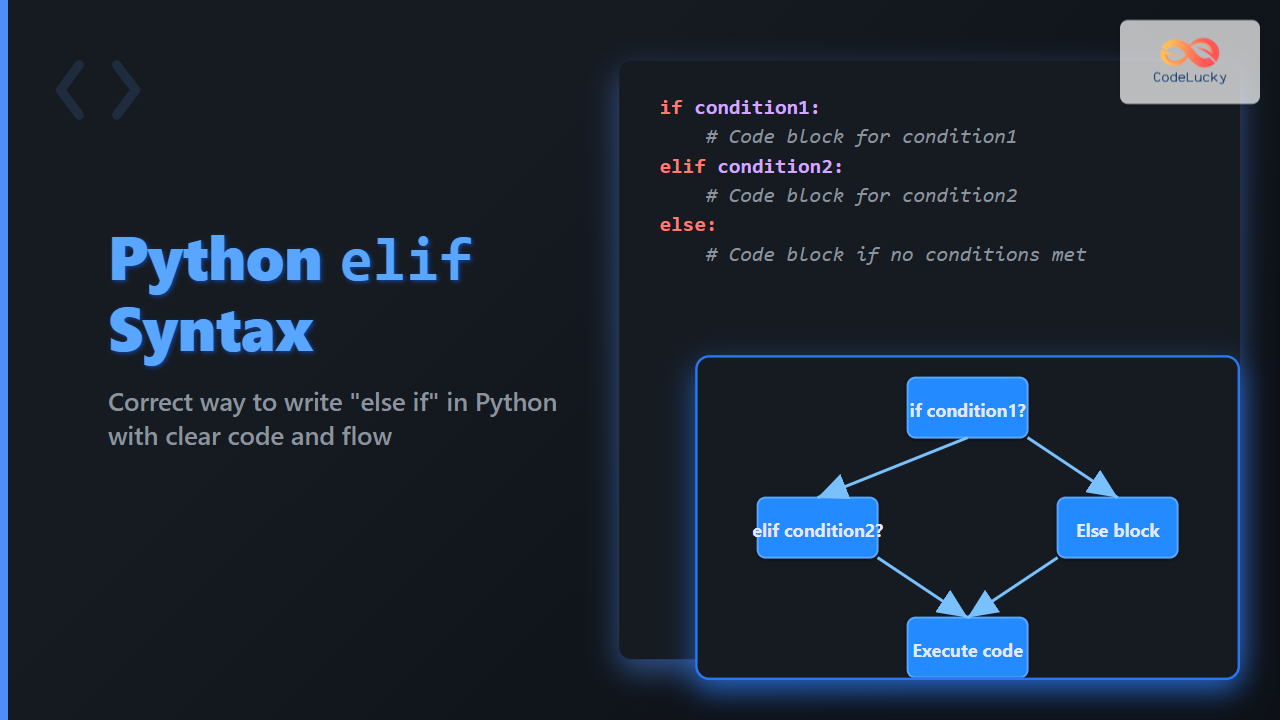
In Python programming, controlling the flow of execution based on conditions is key to building dynamic and intelligent applications. A fundamental construct used for this purpose is if-else statements. Many programmers coming from other languages often ask: What is the correct syntax for ‘else if’ in Python? Unlike some languages that use else if as two words, Python uses a unique keyword to express this logic – elif.
Understanding elif: The Python Equivalent of else if
In Python, there is no separate else if keyword. Instead, Python uses elif (short for ‘else if’) as a single keyword to handle multiple conditional branches. This makes the code cleaner and easier to read.
Basic Syntax of if-elif-else Structure
if condition1:
# block of code for condition1
elif condition2:
# block of code for condition2
else:
# block of code if none of the above conditions are true
The following points explain the syntax elements:
ifinitiates the first condition check.elifallows checking additional conditions if the previous ones are false.elsecovers any case where none of theiforelifconditions are true.
Practical Examples with Outputs
Example 1: Checking Number Sign
num = 0
if num > 0:
print("The number is positive")
elif num == 0:
print("The number is zero")
else:
print("The number is negative")
Output:
The number is zero
Example 2: Grading System Based on Scores
score = 85
if score >= 90:
grade = "A"
elif score >= 80:
grade = "B"
elif score >= 70:
grade = "C"
elif score >= 60:
grade = "D"
else:
grade = "F"
print(f"Your grade is: {grade}")
Output:
Your grade is: B
Interactive Example: Try It Yourself
Below is an interactive Python code snippet that you can copy and run in your Python environment to observe the if-elif-else syntax in action.
def check_temperature(temp):
if temp > 30:
return "It's a hot day"
elif 15 <= temp <= 30:
return "It's a pleasant day"
else:
return "It's cold today"
temperature = int(input("Enter the temperature in °C: "))
print(check_temperature(temperature))
When to Use elif Instead of Multiple if Statements
Using elif links conditions into a chain where only the first true condition’s block executes. This improves efficiency because after the first true condition is met, Python skips checking the rest. Using multiple independent if statements instead causes all conditions to be checked regardless, which may lead to unintended behaviors.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Writing
else ifseparated by a space, which will cause a syntax error in Python. - Forgetting the colon (
:) at the end ofif,elif, andelselines. - Incorrect indentation of the blocks under
if,elif, andelse. Python relies on indentation to define scope.
Summary of Correct else if Usage in Python
| Concept | Python Syntax | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| if condition | if condition: |
Checks the first condition |
| else if condition | elif condition: |
Checks if previous if or elif were false |
| else | else: |
Runs if all above conditions are false |
Visual Explanation of if-elif-else Statement Lifecycle
Understanding and using the elif keyword properly ensures that Python programs are efficient, clean, and easy to read. This eliminates ambiguity and errors related to conditional branching common in many other languages.
Try practicing writing multiple conditional statements with if-elif-else in your Python projects for robust control flow logic that handles complex decision-making gracefully.