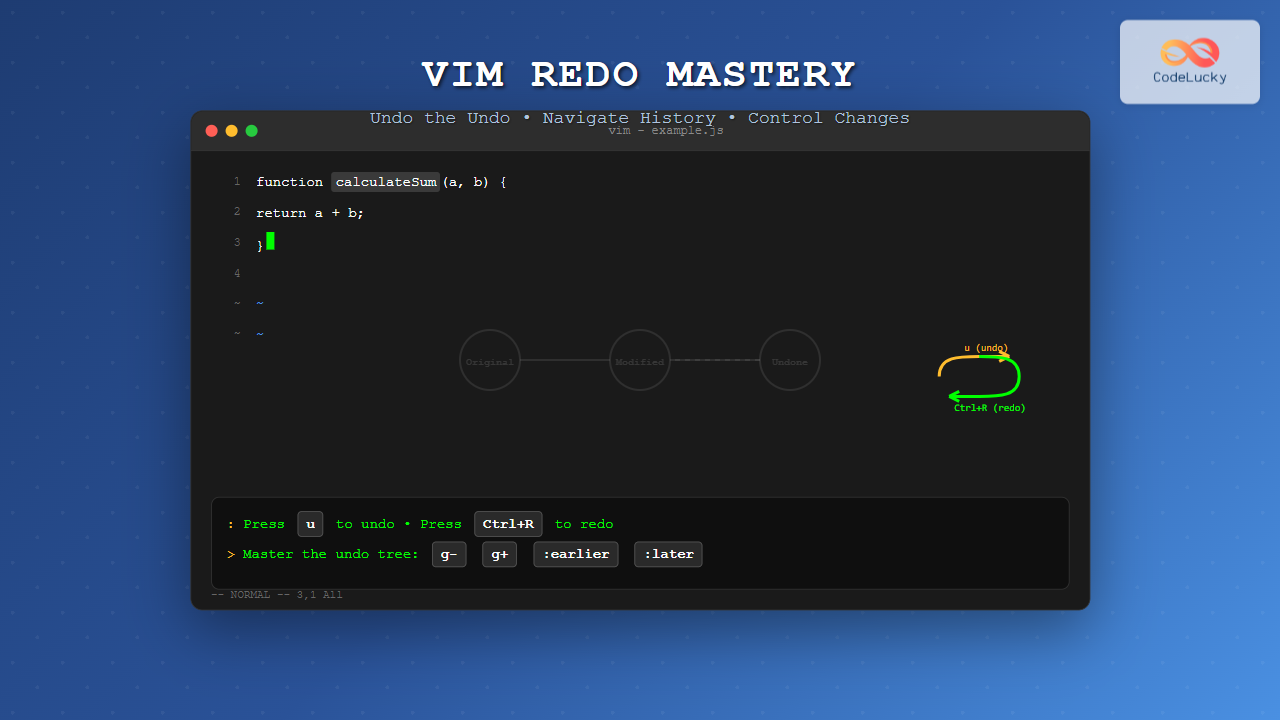
Vim’s undo and redo system is one of its most powerful features, allowing you to navigate through your editing history with precision. While most users know about undoing changes with u, the redo operation is equally important but less intuitive. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore how to redo in Vim and master the complete undo/redo workflow.
The Basic Redo Command
The primary command to redo in Vim is Ctrl+R. This command reverses the most recent undo operation, effectively “undoing the undo.”
Ctrl+R # Redo the last undone changePractical Example: Basic Redo Operation
Let’s walk through a simple example to demonstrate the undo/redo cycle:
Initial text:
Hello WorldStep 1: Add an exclamation mark
Hello World!Step 2: Press u to undo
Hello WorldStep 3: Press Ctrl+R to redo
Hello World!Understanding Vim’s Undo Tree System
Unlike simple linear undo systems, Vim maintains an undo tree that preserves all your editing history, including branched changes. This sophisticated system allows for more complex undo/redo operations.
Linear vs Tree Undo Behavior
When you make changes, undo some of them, and then make new changes, Vim creates branches in the undo tree:
Scenario:
- Start with:
Hello - Add ” World”:
Hello World - Add “!”:
Hello World! - Undo twice: back to
Hello - Add ” Vim”:
Hello Vim
At this point, you have two branches in your undo tree. The original “Hello World!” branch still exists but isn’t accessible through simple Ctrl+R.
