Verbs are the heart of any sentence — they express action, state, or occurrence. Mastering verbs lays the foundation for effective English communication. This beginner-friendly guide from CodeLucky.com explains all about regular and irregular verbs with examples, tables, and visual diagrams to make learning smooth and interactive.
What Are Verbs?
A verb is a word that shows an action (like run, eat), a state (like be, seem), or an occurrence (like happen). Every meaningful English sentence needs a verb. For example:
- She runs every morning.
- They are tired.
- It rained yesterday.
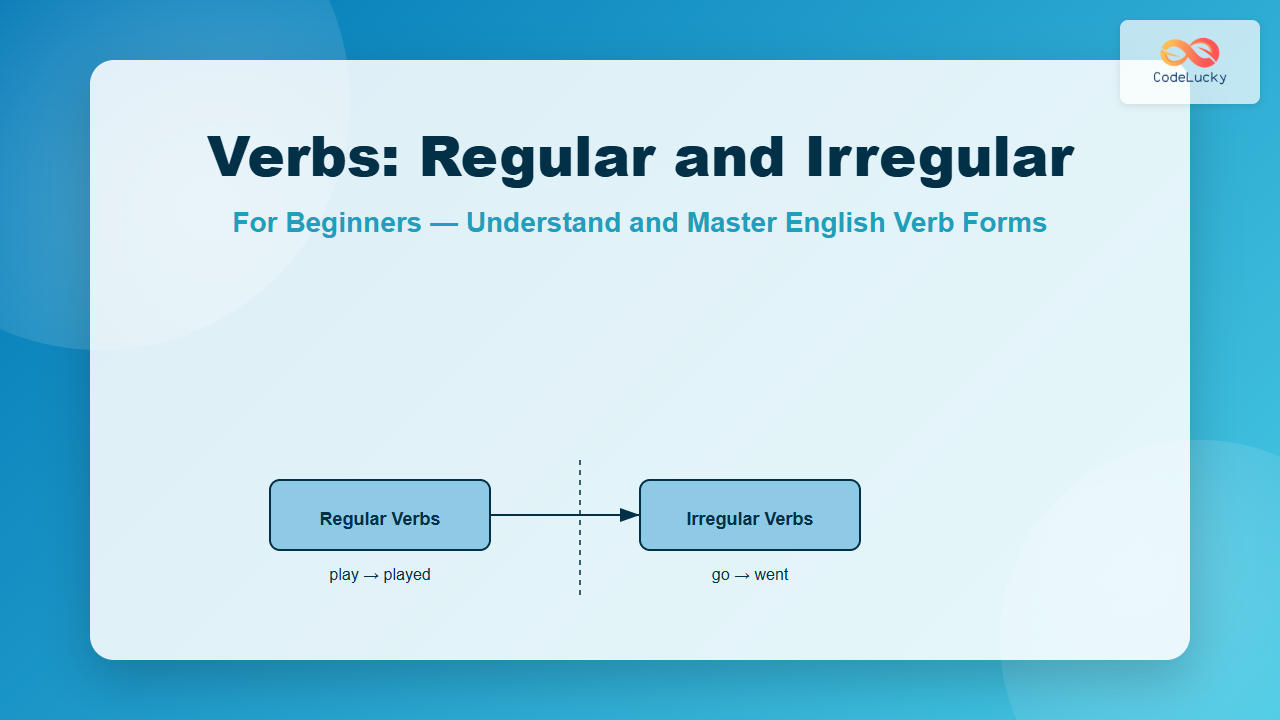
Types of Verbs: Regular vs Irregular
English verbs are broadly divided into two main types based on how they form their past tense and past participle:
Regular Verbs
Regular verbs follow a simple and predictable rule: you just add -ed (or -d) to the base form of the verb to create the past tense and past participle.
Examples of Regular Verbs
| Base Form | Past Tense | Past Participle | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| work | worked | worked | I worked all day. |
| play | played | played | He played cricket yesterday. |
| watch | watched | watched | They watched a movie. |
| call | called | called | She called her friend. |
Rule Patterns for Regular Verbs
- If a verb ends in e, just add d (e.g., love → loved).
- If a verb ends in a consonant + y, change y → ied (e.g., study → studied).
- If a one-syllable verb ends in consonant-vowel-consonant (CVC), double the final consonant and add ed (e.g., stop → stopped).
Irregular Verbs
Irregular verbs don’t follow a fixed rule. Their past tense and past participle forms vary and must be memorized. These verbs are used often, so learning them is crucial for fluency.
Examples of Irregular Verbs
| Base Form | Past Tense | Past Participle | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| go | went | gone | I have gone there before. |
| eat | ate | eaten | She ate lunch. |
| see | saw | seen | We have seen that movie. |
| buy | bought | bought | They bought new clothes. |
| write | wrote | written | He has written a letter. |
Common Groups of Irregular Verbs
Though irregular verbs don’t follow one rule, many fall into recognizable patterns. Here are some helpful groups:
| Pattern Group | Example Verbs |
|---|---|
| Same in all forms | cut, put, let, hit |
| Vowel changes only | sing → sang → sung, begin → began → begun |
| Endings change from -d → -t | send → sent, build → built |
| Completely unique forms | go → went → gone, be → was/were → been |
Interactive Practice: Identify Verb Type
Try this! Identify whether the following are regular or irregular verbs:
- Jump → _________
- Go → _________
- Play → _________
- See → _________
- Call → _________
Answers: (1) Regular, (2) Irregular, (3) Regular, (4) Irregular, (5) Regular.
Visual Summary
Tips to Master Verbs
- Practice with flashcards for irregular verbs.
- Group verbs by similar patterns.
- Read short stories and underline verbs.
- Write daily sentences using new verbs.
- Use online quizzes and verb form games.
Conclusion
Understanding regular and irregular verbs is essential for constructing sentences correctly and speaking English naturally. Start with regular verbs since they follow clear rules, then gradually memorize irregular forms using patterns and practice. With consistent learning, you’ll master English verbs and express yourself confidently in real conversations.
Continue exploring CodeLucky.com for more beginner-friendly English grammar lessons with interactive visuals and step-by-step explanations.