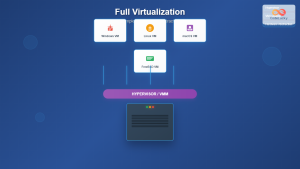
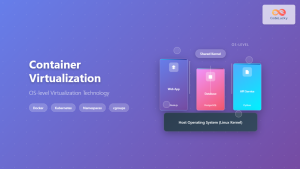
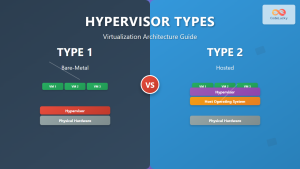
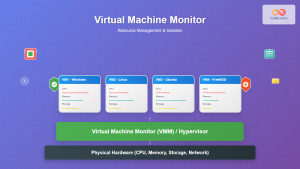
Virtual machine cloning is a fundamental virtualization technique that creates identical copies of existing VMs, enabling rapid deployment, testing environments, and disaster recovery scenarios. This comprehensive guide explores various VM duplication methods, their use cases, and implementation across different virtualization platforms.
Understanding Virtual Machine Cloning
VM cloning creates an exact replica of a virtual machine, including its operating system, applications, configurations, and data. Unlike traditional backup methods, cloning produces a fully functional, bootable copy that can run independently or alongside the original VM.
Key Benefits of VM Cloning
- Rapid Deployment: Deploy pre-configured environments in minutes instead of hours
- Consistent Environments: Ensure identical configurations across development, testing, and production
- Resource Efficiency: Save time and reduce manual configuration errors
- Disaster Recovery: Create backup copies for quick restoration
- Testing Isolation: Safely test changes without affecting production systems
Types of Virtual Machine Clones
Full Clone (Independent Clone)
A full clone creates a complete, independent copy of the source VM, including all virtual disk files. This type provides maximum flexibility and independence but requires significant storage space.
Characteristics:
- Complete independence from source VM
- Requires full disk space allocation
- Can be moved to different hosts
- Performance identical to original
- Higher storage overhead
VMware vSphere Full Clone Example:
# Using PowerCLI
New-VM -Name "WebServer-Clone" -VM "WebServer-Original" -VMHost "ESXi-Host01" -Datastore "DataStore01"
# Using vCenter GUI:
# 1. Right-click source VM → Clone → Clone to Virtual Machine
# 2. Select "Create a full clone"
# 3. Configure name, location, and compute resources
# 4. Complete the wizard
Linked Clone (Dependent Clone)
Linked clones share virtual disk files with the parent VM through a snapshot mechanism. They consume minimal storage initially but depend on the parent VM’s availability.
VirtualBox Linked Clone Creation:
# Create snapshot first
VBoxManage snapshot "OriginalVM" take "BaseSnapshot"
# Create linked clone
VBoxManage clonevm "OriginalVM" --snapshot "BaseSnapshot" --name "LinkedClone01" --options link --register
# Alternative GUI method:
# 1. Create snapshot of source VM
# 2. Machine → Clone → Select "Linked clone"
# 3. Choose base snapshot and configure settings
Template-Based Cloning
Templates are master images optimized for cloning, typically with generalized configurations and removed unique identifiers. They provide the most efficient method for mass deployment.