Advanced Redo Commands
Numbered Redo Operations
You can redo multiple changes at once by prefixing Ctrl+R with a number:
3<Ctrl+R> # Redo the next 3 undone changesRedo Until Specific Point
Vim allows you to redo until a specific time or file save:
:redo # Redo one change (command mode alternative)
:red # Abbreviated form of :redoTime-Based Undo and Redo
One of Vim’s most powerful features is time-based navigation through your editing history:
:earlier 5m # Undo to 5 minutes ago
:later 2m # Redo to 2 minutes forward
:earlier 10s # Undo to 10 seconds ago
:later 1h # Redo to 1 hour forwardFile Save-Based Navigation
You can also navigate based on file saves:
:earlier 2f # Undo to 2 file saves ago
:later 1f # Redo to 1 file save forwardUndo Tree Navigation
For complex undo tree navigation, Vim provides several commands:
g- # Go to older text state
g+ # Go to newer text state
:undolist # Show the undo tree structure
:undojoin # Join next change with previous undo blockVisualizing Undo History
The :undolist command shows your undo history in a table format:
:undolist
number changes when saved
3 2 2 seconds ago
4 1 1 seconds ago 1Interactive Example: Complex Redo Workflow
Let’s work through a complex example that demonstrates the full power of Vim’s undo/redo system:
Starting Code:
function calculateSum(a, b) {
return a + b;
}Step 1: Add error handling
function calculateSum(a, b) {
if (typeof a !== 'number' || typeof b !== 'number') {
throw new Error('Invalid input');
}
return a + b;
}Step 2: Add documentation
/**
* Calculates the sum of two numbers
* @param {number} a - First number
* @param {number} b - Second number
* @returns {number} Sum of a and b
*/
function calculateSum(a, b) {
if (typeof a !== 'number' || typeof b !== 'number') {
throw new Error('Invalid input');
}
return a + b;
}Step 3: Undo documentation (u)
function calculateSum(a, b) {
if (typeof a !== 'number' || typeof b !== 'number') {
throw new Error('Invalid input');
}
return a + b;
}Step 4: Add different comment style
// Simple function to add two numbers
function calculateSum(a, b) {
if (typeof a !== 'number' || typeof b !== 'number') {
throw new Error('Invalid input');
}
return a + b;
}Step 5: Use Ctrl+R to restore JSDoc
/**
* Calculates the sum of two numbers
* @param {number} a - First number
* @param {number} b - Second number
* @returns {number} Sum of a and b
*/
function calculateSum(a, b) {
if (typeof a !== 'number' || typeof b !== 'number') {
throw new Error('Invalid input');
}
return a + b;
}Common Redo Scenarios and Solutions
Scenario 1: Accidental Multiple Undos
Problem: You pressed u too many times and went back too far.
Solution: Use Ctrl+R to redo forward to your desired state.
# If you undid 5 changes accidentally:
5<Ctrl+R> # Redo 5 changes at onceScenario 2: Lost Changes After Branch Creation
Problem: You made changes, undid them, made different changes, and now want to access the original changes.
Solution: Use g- and g+ to navigate through the undo tree.
Scenario 3: Time-Based Recovery
Problem: You want to go back to how your file looked 10 minutes ago.
Solution: Use time-based undo/redo commands.
:earlier 10m # Go back 10 minutes
# Make your assessment
:later 5m # Come forward 5 minutes if neededUndo/Redo Best Practices
1. Configure Persistent Undo
Enable persistent undo to maintain undo history across Vim sessions:
" Add to your .vimrc
set undofile
set undodir=~/.vim/undodir2. Set Appropriate Undo Levels
" Configure undo levels
set undolevels=1000 # Number of undo levels
set undoreload=10000 # Number of lines to save for undo on buffer reload3. Use Undo Breakpoints
Create undo breakpoints to group related changes:
Ctrl+G u # Create an undo breakpoint in insert modeKeyboard Shortcuts Summary
| Command | Action | Mode |
|---|---|---|
u |
Undo last change | Normal |
Ctrl+R |
Redo last undone change | Normal |
g- |
Go to older text state | Normal |
g+ |
Go to newer text state | Normal |
:undo |
Undo (command mode) | Command |
:redo |
Redo (command mode) | Command |
:earlier {time} |
Undo to specific time | Command |
:later {time} |
Redo to specific time | Command |
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Redo Not Working
If Ctrl+R doesn’t work, check:
- Terminal key binding: Some terminals might intercept
Ctrl+R - No changes to redo: You might already be at the newest state
- Different branch: Your changes might be on a different undo tree branch
Lost Undo History
Undo history is lost when:
- The buffer is reloaded without undoreload being set
- You exit Vim without persistent undo enabled
- The undo file becomes corrupted
Advanced Tips and Tricks
Undo in Visual Mode
When you undo in visual mode, Vim automatically reselects the text that was changed:
V # Enter visual line mode
u # Undo and maintain selectionUndo Specific Operations
You can undo specific types of operations using various commands:
:s/old/new/g # Substitute operation
u # Undo the entire substitute operation
Plugin Recommendations
Consider these plugins to enhance your undo/redo experience:
- undotree: Provides a visual representation of the undo tree
- gundo: Another excellent undo tree visualizer
- mundo: Modern alternative to gundo with improved features
Mastering Vim’s undo and redo system, especially the Ctrl+R command, will significantly improve your editing efficiency. The combination of linear undo/redo, time-based navigation, and tree-based history makes Vim’s system one of the most powerful among text editors. Practice these commands regularly, and they’ll become second nature, allowing you to navigate your editing history with confidence and precision.