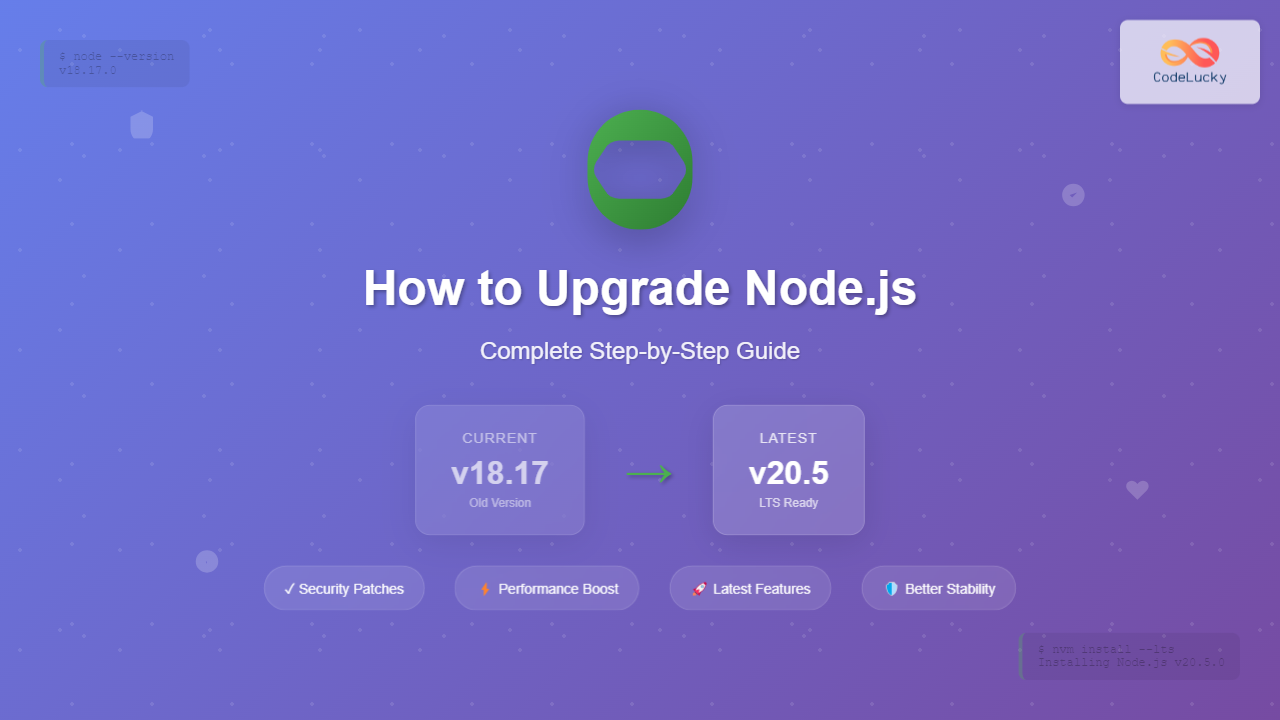
Keeping Node.js up to date is crucial for accessing the latest features, performance improvements, and security patches. This comprehensive guide will walk you through multiple methods to upgrade Node.js to the latest version, ensuring you choose the best approach for your development environment.
Why Upgrade Node.js?
Before diving into the upgrade process, let’s understand why staying current with Node.js versions is essential:
- Security Patches: Each version includes critical security fixes
- Performance Improvements: Newer versions often provide better performance
- Latest Features: Access to new JavaScript features and APIs
- Better Error Handling: Enhanced debugging and error reporting
- Ecosystem Compatibility: Support for latest npm packages
Checking Your Current Node.js Version
First, let’s check your current Node.js version to understand what you’re working with:
node --version
# or
node -vExpected Output:
v18.17.0You can also check npm version alongside:
npm --versionMethod 1: Using Node Version Manager (NVM) – Recommended
NVM is the most flexible and developer-friendly way to manage Node.js versions. It allows you to install, switch between, and manage multiple Node.js versions effortlessly.
Installing NVM (if not already installed)
For macOS and Linux:
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.0/install.sh | bash
# or using wget
wget -qO- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.0/install.sh | bashFor Windows:
Download and install nvm-windows from the official GitHub repository.
Using NVM to Upgrade Node.js
Once NVM is installed, restart your terminal and follow these steps:
# Check available Node.js versions
nvm list-remote
# Install the latest LTS version
nvm install --lts
# Install the latest current version
nvm install node
# Install a specific version
nvm install 20.5.0Expected Output:
Downloading and installing node v20.5.0...
