure they remain valuable and maintainable as the codebase evolves. Remove or update tests that no longer provide meaningful validation.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Teams implementing CI often encounter predictable challenges that can derail adoption if not addressed proactively. Understanding these challenges and their solutions helps ensure successful implementation.
Flaky Tests
Intermittent test failures undermine confidence in CI systems and create alert fatigue among team members. Address flaky tests by improving test isolation, managing external dependencies, and implementing retry mechanisms for genuinely intermittent failures.
Establish processes for identifying, tracking, and systematically addressing flaky tests. Consider quarantining consistently problematic tests while they’re being fixed to prevent them from blocking development progress.
Slow Build Times
Long CI pipeline execution times discourage frequent commits and reduce development velocity. Optimize build performance through caching strategies, incremental builds, and parallel execution.
Consider implementing tiered testing strategies where fast smoke tests provide immediate feedback while comprehensive test suites run in background processes.
Integration Complexity
Complex applications with multiple dependencies can create challenging integration scenarios. Use containerization, infrastructure as code, and service virtualization to create consistent, reproducible integration environments.
Implement comprehensive monitoring and logging in CI environments to quickly diagnose integration issues and understand system behavior during testing.
Measuring CI Success
Effective measurement helps teams understand CI impact and identify improvement opportunities. Key metrics provide insights into both technical performance and business value delivery.
Technical Metrics
Build frequency indicates how often the team integrates changes, with higher frequency generally correlating with reduced integration risk. Build success rate measures CI system reliability and code quality trends.
Build duration affects developer productivity and feedback loop effectiveness. Mean time to recovery (MTTR) for build failures indicates team responsiveness and CI system resilience.
Business Metrics
Deployment frequency and lead time measure the speed of value delivery to users. Change failure rate indicates the quality of releases, while time to restore service measures organizational resilience.
These metrics align CI practices with business objectives, demonstrating the value of engineering investments in automation and process improvement.
Advanced CI Concepts
As teams mature in their CI practices, advanced concepts can further optimize development workflows and system reliability.
Pipeline as Code
Defining CI pipelines in version-controlled code ensures consistency, enables collaborative improvement, and provides audit trails for pipeline changes. This approach treats infrastructure configuration with the same rigor as application code.
Deployment Integration
Extending CI into continuous deployment creates end-to-end automation from code commit to production release. This integration requires sophisticated testing strategies, feature flagging, and rollback mechanisms.
Security Integration
Incorporating security scanning, dependency vulnerability checks, and compliance validation into CI pipelines shifts security left in the development process, catching issues early when they’re easier and less expensive to address.
Conclusion
Continuous Integration represents a fundamental shift in how development teams approach code integration and quality assurance. By automating integration processes, providing rapid feedback, and maintaining consistently deployable codebases, CI enables teams to deliver higher-quality software more efficiently.
Successful CI implementation requires commitment to cultural change, investment in automation infrastructure, and continuous refinement of processes and practices. Teams that embrace CI principles and implement them systematically experience significant improvements in development velocity, code quality, and team collaboration.
As software development continues evolving toward more frequent releases and complex distributed systems, continuous integration remains an essential foundation for effective development practices. The investment in CI capabilities pays dividends through reduced integration risk, faster bug detection, and improved team productivity that compounds over time.