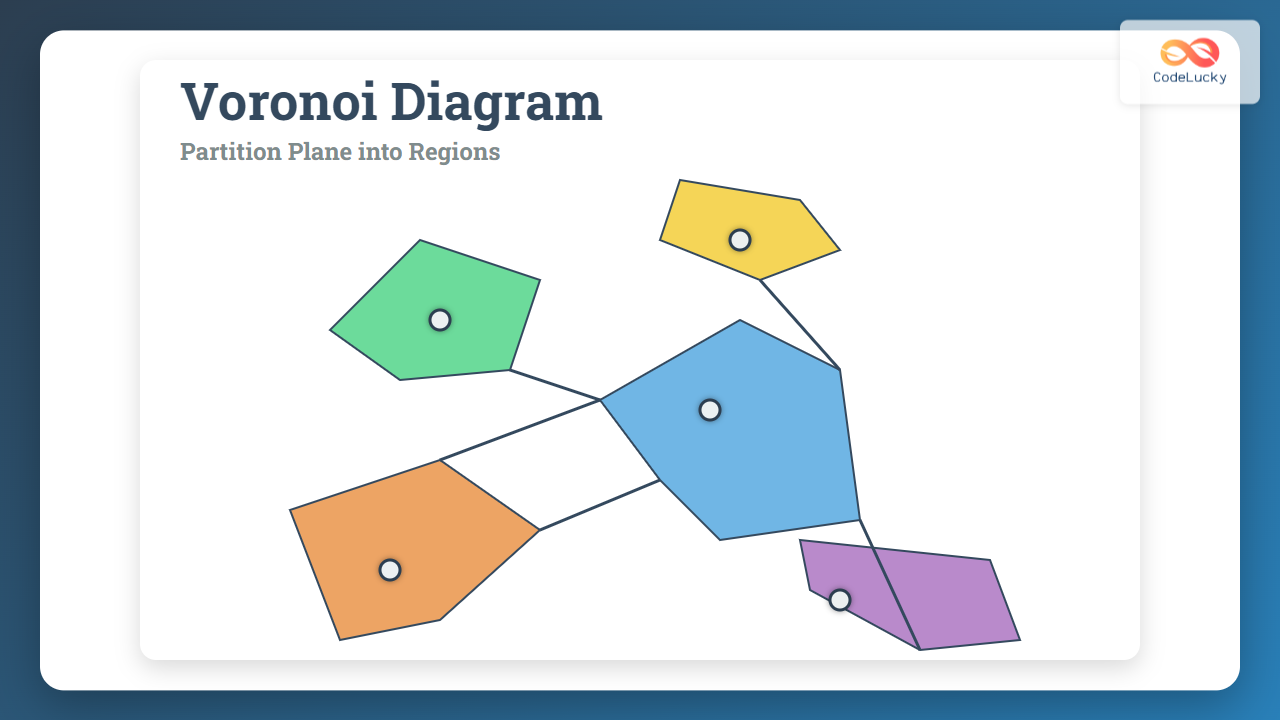
The Voronoi Diagram is a fundamental concept in computational geometry that partitions the plane into regions based on distance to a set of given points. Each region contains all points closer to one particular input point than to any other. This partitioning has numerous applications, from geographic mapping, robotics, to computer graphics and spatial analysis.
What is a Voronoi Diagram?
A Voronoi Diagram is constructed from a set of distinct points called sites or generators. The diagram divides the 2D space into polygonal regions where each region corresponds to a site. Every point inside a region is closer to that region’s site than any other site.
Formally, given a set of sites \(S = \{s_1, s_2, …, s_n\}\), the Voronoi region \(V_i\) associated with site \(s_i\) is:
\(V_i = \{ x \in \mathbb{R}^2 : d(x, s_i) < d(x, s_j) \quad \forall j \neq i \}\)
where \(d(x, s_i)\) is the Euclidean distance between \(x\) and \(s_i\).
Key Properties of Voronoi Diagrams
- Convex polygons: Each Voronoi cell (region) is a convex polygon or unbounded convex polygon.
- Edges: Edges are the loci of points equidistant to two nearest sites; they are segments of perpendicular bisectors.
- Vertices: Where three or more edges meet, vertices are equidistant to three or more sites.
Construction Methods
There are multiple algorithms to generate Voronoi diagrams, including:
- Fortune’s Sweep Line Algorithm: An efficient \(O(n \log n)\) algorithm using a sweep line sweeping over the plane.
- Divide and Conquer: Recursively dividing points and merging diagrams.
- Incremental Insertion: Adding sites one-by-one and updating the diagram.
Example: Voronoi Diagram for a Set of Points
Consider four points \(P = \{(2,3), (6,7), (8,2), (4,5)\}\). The Voronoi diagram partitions the plane into four regions, each containing the area closer to one of these points.
Interactive Visual Explanation
Below is a simple mermaid diagram illustrating the Voronoi partitioning process based on proximity.
Applications of Voronoi Diagrams
Voronoi diagrams have wide-ranging applications including:
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Defining influence zones around landmarks.
- Robotics: Path planning and obstacle avoidance.
- Cellular Networks: Optimal placement and coverage areas of transmitters.
- Computer Graphics: Procedural texture and mesh generation.
- Biology: Modeling territories or spatial patterns of cells.
Advanced Concepts
Some variations and related constructs include:
- Weighted Voronoi Diagrams: Sites have weights affecting region sizes.
- Higher Dimensions: Voronoi diagrams generalize to 3D and beyond.
- Delaunay Triangulation: Dual graph of the Voronoi diagram, connecting sites whose Voronoi regions share edges.
Conclusion
The Voronoi diagram is a mathematical tool to partition spaces efficiently by proximity, useful in many fields. By understanding its properties and construction, developers and researchers can apply this concept to solve complex spatial problems.
This article presented detailed explanations along with a practical pixel-coloring example to visualize Voronoi partitions clearly.