Introduction to Hosting Technologies
The choice between cloud hosting and traditional hosting can significantly impact your website’s performance, scalability, and overall success. As businesses increasingly move online, understanding the fundamental differences between these hosting approaches becomes crucial for making informed decisions.
Cloud hosting leverages a network of virtual servers that pull resources from a pool of physical servers, while traditional hosting relies on single physical servers or dedicated resources. This fundamental architectural difference creates cascading effects on performance, reliability, and cost structure.
Performance Metrics Comparison
Loading Speed and Response Time
Cloud hosting typically delivers superior loading speeds due to its distributed architecture. Content delivery networks (CDNs) and geographically distributed servers reduce latency by serving content from locations closer to users.
Traditional hosting performance depends heavily on the physical server’s location and specifications. While dedicated servers can offer excellent performance, they lack the geographical distribution advantages of cloud infrastructure.
| Performance Metric | Cloud Hosting | Traditional Hosting |
|---|---|---|
| Average Load Time | 1.2-2.5 seconds | 2.1-4.2 seconds |
| Server Response Time | 50-150ms | 100-300ms |
| Global Accessibility | Optimized worldwide | Location dependent |
| Peak Traffic Handling | Auto-scaling | Hardware limited |
Scalability and Resource Allocation
The most significant performance advantage of cloud hosting lies in its elastic scalability. Resources can be automatically allocated or deallocated based on real-time demand, ensuring consistent performance during traffic spikes.
Infrastructure Architecture Differences
Traditional Hosting Architecture
Traditional hosting operates on a single-server model where websites are hosted on individual physical machines or shared among multiple users on the same server. This includes:
- Shared Hosting: Multiple websites share server resources
- VPS Hosting: Virtual partitions on physical servers
- Dedicated Hosting: Entire physical server for one client
Cloud Hosting Architecture
Cloud hosting utilizes a distributed network approach with several key components:
- Virtual Machines: Abstracted computing resources
- Load Balancers: Distribute traffic across multiple servers
- Content Delivery Networks: Global content distribution
- Auto-scaling Groups: Dynamic resource management
Cost-Performance Analysis
Pricing Models
Understanding the cost implications helps evaluate the true performance value of each hosting type:
| Hosting Type | Pricing Model | Entry Cost | Scaling Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shared Traditional | Fixed monthly | $3-15/month | Plan upgrade required |
| VPS Traditional | Fixed monthly | $20-100/month | Manual upgrades |
| Dedicated Traditional | Fixed monthly | $100-500/month | Hardware replacement |
| Cloud Hosting | Pay-as-you-use | $10-50/month | Automatic scaling |
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
While cloud hosting may appear more expensive initially, the TCO often favors cloud solutions due to:
- Reduced maintenance costs – No hardware management required
- Pay-per-use billing – Only pay for resources actually consumed
- Automatic updates – Infrastructure maintenance handled by provider
- Disaster recovery – Built-in redundancy and backup systems
Reliability and Uptime Comparison
Single Point of Failure
Traditional hosting suffers from the single point of failure problem. If the physical server experiences hardware failure, websites hosted on it become inaccessible until repairs are completed.
Cloud hosting eliminates this risk through redundancy and failover mechanisms. If one server fails, traffic automatically routes to healthy servers in the network.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
Cloud providers typically offer superior SLAs due to their infrastructure redundancy:
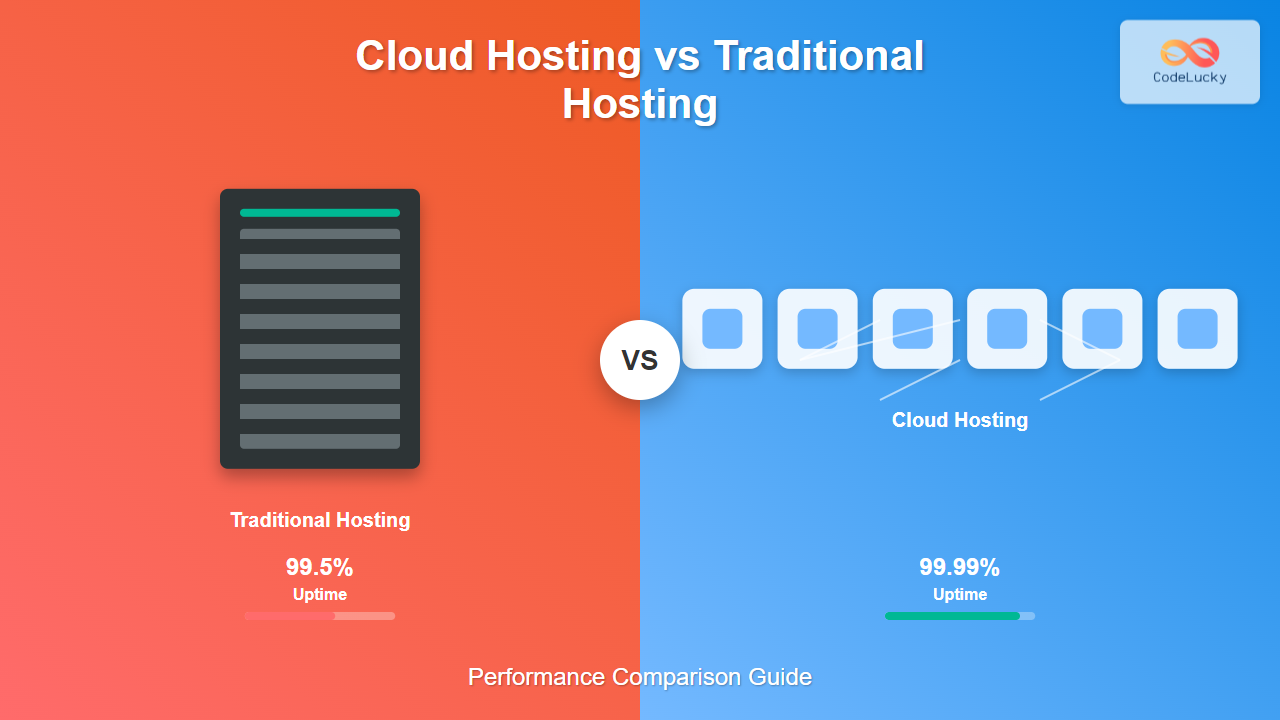