Creating and Using Templates:
# VMware Template Creation
# 1. Prepare source VM (sysprep for Windows, generalize for Linux)
# 2. Convert to template
Convert-VM -VM "SourceVM" -ToTemplate
# Deploy from template
New-VM -Name "NewServer" -Template "ServerTemplate" -VMHost "ESXi-Host" -Datastore "Storage01"
Platform-Specific Cloning Methods
VMware vSphere Cloning
VMware offers multiple cloning approaches through vCenter Server and ESXi hosts:
GUI-Based Cloning Process:
- Access vCenter: Log into vSphere Client
- Select Source VM: Right-click the VM to clone
- Clone Options: Choose “Clone to Virtual Machine” or “Clone to Template”
- Configure Clone: Set name, location, and resource allocation
- Customization: Apply guest OS customization if needed
- Complete: Review settings and initiate cloning
Advanced vSphere Cloning Features:
# PowerCLI advanced cloning with customization
$spec = Get-OSCustomizationSpec "WindowsSpec"
New-VM -Name "WebServer-$i" -VM "WebTemplate" -OSCustomizationSpec $spec -VMHost $host -Datastore $datastore
# Bulk cloning script
1..10 | ForEach-Object {
New-VM -Name "TestVM-$_" -VM "BaseVM" -VMHost "ESXi-Host01" -Datastore "FastStorage"
}
Microsoft Hyper-V Cloning
Hyper-V provides export/import functionality and checkpoint-based cloning:
Export-Import Method:
# Export VM
Export-VM -Name "SourceVM" -Path "C:\VMExports\"
# Import as copy
Import-VM -Path "C:\VMExports\SourceVM\Virtual Machines\[GUID].vmcx" -Copy -GenerateNewId -VhdDestinationPath "C:\VMs\ClonedVM\"
# Hyper-V Manager GUI:
# 1. Right-click VM → Export
# 2. Select export location
# 3. Use Import Virtual Machine wizard
# 4. Choose "Copy the virtual machine" option
Oracle VirtualBox Cloning
VirtualBox offers straightforward cloning through GUI and command-line interfaces:
Command-Line Cloning:
# Full clone with new MAC addresses
VBoxManage clonevm "SourceVM" --name "FullClone" --register
# Linked clone from snapshot
VBoxManage snapshot "SourceVM" take "ClonePoint"
VBoxManage clonevm "SourceVM" --snapshot "ClonePoint" --name "LinkedClone" --options link --register
# Clone with specific settings
VBoxManage clonevm "SourceVM" --name "CustomClone" --basefolder "/path/to/vms" --register
Best Practices for VM Cloning
Pre-Cloning Preparation
Windows Systems:
# Run Sysprep before cloning
cd C:\Windows\System32\Sysprep
sysprep.exe /generalize /oobe /shutdown
# Alternative: Use unattend.xml for automated setup
sysprep.exe /generalize /oobe /shutdown /unattend:C:\unattend.xml
Linux Systems:
# Clear machine-specific identifiers
sudo rm -f /etc/machine-id /var/lib/dbus/machine-id
sudo rm -f /etc/ssh/ssh_host_*
# Clear network configuration
sudo rm -f /etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules
sudo rm -f /etc/netplan/*.yaml
# Clear logs and temporary files
sudo rm -rf /var/log/* /tmp/* /var/tmp/*
sudo history -c && history -w
Post-Cloning Configuration
Essential Post-Clone Tasks:
- Rename Computer: Change hostname and computer name
- Update Network Settings: Assign new IP addresses and DNS
- Regenerate Security Identifiers: Create new SIDs for Windows
- Update Domain Membership: Re-join domain if applicable
- Modify Service Accounts: Update service account passwords
- Validate Applications: Test application functionality
Automated Post-Clone Script Example:
# Windows PowerShell post-clone script
param(
[string]$NewComputerName,
[string]$IPAddress,
[string]$SubnetMask,
[string]$Gateway
)
# Rename computer
Rename-Computer -NewName $NewComputerName -Force
# Configure network
$adapter = Get-NetAdapter | Where-Object {$_.Status -eq "Up"}
Remove-NetIPAddress -InterfaceAlias $adapter.Name -Confirm:$false -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
New-NetIPAddress -InterfaceAlias $adapter.Name -IPAddress $IPAddress -PrefixLength 24 -DefaultGateway $Gateway
# Restart for changes to take effect
Restart-Computer -Force
Performance Optimization and Storage Management
Storage Considerations
Storage Optimization Strategies:
- Thin Provisioning: Allocate storage on-demand
