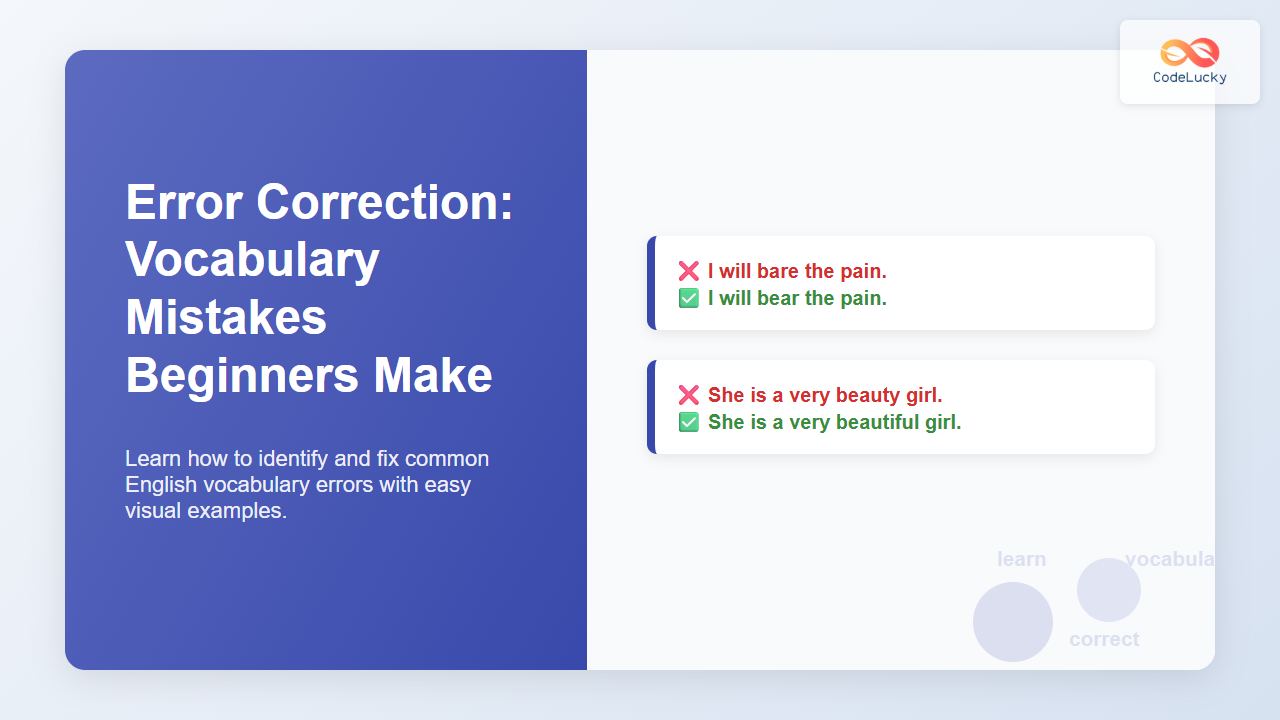
Word Formation is one of the most fascinating parts of English learning. It’s a skill that not only strengthens your grammar but also helps you understand the meaning of new words quickly. When we talk about building words with prefixes, we focus on how adding small letter groups at the beginning of base words can completely change their meaning.
What Is a Prefix?
A prefix is a group of letters added to the beginning of a word to change its meaning. Unlike suffixes (which are added to the end), prefixes alter the root meaning of a word without changing its grammatical category in most cases.
Example:
- Happy → Unhappy (Prefix “un-” changes meaning to opposite)
- Kind → Unkind
- Appear → Disappear
Understanding Word Formation Process
Let’s visualize how prefixes work using a flow relationship diagram. Each prefix joins the root word to form a new meaning:
This diagram shows how prefixes attach directly to root words to create a new form and meaning. While not all combinations are valid, patterns often follow predictable logic in English.
Common Prefixes and Their Meanings
Here are some of the most common English prefixes you will encounter, along with their meanings and examples:
| Prefix | Meaning | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| un- | Not or opposite of | unhappy, uncertain, unfair |
| re- | Again | redo, replay, rewrite |
| pre- | Before | preview, preheat, preplan |
| dis- | Reverse or opposite of | disagree, disconnect, disapprove |
| mis- | Wrongly | mislead, misunderstand, misuse |
| sub- | Under or below | submarine, subway, submerge |
How Prefixes Change Word Meaning
Prefixes often flip or modify the original idea of a word. To visualize, imagine prefixes as “directional changes” in meaning applied to a core idea:
This diagram shows that prefixes primarily serve two functions — expanding the context (like replay means to play again) or reversing the meaning (as in unfit, meaning “not fit”).
Interactive Prefix Practice
To strengthen your understanding, try this short interactive activity:
- Take the base word do.
- Add different prefixes: “un-”, “re-”, “mis-”.
- Resulting words: undo, redo, misdo (rare but meaningful as “do something the wrong way”).
Try doing the same for other words like lead, form, and use.
Prefix Categories by Meaning
Prefixes can be grouped based on the meaning transformation they cause:
- Negation prefixes: un-, in-, dis-, non-
- Time/order prefixes: pre-, post-, re-, fore-
- Quantity/size prefixes: super-, mega-, hyper-, mini-
- Position prefixes: sub-, inter-, extra-, trans-
We can visualize these relationships as a classification tree:
Real-Life Examples of Prefix Application
Let’s see how prefixes are used in sentences:
- Disapprove: “The teacher disapproved of the student’s behavior.”
- Reconnect: “After losing internet, the system tried to reconnect.”
- Unsuccessful: “The plan was unsuccessful despite good efforts.”
- Preheat: “Always preheat the oven before baking.”
Visualization: Word Building in Action
The process of adding prefixes can be compared to building blocks where each layer adds meaning:
Tips for Learning Prefixes Effectively
- Recognize patterns: Identify common prefixes and their effect on meaning.
- Practice regularly: Create new words by combining prefixes with known roots.
- Use visual tools: Diagrams and color-coding help remember word structures.
- Context matters: Some prefixes overlap in meaning—understand their correct use through reading and listening.
Conclusion
Mastering how prefixes shape meaning is a major step toward improving your English vocabulary. With consistent practice, you can decode unfamiliar words quickly and accurately. Remember: every prefix adds a new twist to the original idea, making the English language richer and more expressive.
Next Step: Explore our next article on Suffixes: Adding Meaning at the End to continue your journey in English word formation.