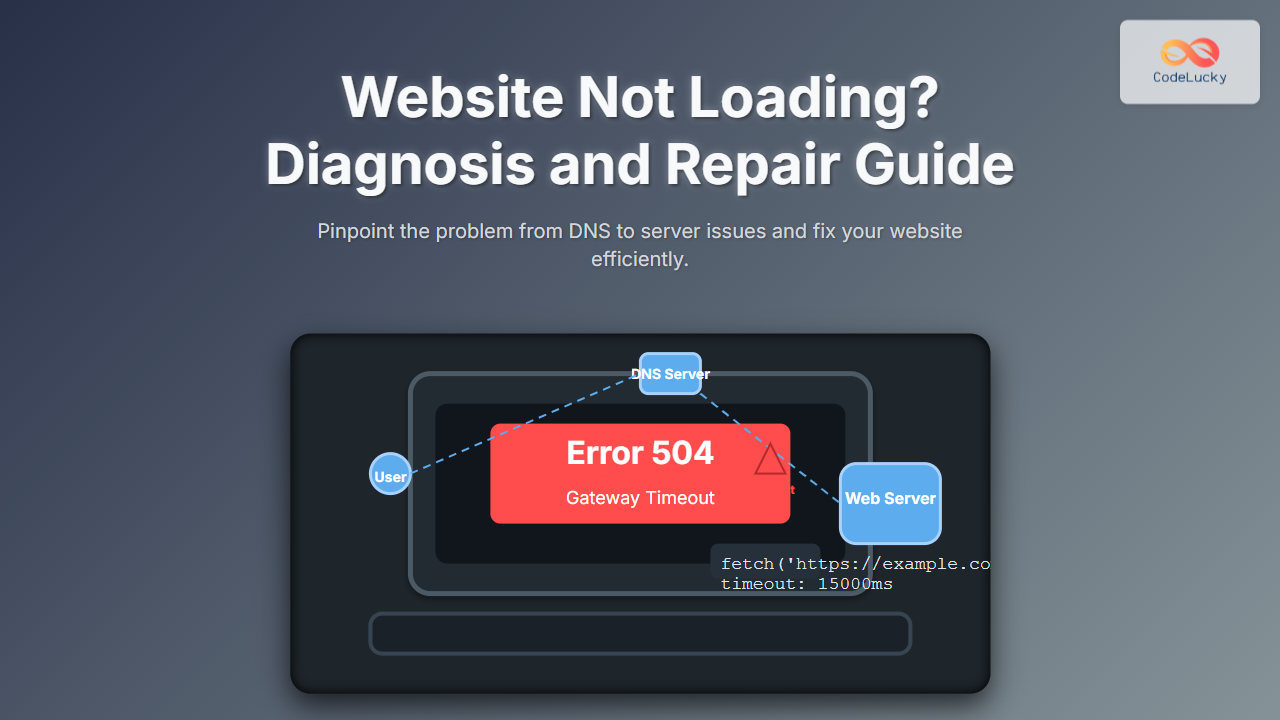
Encountering a website that will not load can be frustrating for both developers and end-users alike. This detailed guide from CodeLucky.com is your go-to resource for diagnosing and repairing website loading issues. Whether you’re a web developer, IT professional, or a curious enthusiast, this article covers the technical causes, practical troubleshooting techniques, and visual aids to help resolve website accessibility problems efficiently.
Why Does a Website Fail to Load?
When a website doesn’t load, it’s often due to issues occurring at various points in the network and server chain, including but not limited to:
- DNS resolution problems
- Server downtime or overload
- Network connectivity issues
- Browser-related issues or cache problems
- Code or configuration errors on the website
Step-by-Step Diagnosis of Loading Failures
Systematically diagnosing the root cause is essential. The following steps outline a methodical approach.
1. Check Domain Name System (DNS) Resolution
DNS translates the domain name you enter into an IP address a browser can connect to. When DNS fails, the browser cannot find the server hosting the website.
nslookup example.com
ping example.com
If nslookup or ping returns errors, the issue likely lies in DNS resolution or domain configuration.
2. Verify Server Availability
Even if DNS resolves, the server hosting the site might be down or unreachable. Use these commands:
ping server_ip_address
traceroute example.com (or tracert example.com on Windows)
If the server does not respond or traceroute fails midway, the problem might be on the server or network path.
3. Inspect HTTP Response with Browser Developer Tools
Modern browsers have developer tools (F12 or Ctrl+Shift+I) to analyze network requests:
- Look for HTTP status codes:
404 Not Found,500 Internal Server Error,503 Service Unavailable, etc. - Check if static resources like CSS and JavaScript files load properly.
- Confirm if the server is responding timely or if requests time out.
4. Clear Browser Cache and Cookies
Sometimes, corrupted cache or cookies cause loading issues. Clearing them often helps:
- Open browser settings → Privacy and security
- Clear browsing data → Cached images/files and cookies
5. Confirm Internet Connectivity and Firewall Settings
Issues such as network firewalls, VPNs, or poor connectivity can block site access. Troubleshoot by:
- Accessing other sites to verify internet connection
- Disabling VPN or proxy to check if site loads
- Reviewing firewall or antivirus that might block site IP or ports
6. Investigate Website Code and Configuration
If the above steps don’t solve the problem, the issue might be in the website’s own code or server configuration, such as:
- Erroneous redirects or .htaccess rules
- Database connection failures
- Exceeding server resource limits (CPU, memory)
- Broken or unresponsive backend services
Examples: Diagnosing Common Scenarios
Example 1: DNS Resolution Failure
$ nslookup example.com
Server: 8.8.8.8
Non-existent domain
This indicates DNS misconfiguration or domain expiry. Check the domain registrar and DNS provider settings.
Example 2: Server Timeout
$ ping 192.0.2.1
Request timed out.
The server might be down, or firewall rules blocking ICMP. Use traceroute to identify network disruptions.
Example 3: HTTP Error 503
Server responds with:
HTTP/1.1 503 Service Unavailable
Retry-After: 120
This usually means the server is temporarily overloaded or under maintenance. Check server load and scheduled maintenance.
Interactive Troubleshooting Example
Use JavaScript in browser console to test network latency and DNS lookup times:
async function checkSitePerformance(url) {
const start = performance.now();
try {
await fetch(url, { mode: 'no-cors' });
const end = performance.now();
console.log(`Fetch succeeded. Time: ${(end - start).toFixed(2)}ms`);
} catch (e) {
console.error('Fetch failed:', e);
}
}
checkSitePerformance('https://example.com');
Summary Repair Actions
- Fix DNS issues: Update DNS records, verify propagation, renew domains.
- Improve server uptime: Restart servers, optimize resources, scale infrastructure.
- Clear caches: At browser, CDN, and server-side levels.
- Validate website code and configs: Debug application logs, fix broken redirects and database connections.
- Check Network and Firewall: Open required ports, disable blocking rules, test from different networks.
Final Thoughts
Diagnosing and repairing a website that won’t load involves carefully ruling out issues from DNS to code-level bugs. Using the outlined approach and tools will empower developers and site owners to restore website availability with confidence. Remember, consistent monitoring and proactive maintenance dramatically reduce downtime and improve user experience.