- Deduplication: Eliminate redundant data blocks
- Compression: Reduce storage footprint
- Tiered Storage: Use appropriate storage tiers
Performance Tuning
Clone Performance Optimization:
# VMware storage optimization
# Enable Storage DRS for automatic load balancing
# Configure Storage I/O Control (SIOC)
# Use SSD storage for frequently accessed clones
# VirtualBox performance tuning
VBoxManage modifyvm "VMName" --ioapic on
VBoxManage modifyvm "VMName" --memory 4096
VBoxManage modifyvm "VMName" --vram 128
VBoxManage modifyvm "VMName" --accelerate3d on
Troubleshooting Common Cloning Issues
Network Conflicts
Issue: Multiple VMs with identical MAC addresses or IP configurations
Solution:
# Generate new MAC address (VirtualBox)
VBoxManage modifyvm "ClonedVM" --macaddress1 auto
# Reset network configuration (Linux)
sudo rm /etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules
sudo reboot
Licensing Problems
Issue: Software activation failures due to hardware fingerprint changes
Solution:
- Use volume licensing for enterprise deployments
- Implement KMS activation for Windows
- Consider virtual machine licensing implications
Domain Join Issues
Issue: Cloned VMs cannot join domain due to duplicate SIDs
Solution:
# Generate new SID (Windows)
# Download and run NewSID utility or use Sysprep
sysprep /generalize /oobe /reboot
Security Considerations
Data Sanitization
Before cloning, ensure sensitive data is removed or encrypted:
- Clear browser caches and saved passwords
- Remove personal documents and downloads
- Clear Windows credential store
- Delete SSH keys and certificates
- Remove application-specific data
Access Control
Implement proper access controls for cloned environments:
# Set appropriate permissions
Set-VMSecurity -VMName "ClonedVM" -SecureBootTemplate MicrosoftWindows
Set-VMFirmware -VMName "ClonedVM" -EnableSecureBoot On
Automation and Scripting
Automated Cloning Workflow
PowerShell Automation Script
# Comprehensive VM cloning script
function New-VMClone {
param(
[string]$SourceVM,
[string]$CloneName,
[string]$VMHost,
[string]$Datastore,
[switch]$LinkedClone
)
try {
if ($LinkedClone) {
$snapshot = New-Snapshot -VM $SourceVM -Name "CloneSnapshot-$(Get-Date -Format 'yyyyMMdd-HHmm')"
$clone = New-VM -Name $CloneName -VM $SourceVM -ReferenceSnapshot $snapshot -VMHost $VMHost -Datastore $Datastore
} else {
$clone = New-VM -Name $CloneName -VM $SourceVM -VMHost $VMHost -Datastore $Datastore
}
# Post-clone configuration
Start-VM -VM $clone
Write-Host "Clone '$CloneName' created successfully"
return $clone
}
catch {
Write-Error "Cloning failed: $($_.Exception.Message)"
}
}
# Usage example
New-VMClone -SourceVM "WebTemplate" -CloneName "WebServer-Prod" -VMHost "ESXi01" -Datastore "SSD-Storage"
Monitoring and Maintenance
Clone Lifecycle Management
Establish processes for managing cloned VMs throughout their lifecycle:
- Inventory Tracking: Maintain records of all clones and their purposes
- Update Management: Ensure clones receive security updates
- Resource Monitoring: Track resource usage across clones
- Cleanup Procedures: Remove unnecessary clones to free resources
Performance Monitoring
# Monitor clone performance metrics
Get-Stat -Entity (Get-VM "CloneName") -Stat "cpu.usage.average","mem.usage.average" -Start (Get-Date).AddHours(-24)
# Storage usage tracking
Get-VM | Get-HardDisk | Select-Object @{N="VM";E={$_.Parent}},@{N="HD";E={$_.Name}},@{N="SizeGB";E={$_.CapacityGB}}
Virtual machine cloning is an essential skill for modern IT professionals, enabling efficient deployment, testing, and disaster recovery scenarios. By understanding the different cloning methods, following best practices, and implementing proper automation, organizations can leverage VM cloning to improve operational efficiency while maintaining security and performance standards. Regular monitoring and maintenance ensure that cloned environments continue to serve their intended purposes effectively throughout their lifecycle.