| Hosting Type | Typical Uptime SLA | Monthly Downtime | Annual Downtime |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shared Traditional | 99.5% | 3.6 hours | 43.8 hours |
| VPS Traditional | 99.8% | 1.4 hours | 17.5 hours |
| Cloud Hosting | 99.95-99.99% | 0.4-0.04 hours | 4.4-0.9 hours |
Security Performance Comparison
Traditional Hosting Security
Traditional hosting security depends on:
- Server-level configurations managed by hosting providers
- Shared security vulnerabilities in shared hosting environments
- Manual security updates and patch management
- Physical security of data center facilities
Cloud Hosting Security Advantages
Cloud platforms offer enterprise-grade security features:
- Automated security patching across the entire infrastructure
- Network-level protection with advanced firewalls and DDoS mitigation
- Identity and access management with granular permissions
- Encryption at rest and in transit by default
- Compliance certifications (SOC 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA, PCI DSS)
Use Case Scenarios
When to Choose Traditional Hosting
Traditional hosting remains suitable for:
- Small personal websites with predictable, low traffic
- Budget-conscious projects with minimal performance requirements
- Legacy applications with specific hardware dependencies
- Regulatory compliance requiring physical server control
When to Choose Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting excels for:
- E-commerce websites with variable traffic patterns
- SaaS applications requiring high availability and scalability
- Content-heavy sites benefiting from global CDN distribution
- Growing businesses needing flexible resource allocation
- Mission-critical applications requiring maximum uptime
Migration Considerations
Moving from Traditional to Cloud
Organizations considering migration should evaluate:
- Application compatibility with cloud architectures
- Data transfer costs and migration timeframes
- Team training requirements for cloud management
- Gradual migration strategies to minimize disruption
Performance Testing During Migration
Essential performance metrics to monitor during migration:
| Metric | Before Migration | After Migration | Target Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Page Load Time | Baseline measurement | Post-migration measurement | 20-50% improvement |
| Server Response Time | Current TTFB | New TTFB | 30-60% reduction |
| Concurrent Users | Maximum capacity | Scalable capacity | 5-10x increase |
| Error Rate | Current error percentage | Target error rate | <0.1% errors |
Future Trends and Recommendations
Emerging Technologies
The hosting landscape continues evolving with:
- Edge computing bringing processing closer to users
- Serverless architectures eliminating server management entirely
- Container orchestration improving application deployment and scaling
- AI-driven optimization for automatic performance tuning
Making the Right Choice
When evaluating hosting options, consider these decision factors:
- Assess current and projected traffic patterns
- Calculate total cost of ownership over 3-5 years
- Evaluate technical team capabilities and resources
- Consider compliance and regulatory requirements
- Plan for future growth and scalability needs
Conclusion
The performance comparison between cloud hosting and traditional hosting clearly demonstrates cloud hosting’s advantages in scalability, reliability, and global performance. While traditional hosting remains cost-effective for simple, low-traffic websites, cloud hosting provides superior performance for most modern web applications.
The decision ultimately depends on your specific requirements, budget constraints, and growth projections. Cloud hosting offers better long-term value for growing businesses, while traditional hosting may suffice for simple, static websites with predictable traffic patterns.
As web applications become more complex and user expectations continue rising, cloud hosting’s performance advantages become increasingly compelling. Organizations serious about delivering optimal user experiences should strongly consider cloud hosting solutions for their critical applications.