Handling sudden traffic fluctuations on your website or application is a challenge many developers and businesses face. Auto-scaling hosting is the modern solution that allows your infrastructure to automatically adjust resources to meet demand. This article explores everything about auto-scaling hosting — what it is, why it’s essential, how it works, and how you can implement it effectively to handle traffic spikes seamlessly.
What is Auto-Scaling Hosting?
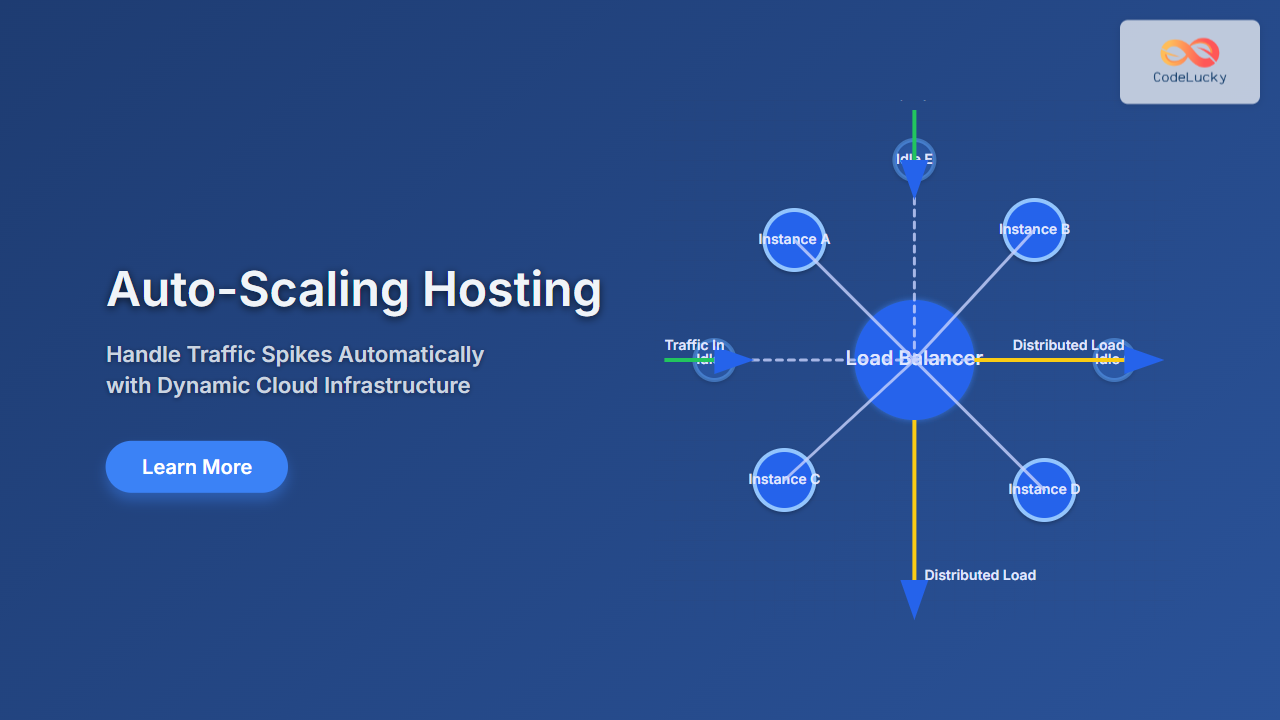
Auto-scaling hosting is a cloud infrastructure feature where server resources like CPUs, memory, and instances increase or decrease dynamically based on traffic or load metrics without manual intervention. It ensures optimal performance during traffic surges and saves cost when demand drops.
Unlike traditional fixed-resource hosting, auto-scaling adapts in real-time to maintain user experience and uptime, preventing crashes or slowdowns caused by unexpected spikes or lulls.
Why Is Auto-Scaling Important?
- Performance Stability: Automatically keeps your app fast and responsive under heavy load.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces over-provisioning by scaling down resources during low traffic.
- Reliability: Avoids downtime by distributing traffic across more instances when demand increases.
- Improved User Experience: Minimizes page load times and errors by adjusting capacity instantly.
How Auto-Scaling Works: A High-Level Overview
Auto-scaling systems monitor predefined performance metrics such as CPU usage, memory consumption, request count, or custom application metrics. When a threshold is crossed, they trigger scaling actions to add or remove server instances or resources.
Types of Auto-Scaling
There are mainly two types of auto-scaling strategies:
- Horizontal Scaling (Scaling Out/In): Adding or removing server instances/nodes. Most common in cloud environments.
- Vertical Scaling (Scaling Up/Down): Increasing or decreasing the resources (CPU, RAM) of an existing instance. Limited by physical machine constraints.
Horizontal scaling is preferred for web applications because it offers better fault tolerance and unlimited scaling potential.
Implementing Auto-Scaling: Example on AWS
Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides a popular Auto Scaling service that integrates with EC2 instances and Elastic Load Balancer.
Step-by-Step Overview
- Create an EC2 Launch Configuration defining the instance type and configuration.
- Set up an Auto Scaling Group connected with the launch configuration, specifying minimum and maximum instances.
- Define Scaling Policies that trigger scale out/in on metrics like CPU utilization.
- Add an Elastic Load Balancer to distribute traffic evenly across instances.
Code Example: Simulating Auto Scaling with Python (Conceptual)
The following Python script simulates monitoring server load and auto-scaling decisions based on CPU usage. This example can be expanded or integrated with cloud SDKs for real deployments.
import time
import random
class AutoScaler:
def __init__(self, min_instances=1, max_instances=5):
self.instances = min_instances
self.min_instances = min_instances
self.max_instances = max_instances
def get_cpu_load(self):
# Simulate collecting CPU load percentage
return random.randint(0, 100)
def scale(self):
load = self.get_cpu_load()
print(f"Current CPU load: {load}% with {self.instances} instances")
if load > 70 and self.instances < self.max_instances:
self.instances += 1
print(f"Scaling up: Increased to {self.instances} instances")
elif load < 30 and self.instances > self.min_instances:
self.instances -= 1
print(f"Scaling down: Decreased to {self.instances} instances")
else:
print("No scaling action required")
auto_scaler = AutoScaler()
for _ in range(10):
auto_scaler.scale()
time.sleep(2)
Interactive Concept: Visualizing Auto-Scaling Behavior
A real-world implementation would involve continuously monitoring metrics and triggering API calls to cloud providers. Interactive dashboards display active instance count and CPU trends for admins to observe the system’s behavior in real time.
Best Practices for Auto-Scaling
- Set Realistic Thresholds: Avoid frequent scaling events by tuning thresholds and cooldown periods.
- Use Load Balancers: Always pair auto-scaling with load balancing to distribute traffic evenly.
- Monitor Critical Metrics: Beyond CPU, monitor memory, network, and custom app metrics.
- Test Your Scaling Policies: Perform load testing to validate scaling responsiveness.
- Security & Cost Control: Use IAM roles and budget alarms to prevent misuse and cost overruns.
When Not to Use Auto-Scaling
Auto-scaling might not be ideal if your application requires:
- Highly consistent hardware specs for licensing or performance.
- Stateful servers that can’t easily share load.
- Extremely predictable and flat traffic profiles.
Conclusion
Auto-scaling hosting is a cornerstone technology for modern web applications, allowing them to handle traffic spikes smoothly without manual intervention. By leveraging dynamic resource management, businesses achieve both high performance and cost efficiency. Whether using cloud providers like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure, understanding and implementing auto-scaling effectively is essential for scalable, resilient web infrastructure.