Downloading https://nodejs.org/dist/v20.5.0/node-v20.5.0-darwin-x64.tar.xz...
Computing checksum with shasum -a 256
Checksums matched!
Now using node v20.5.0 (npm v9.8.0)Setting the Default Version
# Set the latest version as default
nvm alias default node
# Or set a specific version as default
nvm alias default 20.5.0
# Switch to a specific version
nvm use 20.5.0Method 2: Direct Installation from Node.js Website
This method involves downloading and installing the latest version directly from the official Node.js website.
Step-by-Step Process
- Visit nodejs.org
- Click on the LTS version (recommended for most users)
- Download the appropriate installer for your operating system
- Run the installer and follow the installation wizard
- Restart your terminal or command prompt
Verification:
node --version
npm --versionMethod 3: Using Package Managers
Different operating systems have various package managers that can handle Node.js updates.
macOS using Homebrew
# Update Homebrew
brew update
# Upgrade Node.js
brew upgrade node
# Or install if not present
brew install nodeUbuntu/Debian using APT
# Update package list
sudo apt update
# Install Node.js
sudo apt install nodejs npm
# For latest version, use NodeSource repository
curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_lts.x | sudo -E bash -
sudo apt-get install -y nodejsWindows using Chocolatey
# Install or upgrade Node.js
choco upgrade nodejs
# Or install if not present
choco install nodejsMethod 4: Using npm to Update Node.js
While not the most common method, you can use npm itself to update Node.js on some systems:
# Install n (Node.js version manager)
sudo npm install -g n
# Install latest stable version
sudo n stable
# Install latest version
sudo n latest
# Install specific version
sudo n 20.5.0Handling Project Dependencies
After upgrading Node.js, it’s important to ensure your project dependencies are compatible:
Updating npm Packages
# Update npm to latest version
npm install -g npm@latest
# Update all packages in current project
npm update
# Check for outdated packages
npm outdated
# Update specific package
npm install package-name@latestTroubleshooting Common Issues
Permission Errors
If you encounter permission errors, especially on macOS and Linux:
# Change npm's default directory
mkdir ~/.npm-global
npm config set prefix '~/.npm-global'
# Add to your profile
export PATH=~/.npm-global/bin:$PATH
source ~/.profilePath Issues
If Node.js is not recognized after installation:
# Check current PATH
echo $PATH
# Find Node.js installation
which node
# Add to PATH if needed (add to your .bashrc or .zshrc)
export PATH=/usr/local/bin:$PATHVersion Conflicts
When multiple Node.js versions exist:
# List all installed versions with nvm
nvm list
# Remove old version
nvm uninstall 16.14.0
# Clear npm cache
npm cache clean --forceBest Practices for Node.js Version Management
- Use NVM: For development environments to easily switch between versions
- LTS Versions: Prefer LTS (Long Term Support) versions for production
- Regular Updates: Keep your Node.js version updated quarterly
- Testing: Always test your applications after upgrading
- Documentation: Document the Node.js version in your project README
- CI/CD: Specify exact Node.js versions in your deployment pipelines
Verifying Successful Upgrade
After upgrading, perform these verification steps:
# Check Node.js version
node --version
# Check npm version
npm --version
# Verify installation paths
which node
which npm
# Test basic functionality
node -e "console.log('Node.js is working!')"Expected Output:
v20.5.0
9.8.0
/usr/local/bin/node
/usr/local/bin/npm
Node.js is working!Managing Multiple Projects with Different Node.js Versions
For developers working on multiple projects requiring different Node.js versions:
# Create .nvmrc file in project root
echo "18.17.0" > .nvmrc
# Use version specified in .nvmrc
nvm use
# Install dependencies with correct Node.js version
npm installConclusion
Upgrading Node.js to the latest version is essential for maintaining a secure, performant, and feature-rich development environment. While there are multiple methods available, using NVM provides the most flexibility for developers who need to manage multiple versions across different projects.
Remember to always test your applications thoroughly after upgrading, update your project dependencies, and choose LTS versions for production environments. Regular updates ensure you benefit from the latest improvements while maintaining stability and security.
Whether you choose NVM, direct installation, or package managers, the key is to establish a consistent upgrade routine that fits your development workflow and project requirements.
- Why Upgrade Node.js?
- Checking Your Current Node.js Version
- Method 1: Using Node Version Manager (NVM) – Recommended
- Method 2: Direct Installation from Node.js Website
- Method 3: Using Package Managers
- Method 4: Using npm to Update Node.js
- Handling Project Dependencies
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Best Practices for Node.js Version Management
- Verifying Successful Upgrade
- Managing Multiple Projects with Different Node.js Versions
- Conclusion